Thin film transistor array substrate for a liquid crystal display
a technology of thin film transistors and liquid crystal displays, applied in non-linear optics, identification means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of contact failure, reduced aperture ratio, complicated processing steps, etc., and achieve good performance and reduce the number of masks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first preferred embodiment
[0084]FIGS. 1 to 5 illustrate a TFT array substrate according to a first preferred embodiment of the present invention.
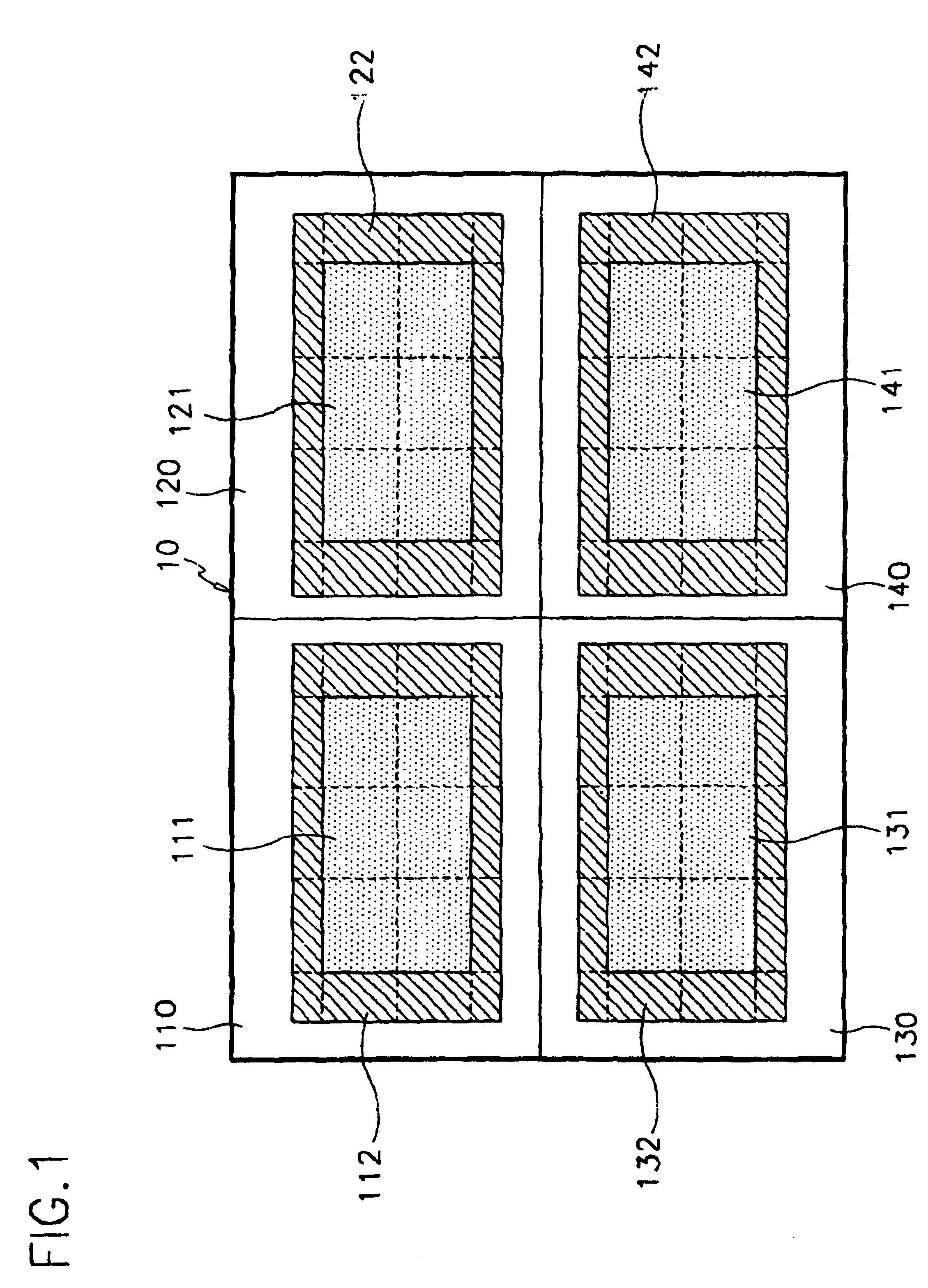
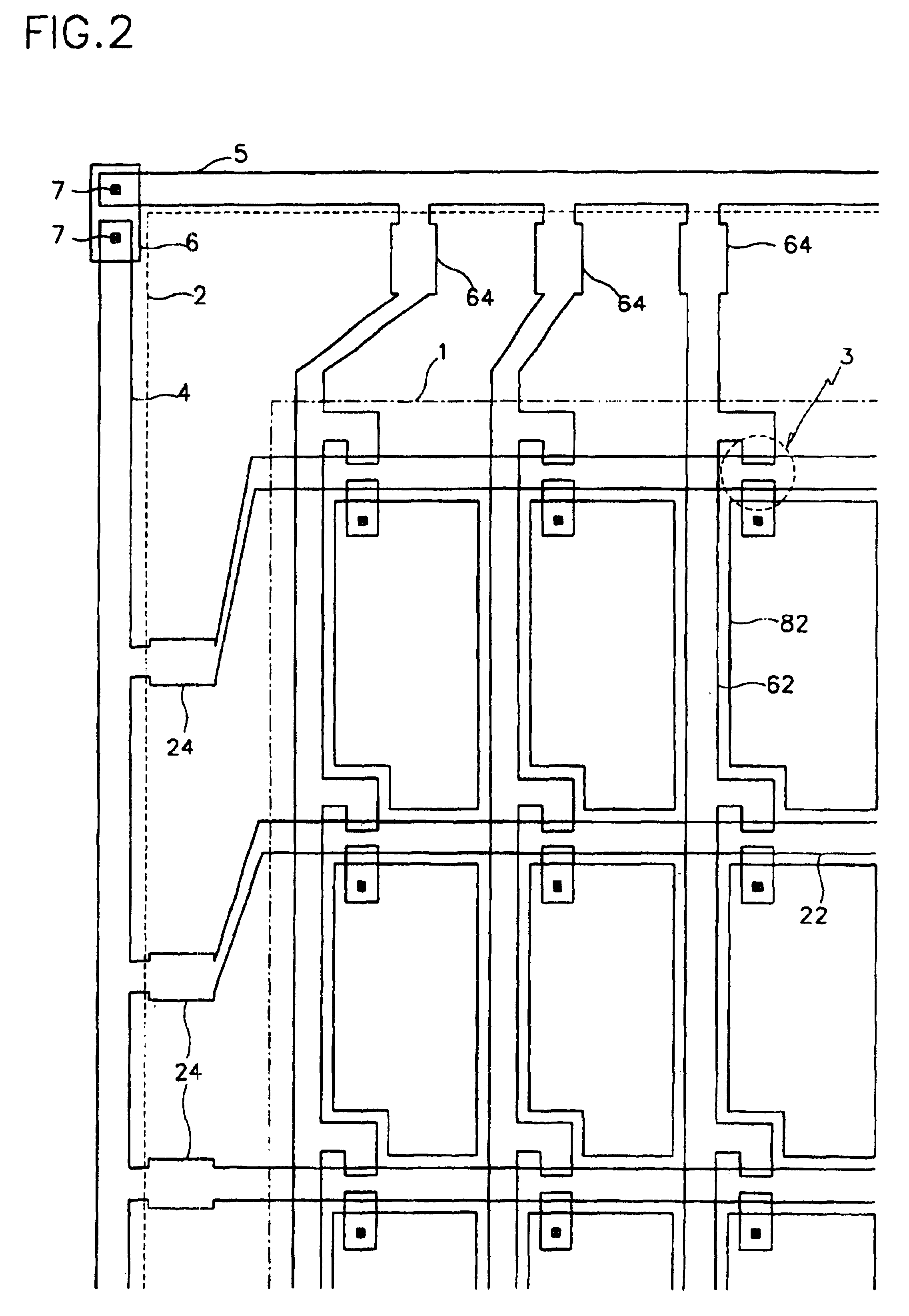
[0085]A plurality of panel regions for LCDs may be made at one insulating substrate at the same time. For example, as shown in FIG. 1, four panel regions 110, 120, 130 and 140 are made with display areas 111, 121, 131 and 141, and peripheral areas 112, 122, 132 and 142. TFTs, lines and pixel electrodes for the main components are repeatedly arranged at the display areas 111 to 141, whereas pads and other static electricity protection circuits for the components connected to the driving circuits are provided at the peripheral areas 112 to 142.
[0086]The display areas 111 to 141 and the peripheral areas 112 to 142 are divided into several regions, and each region is light-exposed by a stepper. A photoresist film coated the substrate is exposed to light using identical or different masks per region. After the exposure, the photoresist film is wholly developed to form a ...
second preferred embodiment
[0138]FIGS. 18 to 23 illustrate a method for fabricating a TFT array substrate according to a second preferred embodiment of the present invention. In this preferred embodiment, the processing steps are the same as those related to the first preferred embodiment up to the step of depositing the passivation layer 70 onto the substrate 10.
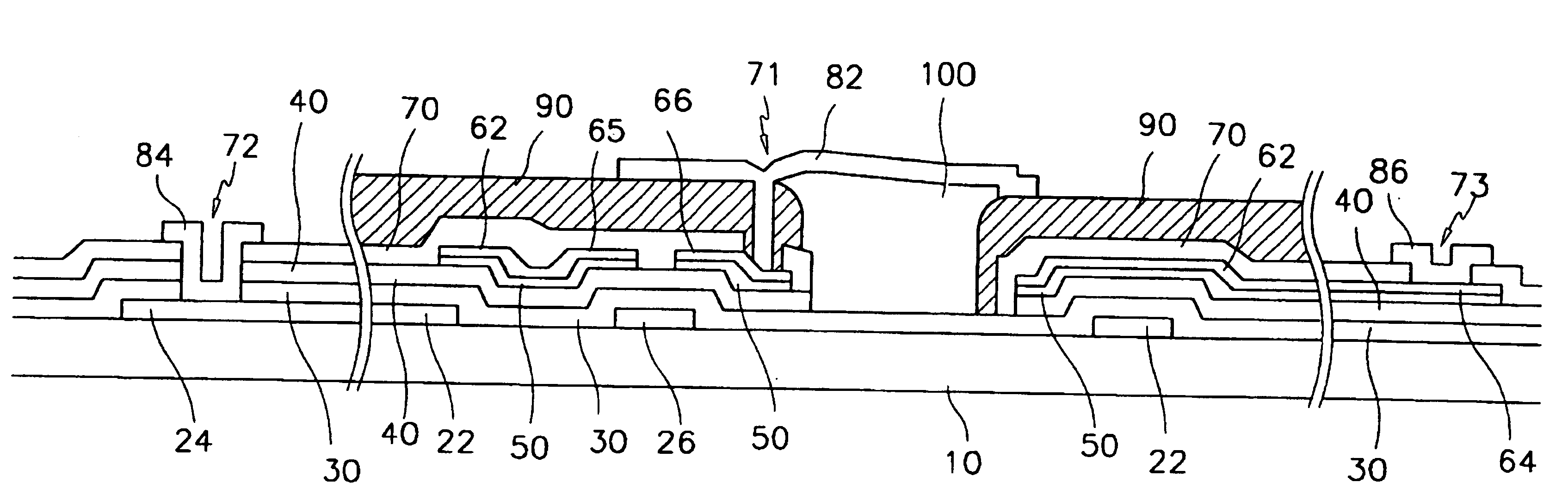
[0139]As shown in FIG. 18, a photoresist film PR is coated onto the passivation layer 70. The photoresist film PR is exposed to light through a third mask, and developed to form a photoresist pattern. That is, the portion B of the photoresist film PR over the gate pad 24, data pad 64 and drain electrode 66 is completely removed. The portion C of the photoresist film PR adjacent to the portion B over the drain electrode 66 and the data pad 64 and positioning at the pixel area is partially removed such that it has a small thickness. The remaining portion A of the photoresist film PR is left without being consumed.
[0140]Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 19, ...
third preferred embodiment
[0148]FIGS. 24 to 29 illustrate the steps of fabricating a TFT array substrate according to a third preferred embodiment of the present invention where a photosensitive organic layer is used for the passivation layer. In this preferred embodiment, the processing steps are similar to those related to the first preferred embodiment prior to the step of depositing a passivation layer onto the substrate 10.
[0149]As shown in FIG. 24, a photosensitive passivation layer 80 of a photosensitive organic material is deposited onto the substrate 10 to a thickness of 3,000 Å. The photosensitive passivation layer 80 is then exposed to light through a third mask, and developed to form a photoresist pattern. That is, the portion B of the photosensitive passivation layer 80 over the gate pad 24, the data pad 64 and the drain electrode 66 is completely removed. The portion C of the photosensitive passivation layer 80 adjacent to the portion B over the drain electrode 66 and the data pad 64 and positi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com