Method for processing heavy metal wastewater
A technology for heavy metals and wastewater, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of hydrogen sulfide secondary pollution, high treatment cost, long reaction residence time, etc., and achieve low cost , remove the effect of high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
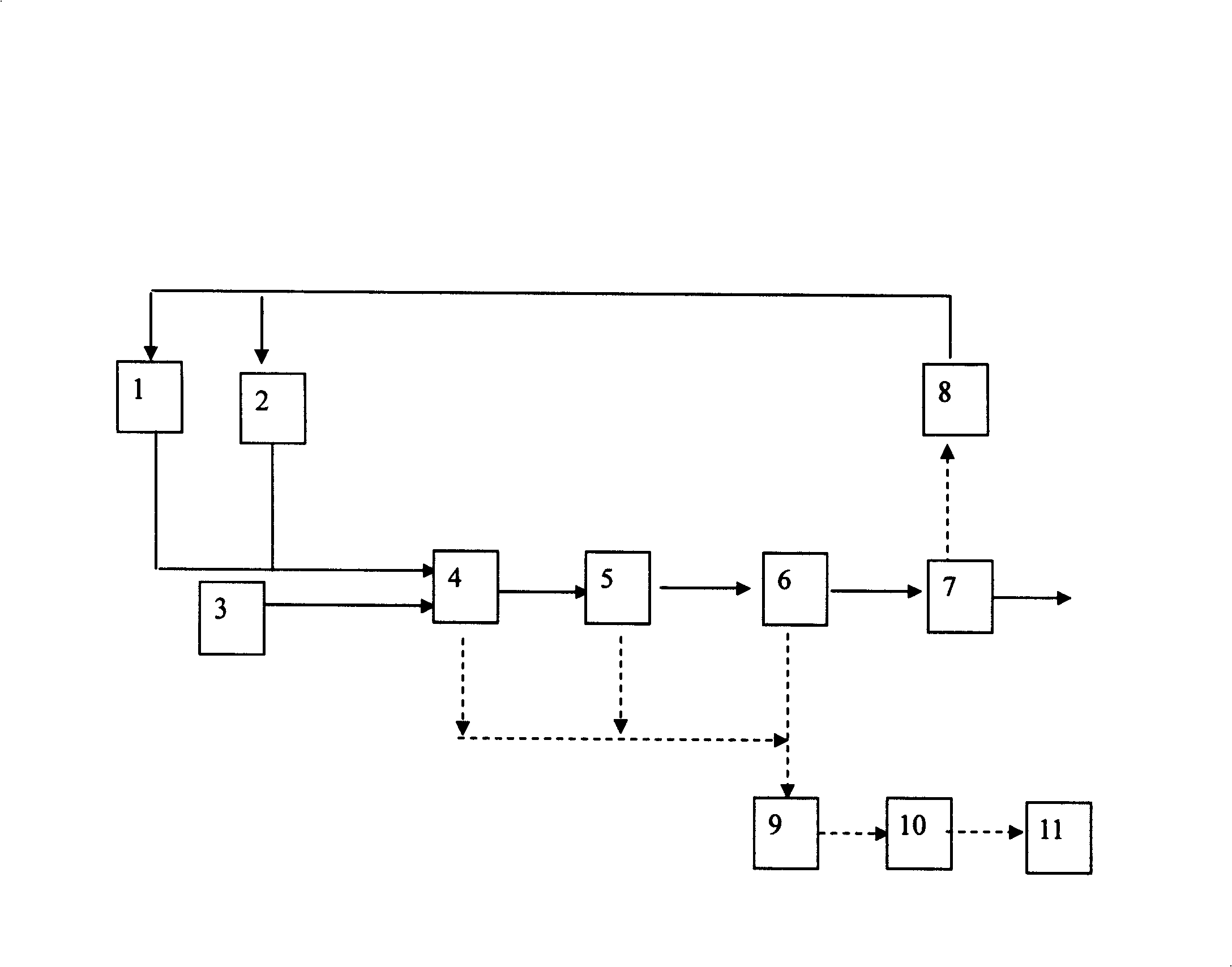
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
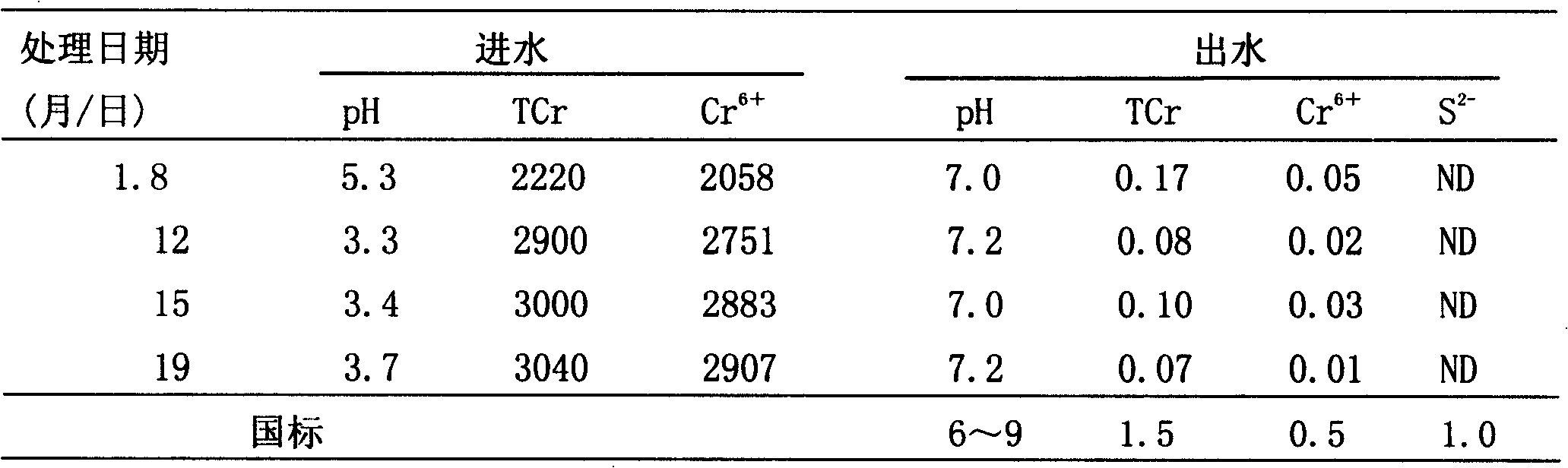
[0033] Example 1: Treatment of high-concentration chromium-containing wastewater in a certain workshop of a cold-rolling factory
[0034] Add the medium containing 0.5% lactic acid protein salt, 1% ferrous salt and 1% sulfate and K, Mg, Ca, Cu, Mn, B, Si, Mo elements in the incubator to adjust pH7. 0~7.4, add compound bacterial agent, control temperature 30°C, anaerobic or facultative culture for 36 hours, generate nano-FeS x compound for use.
[0035] Processing 0.4m per hour 3 High concentration chromium wastewater, wastewater (W) and bionano FeS x The ratio of (BN) is 2:1, after static mixing, reactor reaction for 30min. Add 1‰ of cationic polyacrylamide (PAM) to flocculate and precipitate and filter to measure chromium and sulfide in water. It can be seen from Table 1 that the total chromium (TCr≤0.17mg / L) and hexavalent chromium (Cr 6+ ≤0.05mg / L) are better than the first-level emission standard of the national standard (TCr1.5mg / L, Cr 6+ 0.5mg / L), no S was detected...
Embodiment 2
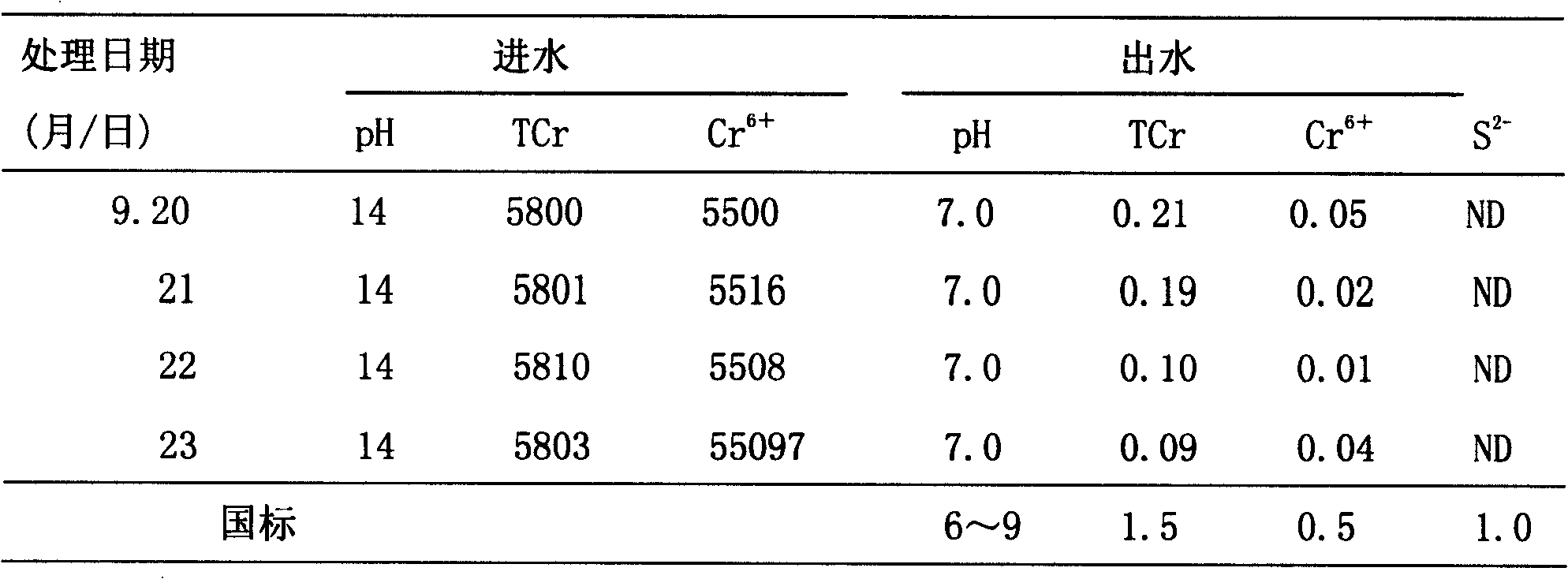
[0039] Example 2: Treatment of leachate from a certain chromium slag mountain
[0040] Add the culture medium that contains 5% lactic acid protein salt, 10% ferrous salt and 10% sulfate and K, Mg, Ca, Cu, Mn, B, Si, Mo elements in the incubator, adjust pH7. 0~7.4, add compound bacterial agent, control temperature 35°C, anaerobic or facultative culture for 48 hours, generate nano-FeS x compound for use.
[0041] The leachate contains Cr 6+ 5500mg / L, TCr 5800mg / L, pH14, treatment 9m per hour 3 Leachate, W / BN=1:1. After static mixing, reactor reaction, precipitation and filtration, the results are listed in Table 2. It can be seen that TCr≤0.21mg / L and Cr in the effluent 6+ ≤0.05mg / L are superior to the first-level discharge standard of the national standard, and no S is detected in the effluent 2- . The recovery rate of Cr in the sludge is greater than 97.5%.
[0042] Table 2 Treatment results of leachate from a chromium slag mountain Unit: mg / L
[0043]
[0044] Not...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: A certain mining waste liquid treatment
[0046] Add the medium containing 3% lactic acid protein salt, 6% ferrous salt and 6% sulfate and K, Mg, Ca, Cu, Mn, B, Si, Mo elements in the incubator to adjust pH7. 0~7.4, add compound bacterial agent, control temperature at 39°C, anaerobic or facultative culture for 72 hours, generate nano-FeS x compound for use.
[0047] The waste liquid contains Cr 6+ 1280mg / L, V3800mg / L, pH2~3, 1m per hour 3 Waste liquid, W / BN=1:3. After static mixing, reactor reaction, precipitation and filtration, the results are listed in Table 3. It can be seen that Cr in the effluent 6+ ≤0.05mg / L, TCr≤0.15mg / L, V≤0.01mg / L, all better than the national standard and the primary discharge standard of Sichuan Province, no S was detected in the effluent 2- . The recovery rate of Cr in the sludge is greater than 96%, and the recovery rate of vanadium is greater than 93%.
[0048] Table 2 Treatment results of leachate from a chromium sl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com