Electrochemical deposition preparation method of high efficient light-emitting film
A light-emitting thin-film, high-efficiency technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
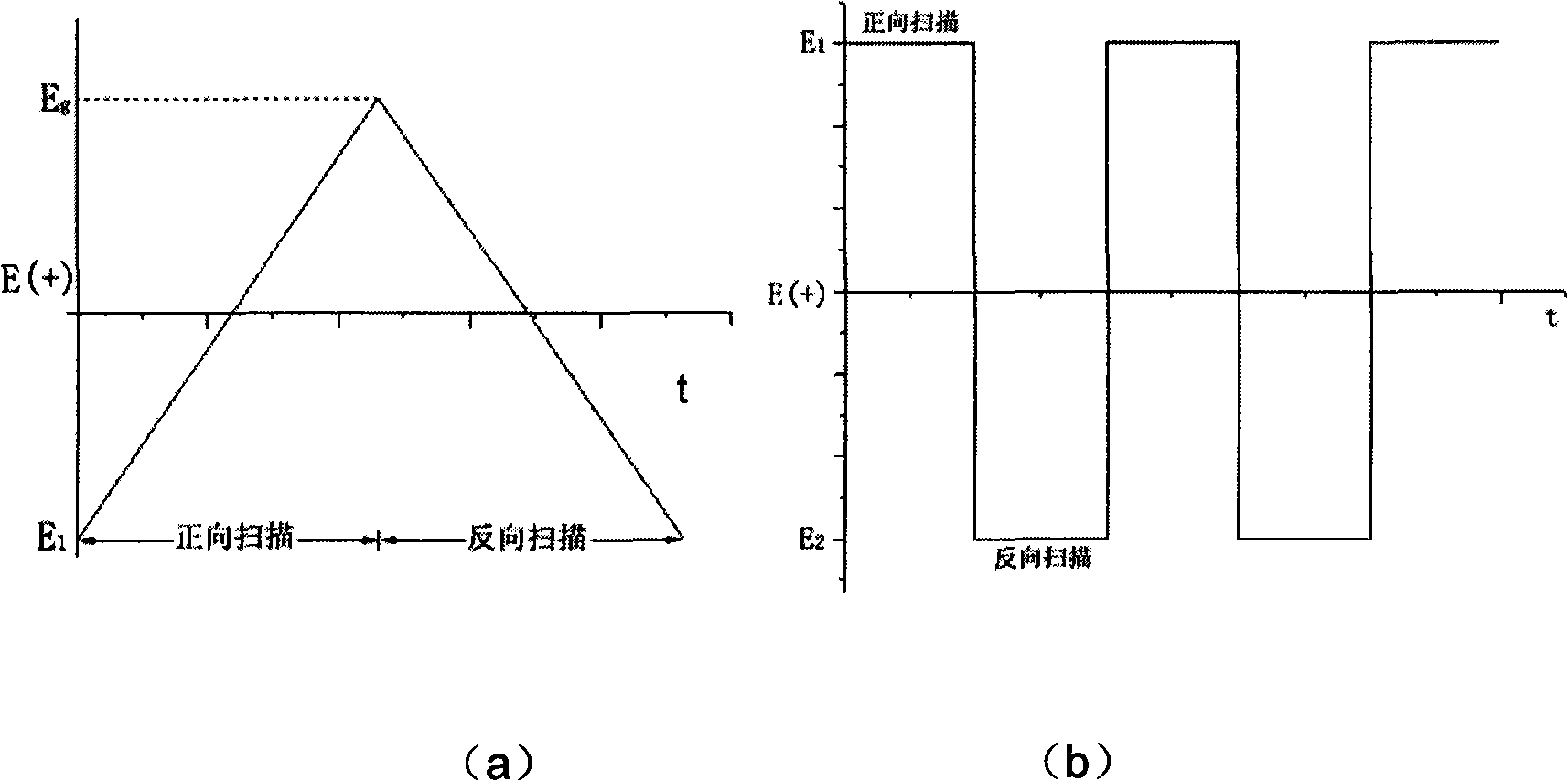
[0106] Example 1: Electrochemical preparation of luminescent film
[0107] 1. Preparation of electrolyte
[0108] Dissolve the luminescent compound TCPC with electroactive groups (the synthesis of the luminescent compound is detailed in Chinese Patent: 200610016555.0) in the electrolyte solution, and the concentration of the luminescent compound is 1 mg / ml. The supporting electrolyte is tetrabutylammonium hexafluoroarsenate with a concentration of 0.1 mol / liter. The solvent is a mixed solution of acetonitrile and dichloromethane with a volume ratio of 3:2. The luminescent compound used in the present invention is slightly soluble in acetonitrile, and in order to increase the concentration of the compound, dichloromethane is added to increase the solubility of the luminescent compound.
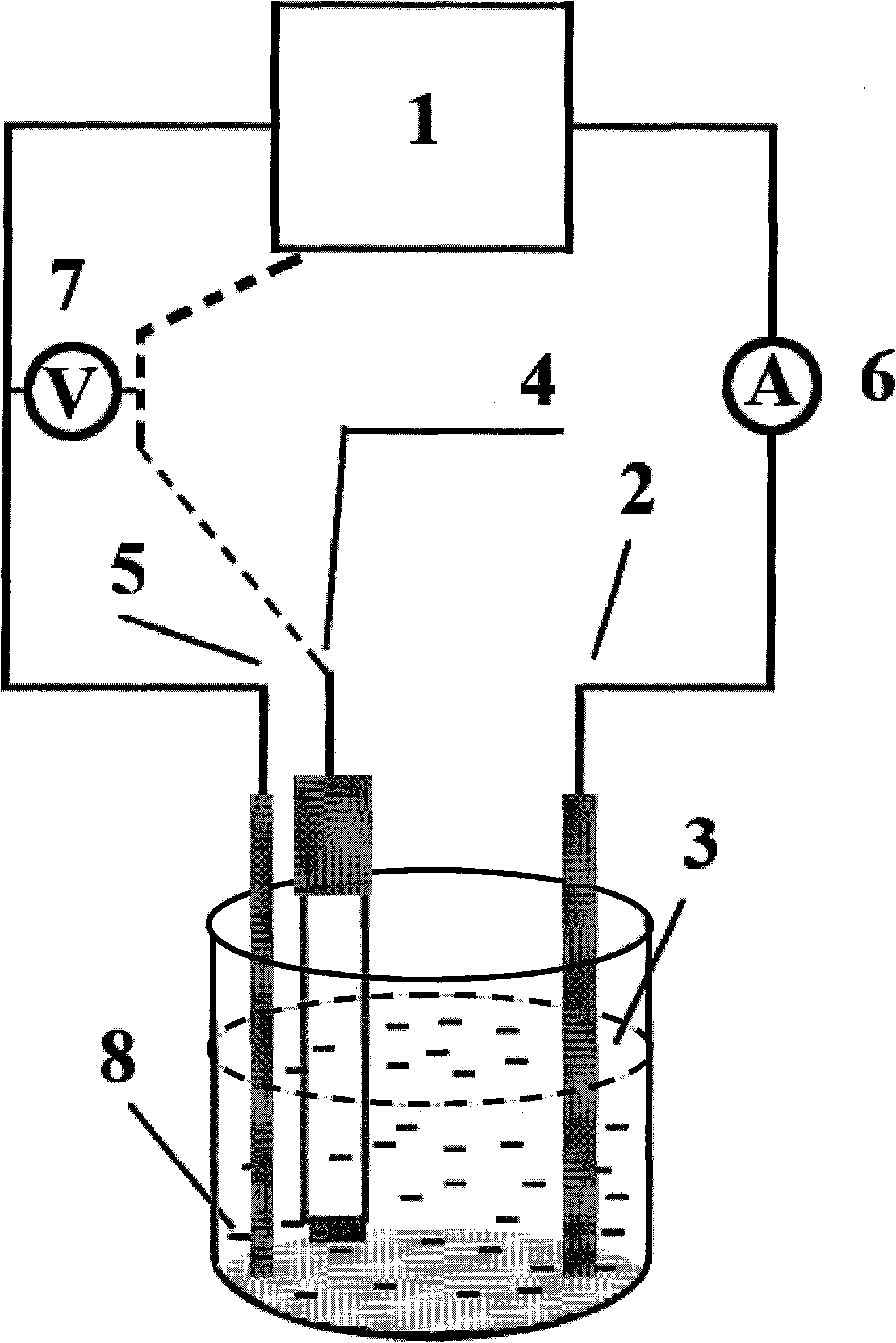
[0109] 2. The use of electrodes
[0110] The working electrode is an ITO (indium tin oxide) electrode with an area of 1 to 2 square centimeters. The auxiliary electrode is a titanium plat...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Example 2: Application of high-efficiency electrochemical deposition of luminescent thin films in organic electroluminescent devices
[0124] 1. Preparation of single-layer electroluminescent devices
[0125] The electrodeposited film prepared by cyclic voltammetry was cleaned and then dried under vacuum for 1 hour at a temperature of 25°C. Obtain the dry film under vacuum conditions, vapor-deposit metal barium (50nm) and aluminum (200nm) as the cathode of the electroluminescent device, the thickness of the deposited luminescent film is about 150nm, and the thickness is measured by atomic force microscope.
[0126] Figure 9 The variation curves of voltage-brightness-current density (a) and voltage-current efficiency-energy efficiency (b) of this device are shown. This device starts to emit light from 7V, and the maximum brightness is 6896cd / m 2 , the maximum luminous efficiency is 2.284cd / A, the maximum energy efficiency is 0.512lm / W, and the luminous peak of the de...
Embodiment 3
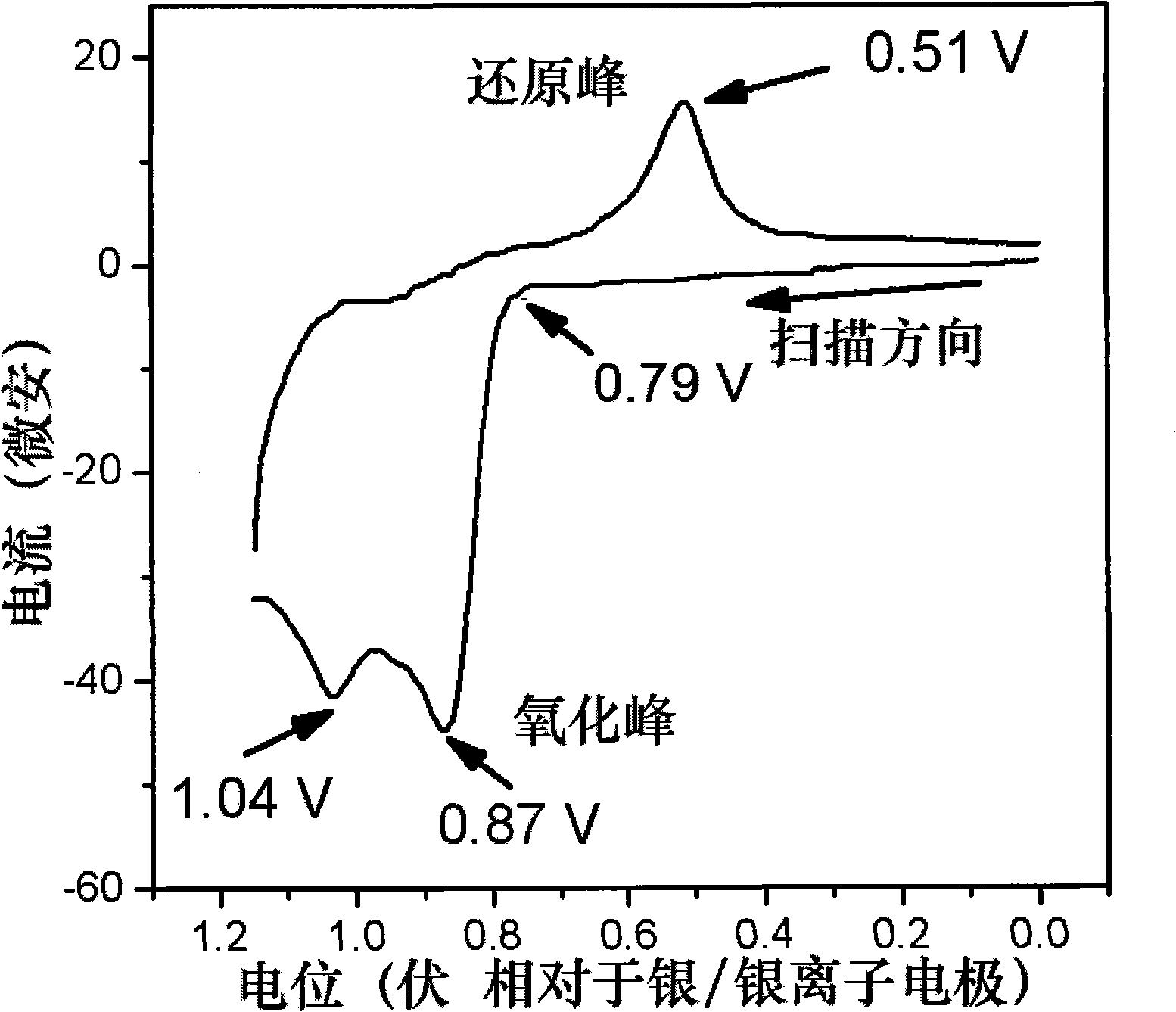
[0135] Spectral tests before and after electrochemical polymerization: such as Figure 12 As shown, 1 is the absorption spectrum of the luminescent compound before electrochemical polymerization, and 2 is the absorption spectrum after electrochemical polymerization. It can be seen from the figure that the absorption peak of the electrochemically polymerized film trifluorene has no obvious change compared with the spin-coated film, indicating that in the electrochemical polymerization, the electrochemical process does not affect the main chain of light emission. After electrochemical polymerization, carbazole is polymerized to generate conjugated dimeric N-alkyl carbazole, which increases the delocalization of π electrons and red-shifts the absorption peak of the original carbazole. The absorption spectrum after electrochemical polymerization shows a broad absorption band from 600nm to 900nm, which is attributed to the absorption of dimeric carbazole cations, indicating that th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com