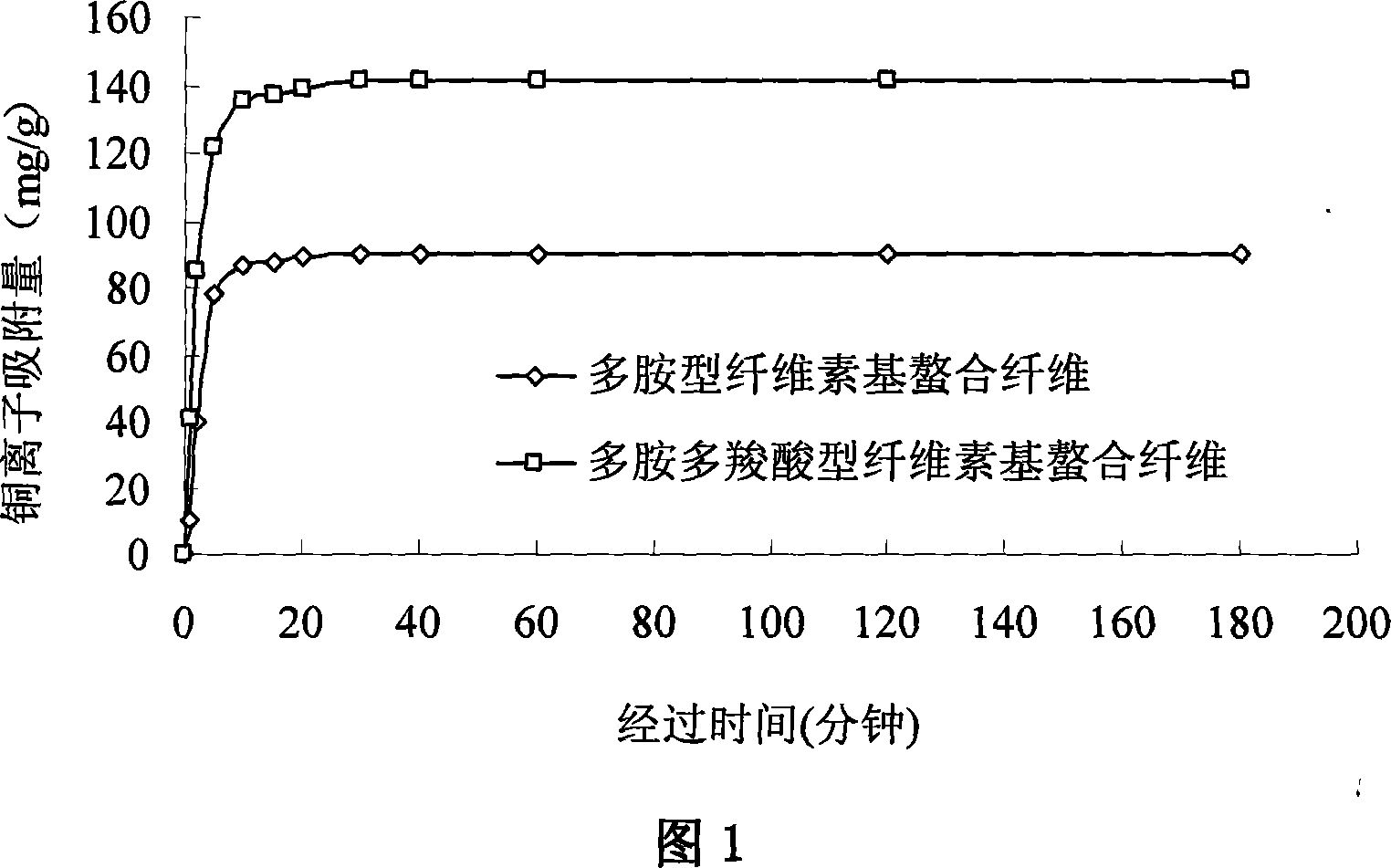
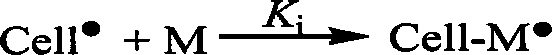Cellulose-base chelated fiber and its synthesizing method and use
A cellulose fiber and chelating fiber technology, applied in the field of chemical modification of cellulose fibers, can solve the problems of slow diffusion, difficult incineration, and high hydrophobicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Epoxy-activated bleached eucalyptus pulp was prepared by bleaching eucalyptus pulp and glycidyl methacrylate at a mass ratio of 1:2; The mass ratio of 3.4 is used to make polyamine-type bleached eucalyptus pulp; the mass ratio of polyamine-type bleached eucalyptus pulp to chloroacetic acid is 1:2 to make polyamine-polycarboxylic acid-type bleached eucalyptus pulp.
Embodiment 2
[0072] masson pine thermomechanical pulp and glycidyl methacrylate with a mass ratio of 1:1.5 to make epoxy-activated masson pine thermomechanical pulp; epoxy-activated masson pine thermomechanical pulp and diethylenetriamine with 1 : 3 mass ratio to make polyamine masson pine thermomechanical pulp; polyamine masson pine thermomechanical pulp and chloroacetic acid in a mass ratio of 1:1 to make polyamine polycarboxylic acid masson pine thermomechanical pulp .
Embodiment 3
[0074] Put 2.5g of dry bleached eucalyptus pulp in 250ml of distilled water with nitrogen protection to disperse evenly, add 5.0g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.2ml of emulsifier A and 10ml of 0.1mol / L cerium ammonium nitrate Solution (prepared with 1mol / L nitric acid) and uniformly dispersed, treated at 60°C for 2 hours, then filtered out the fibers, soaked in butanone for 30 minutes at room temperature, filtered, washed with hot distilled water, dried, and finally treated with butanone Extracted for 24 hours to obtain 4.8 g of bleached kraft eucalyptus pulp grafted with glycidyl methacrylate.
[0075] Get 1.0g of glycidyl methacrylate grafted bleached eucalyptus pulp and water, 3.8ml ethylenediamine, and react in medium N,N-dimethylformamide at 70°C for 3 hours, Obtained 1.12g polyamine type chelate fiber. This polyamine type chelating fiber 0.1g is added respectively in the 50ml cupric nitrate and the lead nitrate solution that metal ion concentration is 500mg / L, and control ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com