Controlled local delivery of chemotherapeutic agents for treating solid tumors
a chemotherapeutic agent and local delivery technology, applied in the direction of drugs, peptide/protein ingredients, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of poor bioavailability and/or short half-lives in vivo, and achieve the effects of preserving bioactivity and bioavailability of the agent, short half-lives, and poor bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
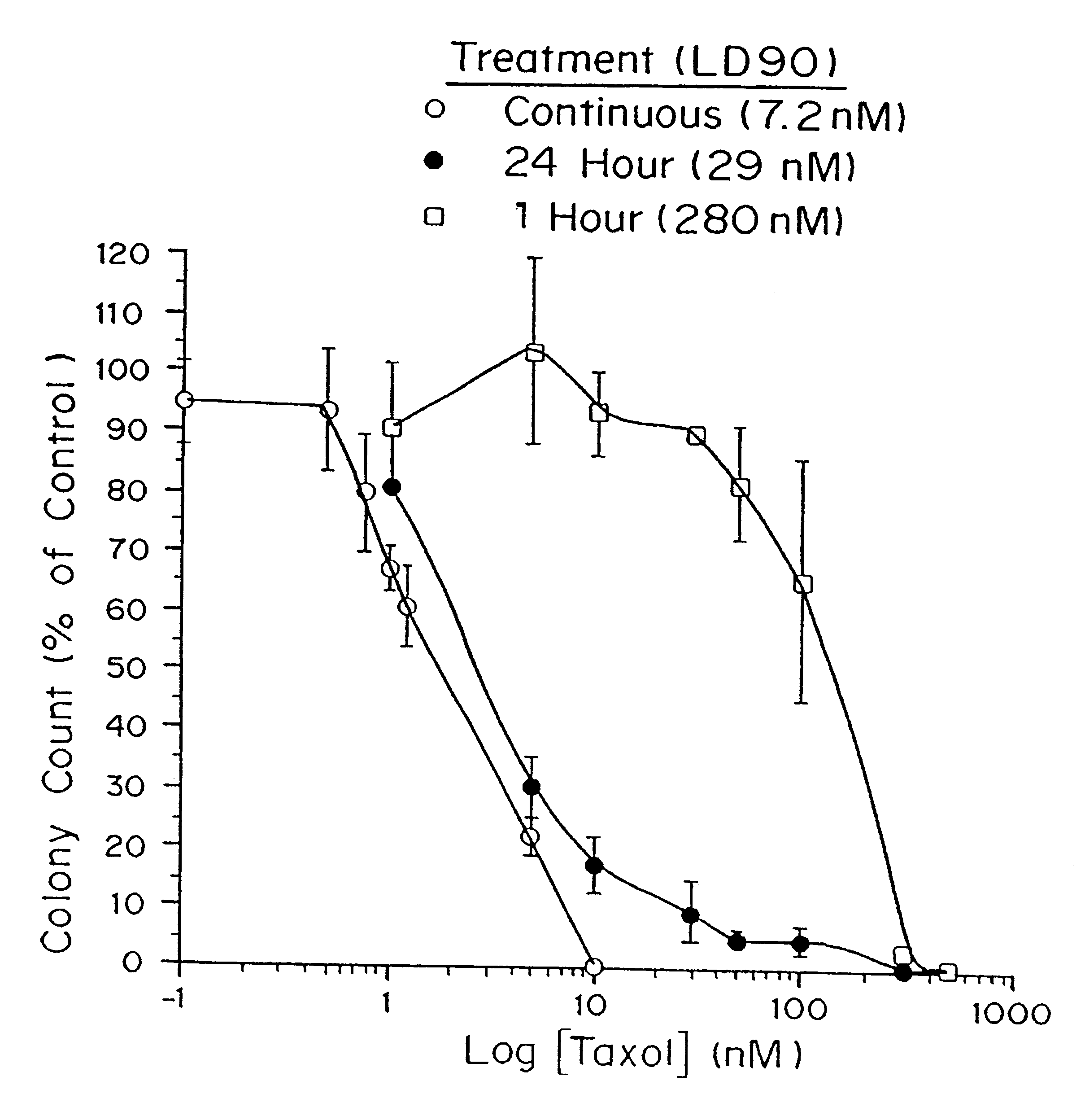
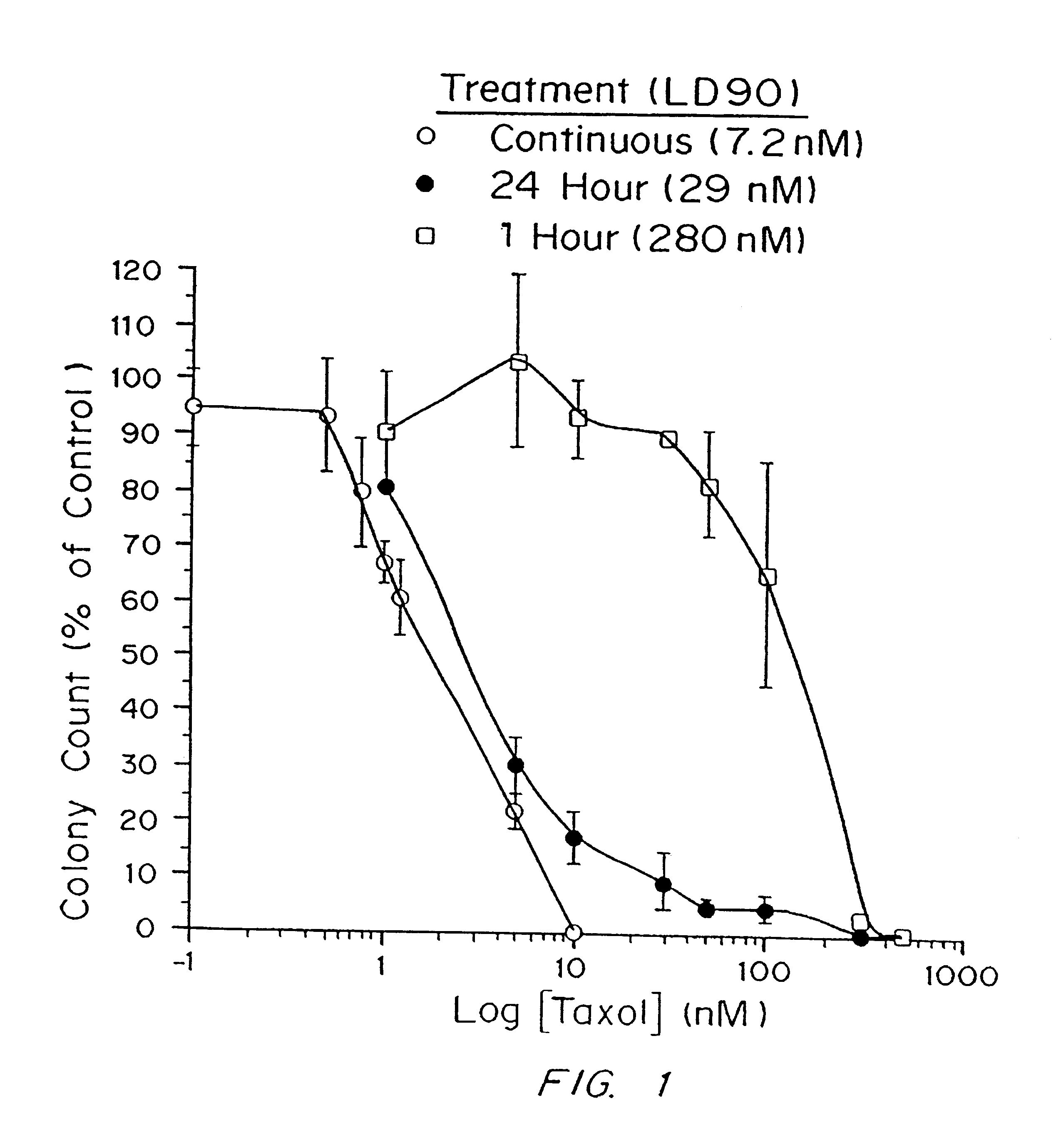
In Vitro Efficacy of Paclitaxel
Cell culture. Tumor sensitivity to paclitaxel was measured by the clonogenic assay described by Rosenblum, et al., Cancer 41:2305-2314 (1978) and Salcman, et al., Neurosurgery 29:526-531 (1991) with rat glioma (9L, F98), human glioma (H80, U87, U373), and human medulloblastoma (D324) cell lines. Cells were grown and propagated in minimum essential medium (MEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, L-glutamine, penicillin, and streptomycin and incubated at 37.degree. C. in an atmosphere containing 5% CO.sub.2. At the start of each assay, 600 tumor cells in 2 ml of medium were plated on Falcon 6-well tissue-culture plates (Becton-Dickenson, Lincoln Park, N.J.). After incubating for 24 h, the medium was removed from the places and replaced with 2 ml of medium containing paclitaxel and 0.1% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The treatment solutions were prepared as described by Roytta et al., Prostate 11:95-106 (1987). The paclitaxel treatment solution was then...
example 2
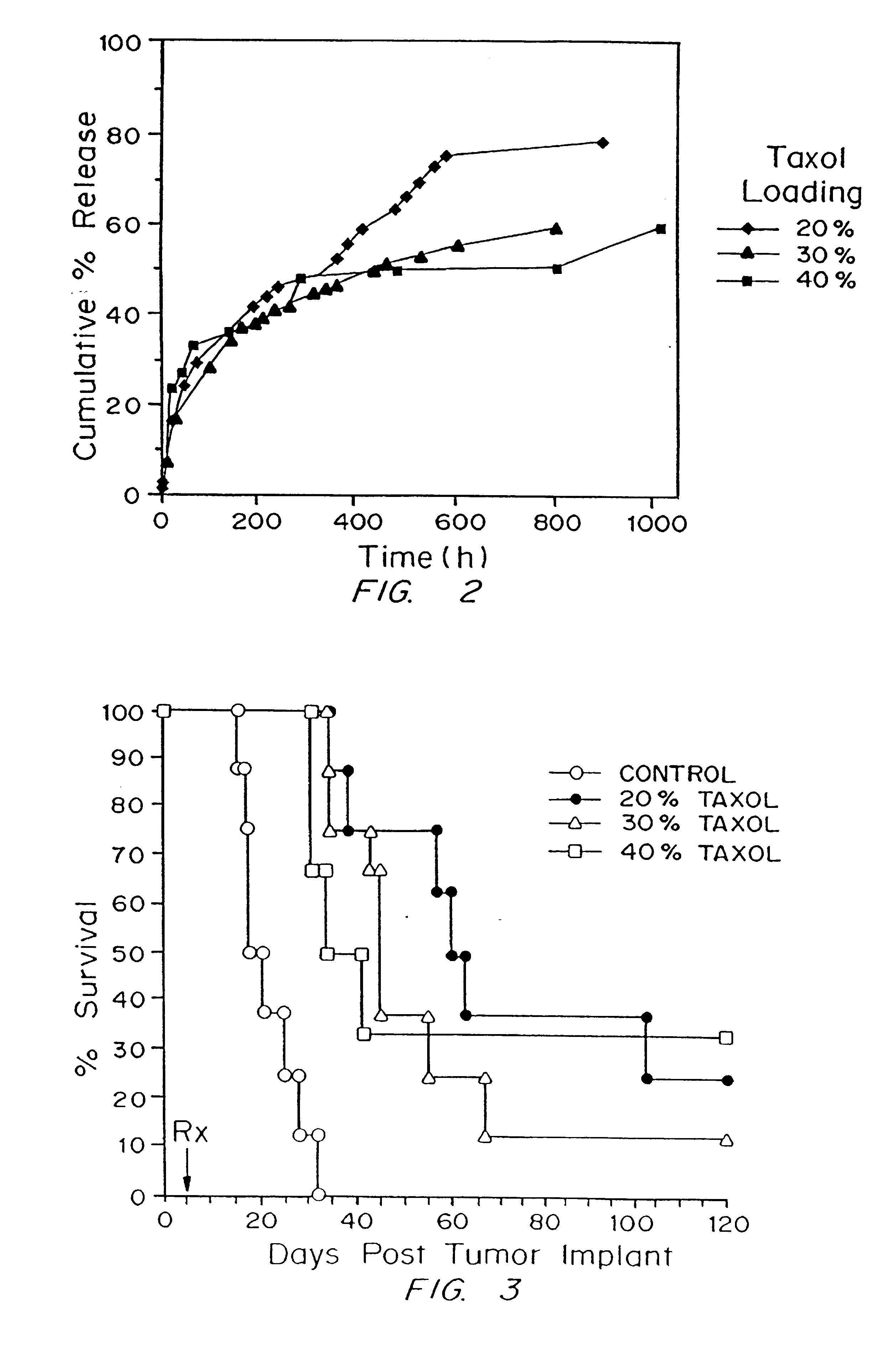
Preparation of Paclitaxel Implant
Solid paclitaxel, obtained from Napro Biotherapeutics (Boulder, Colo.) or from the National Cancer Institute (Bethesda, Md.), was mixed with poly[bis(p-carboxyphenoxy)propane-sebacic acid] copolymer (PCPP-SA) (20:80) synthesized according to the method of Domb, A. J., and R. Langer (J. Polym. Sci. 25:3373-3386 (1987)), the teachings of which are incorporated herein by reference, to give a mixture containing 0, 20, 30, or 40% paclitaxel by weight. The paclitaxel-polymer mixture was dissolved in methylene chloride (Fluka, Switzerland) to give a 10% solution (w:v). The solvent was evaporated with a nitrogen stream to yield a dry powder. Paclitaxel-polymer discs (10 mg final weight) were prepared by compression molding 11 mg of the paclitaxel-polymer powder with a stainless steel mold (internal diameter, 2.5 mm) under light pressure from a Carver Press at 200 psi. The discs were sterilized under UV light for 45 minutes.
example 3
Demonstration of Paclitaxel Delivery from a Biodegradable Matrix into the Surrounding Medium in Vitro
The efficiency of the delivery of paclitaxel incorporated into a biodegradable polymer into the surrounding medium was assessed in vitro as follows.
Preparation of polymer discs. Polymer discs were prepared as described above except that .sup.3 H-labeled paclitaxel (Atomic Energy Commission, Nuclear Research Center, Beer Sheva, Israel) was used in the polymer preparation. The .sup.3 H-labeled paclitaxel had a final specific activity of 0.019 .mu.Ci / mg and was obtained by mixing .sup.3 H-labeled paclitaxel at 6.2 Ci / mmol with 100 mg of unlabeled paclitaxel (Napro Biotherapeutics, Boulder, Colo.; or National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md.) in methanol and then evaporating the solvent.
Protocol. The paclitaxel-loaded polymer discs were placed in a microporous polyethylene specimen capsule (8.times.8 mm internal diameter and height), which was immersed in 7 ml of 0.1M phosphate buffer, pH...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com