Solid surface modification method and apparatus
a technology of solid surface and modification method, applied in the direction of vehicle route interaction device, railway components, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory adhesive strength, inability to perform partial modification, and inability to obtain satisfactory adhesive strength, etc., to achieve high interference efficiency, reduce contact area, and high surface treatment efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Modification of a fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet was performed by using the apparatus illustrated in FIG. 1. In this example, pure water and tap water were used as the compound solution 2. That is, a thin even liquid film of each of pure water and tap water was formed between the synthetic quartz glass plate 3 and a fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet by pressing the glass plate 3. In this state, an ArF laser beam was irradiated with an energy density of 6.5 mJ / cm.sup.2. Consequently, hydrophilicity was brought about for both pure water and tap water, with the result that a contact angle with water of 30.degree. was obtained.
Note that, for comparison, an identical fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet was dipped in the same solution, and an ultraviolet laser beam was irradiated to perform surface modification for the fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet. As a result, irradiation of an ArF laser beam with an energy density of 6.5 mJ / cm.sup.2 was required to obtain a contact angle with water of 30.degree. when pure water ...
example 2
The apparatus shown in FIG. 1 was used to modify a fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet. In this example, formic acid was used as the compound in solution 2. That is, a thin even liquid film of formic acid was formed between the synthetic quartz glass plate 3 and a fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet by pressing the glass plate 3. In this state, an ArF laser beam was irradiated with an energy density of 25 mJ / cm.sup.2. Consequently, a contact angle with water of 10.degree. was obtained.
Note that, for comparison, an identical fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet was dipped in formic acid, and an ultraviolet laser beam was irradiated to perform surface modification for the fluoroplastic (FEP) sheet. However, modification was impossible because bubbles were generated.
example 3
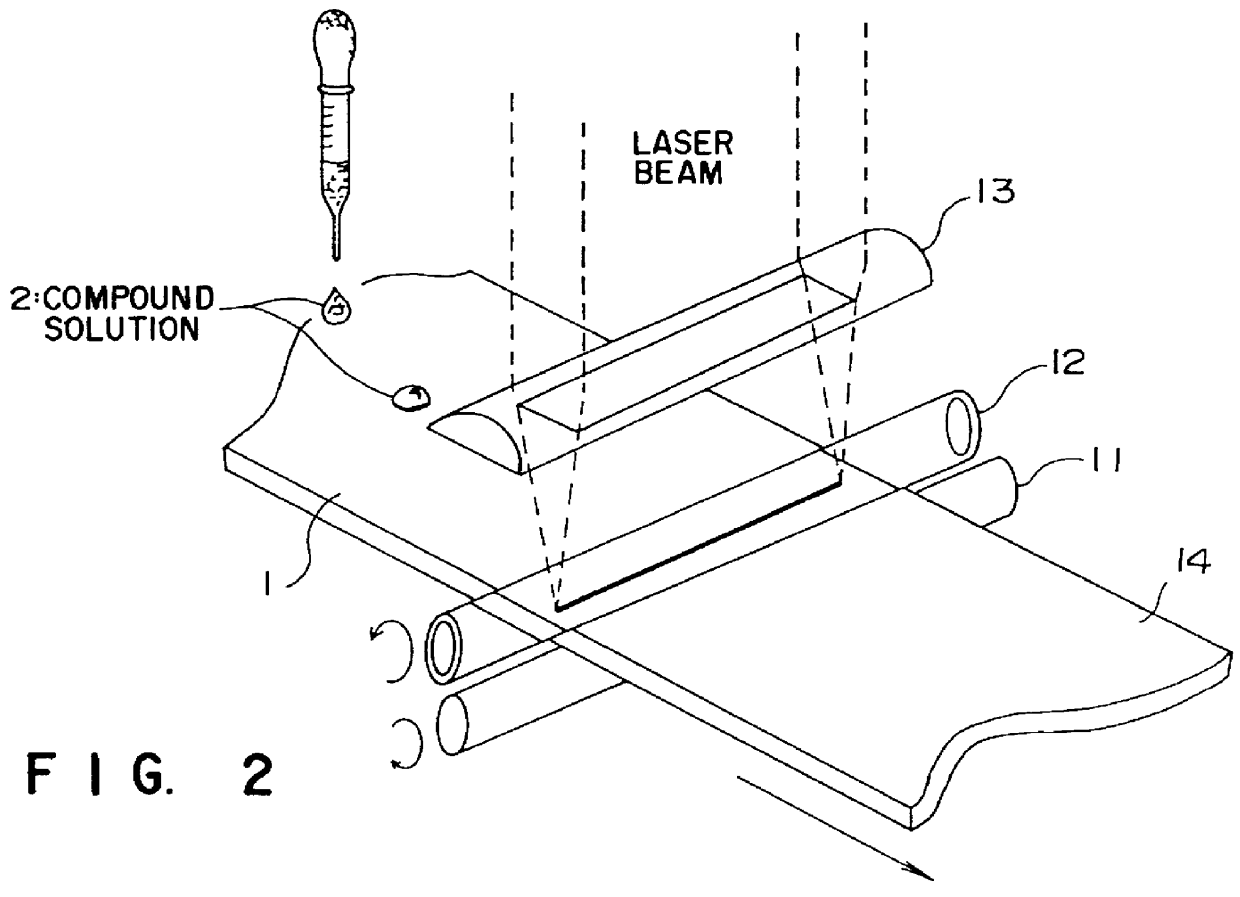
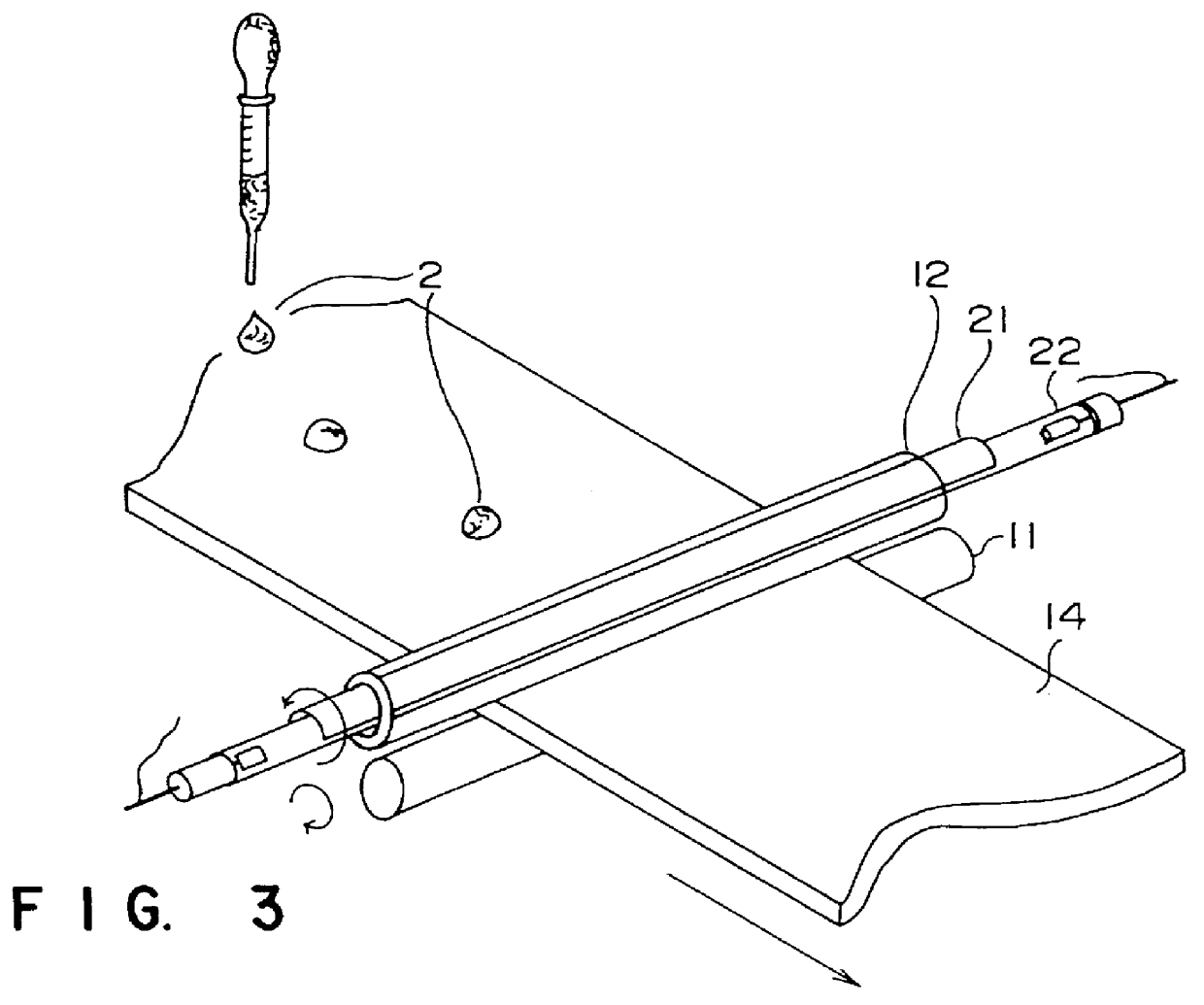
A fluoroplastic (PTFE) sheet was modified by using the apparatuses illustrated in FIGS. 2 and 3. That is, continuous surface modification was done by dropping droplets of methylalcohol (CH.sub.3 OH) one by one on the surface of a fluoroplastic (PTFE) sheet while the fluoroplastic sheet was moved. When an ArF laser beam was irradiated as 3000 shots with an energy density of 25 mJ / cm.sup.2, a contact angle with water of 45.degree. and a contact angle with benzene of 15.degree. were obtained. This demonstrates that the modified surface had both hydrophilic and lipophilic natures.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adhesivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Transparency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com