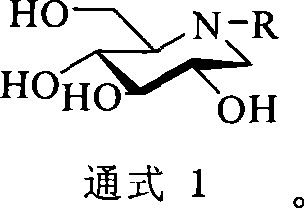
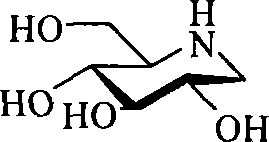
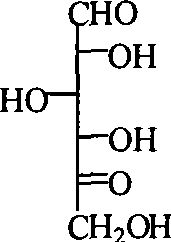
1-deoxidization nojiri toxin derivant, production method and uses thereof
A technology for deoxidizing Nojiri and derivatives, applied in organic chemistry and other directions, can solve problems such as high cost, difficulty in expanding production, and difficulty in chemical synthesis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Preparation of 1,2,5,6-position propylidene protected D-glucoside
[0027] Dissolve 15g D-glucose in 300ml acetone, add ZnCl 2 8g, electromagnetically stirred at room temperature for 10h, neutralized with 50% NaOH to neutral after detection, filtered with suction, evaporated to dryness, crystallized with cyclohexane to obtain 13.4g of white double-protected needle crystals, melting point 110.2℃~111.0℃ , yield 89.3%. (Document: 111.5~112.7℃)
[0028] 1 H-NMR δ: 5.95 (1H, d, J=3.6HZ, 1-H); 4.54 (1H, d, J=3.6Hz, 2-H); 4.37~4.32 (2H, m, 3-H, 4 -H); 4.17 (1H, dd, J = 6.4Hz, 8.8Hz, 5-H); 4.08 (1H, dd, J = 2.4Hz, 7.2Hz, 6-H); 3.98 (1H, dd, J = 5.2Hz, 8.4Hz, 6-H); 1.50, 1.45, 1.37, 1.32 (each3H, s, 4CH 3 ).
[0029] Anal. Clcd for C 12 h 20 o 6 : C, 55.35; H, 7.74 Found: C, 55.37; H, 7.76.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 Preparation of 1,2-position propylidene protected D-glucoside
[0031] Dissolve 18g of 1,2,5,6-position propylidene-protected D-glucoside in 80ml of methanol, add 80ml of 0.8% sulfuric acid, stir electromagnetically at room temperature for 24h, then neutralize with barium carbonate, heat to a slight boil, and filter And the filtrate was evaporated to dryness, and recrystallized with methanol-ether to obtain white needle-like crystals. Yield: 98.2%, melting point: 160.0-161.5°C (literature value: 160.0-161.0°C)
[0032] 1 H-NMR δ: 5.98 (1H, d, J = 3.6HZ, 1-H); 4.55 (1H, d, J = 3.6Hz, 2-H); 4.37 (1H, d, J = 3.2Hz, 3- H); 4.14~4.18(1H, m, 4-H); 4.10(1H, dd, J=2.8Hz, 6.0Hz, 5-H); 3.93(1H, dd, J=3.2Hz, 11.2Hz, 6 -H); 3.78 (1H, dd, J = 6.0Hz, 11.6Hz, 6-H); 1.50, 1.33 (each 3H, s, CH 3 ).
[0033] Anal. Clcd for C 9 h 16 o 6 : C, 49.09; H, 7.32 Found: C, 49.05; H, 7.34.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 Preparation of dicarbonyl D-glucose shown in structural formula 2
[0035] 5.0 g of D-glucoside protected by 1,2-position propylidene and 30.0 g of dibutyltin oxide were dissolved in 200 ml of anhydrous toluene, protected by argon, and refluxed for 4 hours. Lower the temperature of the reaction system to 0-5°C, add bromine dropwise until the reddish-brown color does not fade, continue the reaction for 1 hour, add 50ml of water, extract bibutyltin oxide with toluene, neutralize the aqueous phase with sodium bicarbonate until neutral, freeze Dry, dissolve with ether, filter out inorganic salts, freeze and crystallize to obtain white crystals (98.2% yield, melting point 109.5°C-110.2°C (literature value: 108.0-110.0°C); 1H-NMR δ: 5.89 (1H, d, J = 3.6HZ, 1-H); 4.40 (1H, d, J = 3.6Hz, 2-H); 3.94 (1H, d, J = 2.8Hz, 4- H); 3.73 (1H, d, J = 12.4Hz, 6-H); 3.57 (1H, d, J = 12.4Hz, 6-H); 1.34, 1.22 (each 3H, s, CH 3 ): Anal.Clcd for C 9 h 14 o 6 : C, 49.54; H, 6.47 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com