Method of producing zinc phosphate using phosphorus fertilizer
A technology of zinc phosphate and wet zinc phosphate, which is applied in the direction of phosphate, phosphorus oxyacid, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, low purity, and high impurity content in products, and achieve the effects of low production cost, wide sources, and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
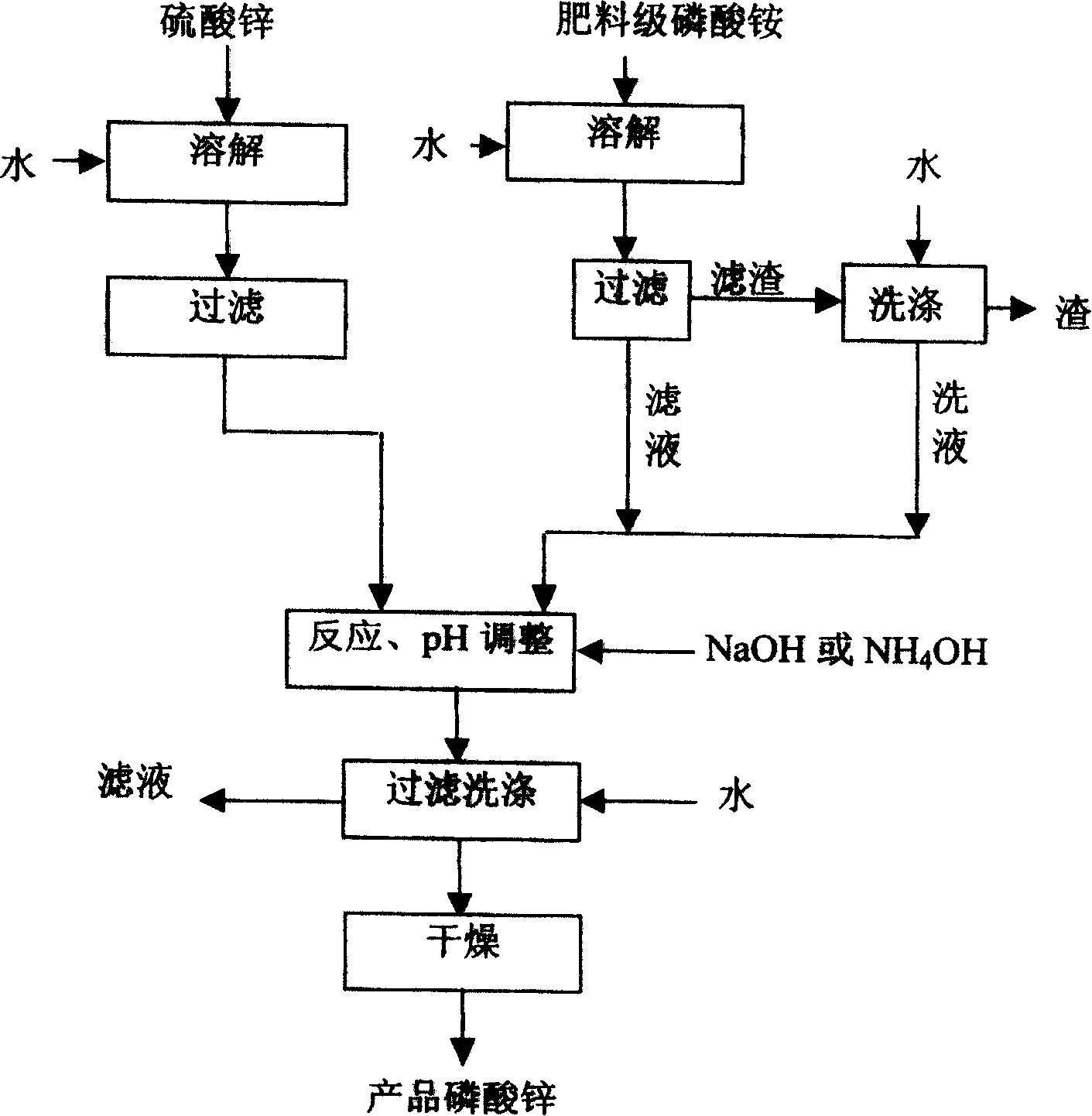
[0034] Dissolve 1.25kg fertilizer grade diammonium phosphate into 1.5kg of 75℃ hot water under stirring, keep the temperature at 75℃, filter after 35 minutes, wash the filter residue with 70℃ hot water once, and combine the lotion and filtrate; 2.6kg sulfuric acid Zinc (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O) A zinc salt solution prepared by dissolving in 2.0 kg of hot water at 70°C, and filtering; the solution prepared by the two raw materials is added to a stirred reactor, and the reaction temperature is maintained at 50°C. After the raw material liquid is added, 40wt% Adjust the pH to 6.8 by sodium hydroxide, and filter the reaction solution after maintaining the temperature for 20 minutes; the filter cake is washed three times with hot water at 70°C, which is three times its weight, to obtain a zinc phosphate wet cake; under normal pressure, at 110°C Dry for 20 minutes to obtain the product zinc phosphate. The analysis results are shown in Table 1:
[0035] Table 1 Product analysis results of Example...
Embodiment 2
[0039] 3kg of fertilizer grade monoammonium phosphate was dissolved in 3.5kg of 75℃ hot water under stirring, kept at 75℃ for 35 minutes and then filtered, the filter residue was washed twice with 60℃ hot water, the washing liquid and the filtrate were combined; 7 kg of zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O) Dissolve in 5kg, 70-80℃ hot water and filter to prepare a 45wt% zinc salt solution, filter; the above two solutions are added to a stirred reactor at the same time, the reaction temperature is maintained at 70-80℃, after the solution is added , Adjust the pH value to 7.2-8 with 40wt% sodium hydroxide, and filter the reactant after maintaining the temperature for 18 minutes; the filter cake is washed twice with 4 times its weight in hot water at 80°C to obtain a zinc phosphate wet filter cake; It was pressed and dried at 110°C for 18 minutes to obtain the product zinc phosphate. The analysis results are shown in Table 2:
[0040] Table 2 Product analysis results of Example 2
[0041] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com