Rapid nucleating agent of polylactic resin
A polylactic acid resin and nucleating agent technology, which is applied in the field of polylactic acid resin additives and polylactic acid resin nucleating agents, can solve the problems of polylactic acid resin poor oxidation resistance and no reduction effect, and achieve crystallization nucleation Sufficient, improved molding processability, high melting heat release enthalpy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Polylactic acid resin S402 (supplied by Hisun Biomaterials Co., Ltd., containing about 4.8% D-configuration poly-L-lactic acid, with a viscosity-average molecular weight of 56,000) and the fast nucleating agent in the following Table 1 were Ratio, after mixing uniformly in the SHR type high-speed mixer, use TE-35 type co-rotating twin-screw extruder at 165 ° C to melt, blend and extrude, draw strands, cool in a water tank, air dry, and granulate. Finally, dry the resin in a vacuum oven at 60°C for four hours.
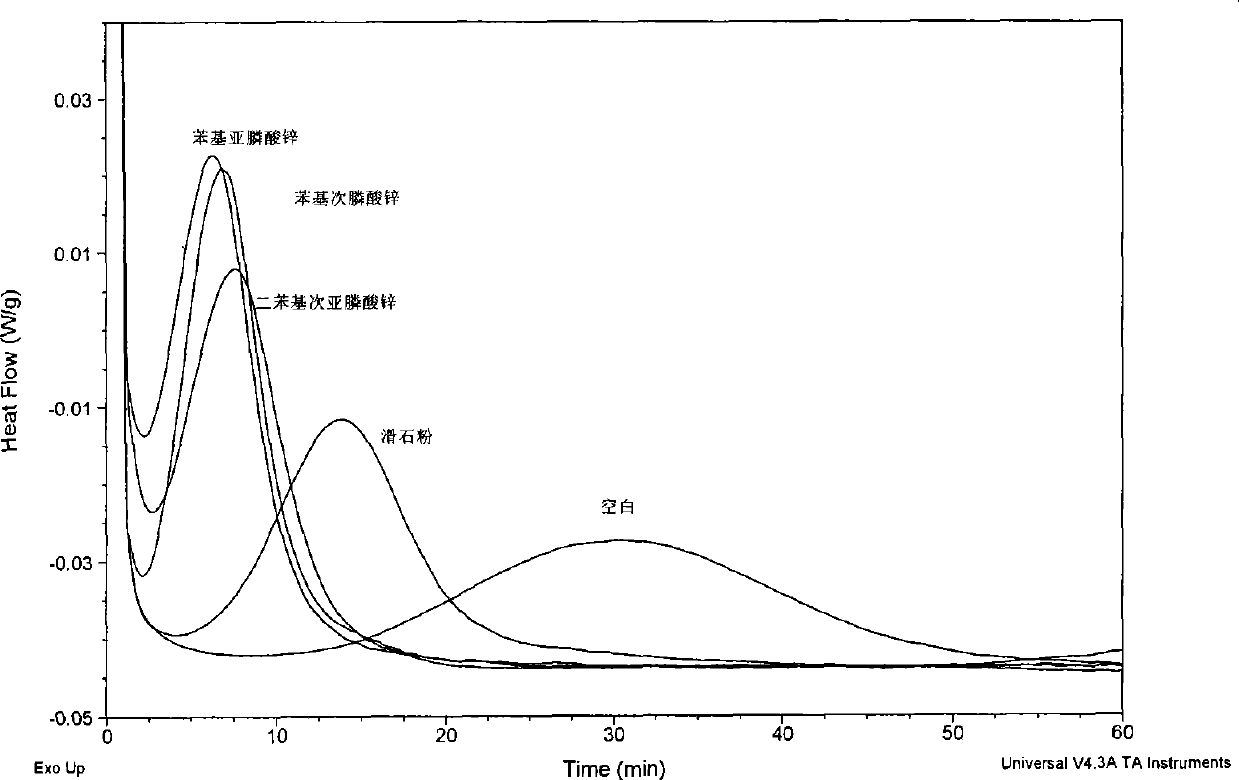
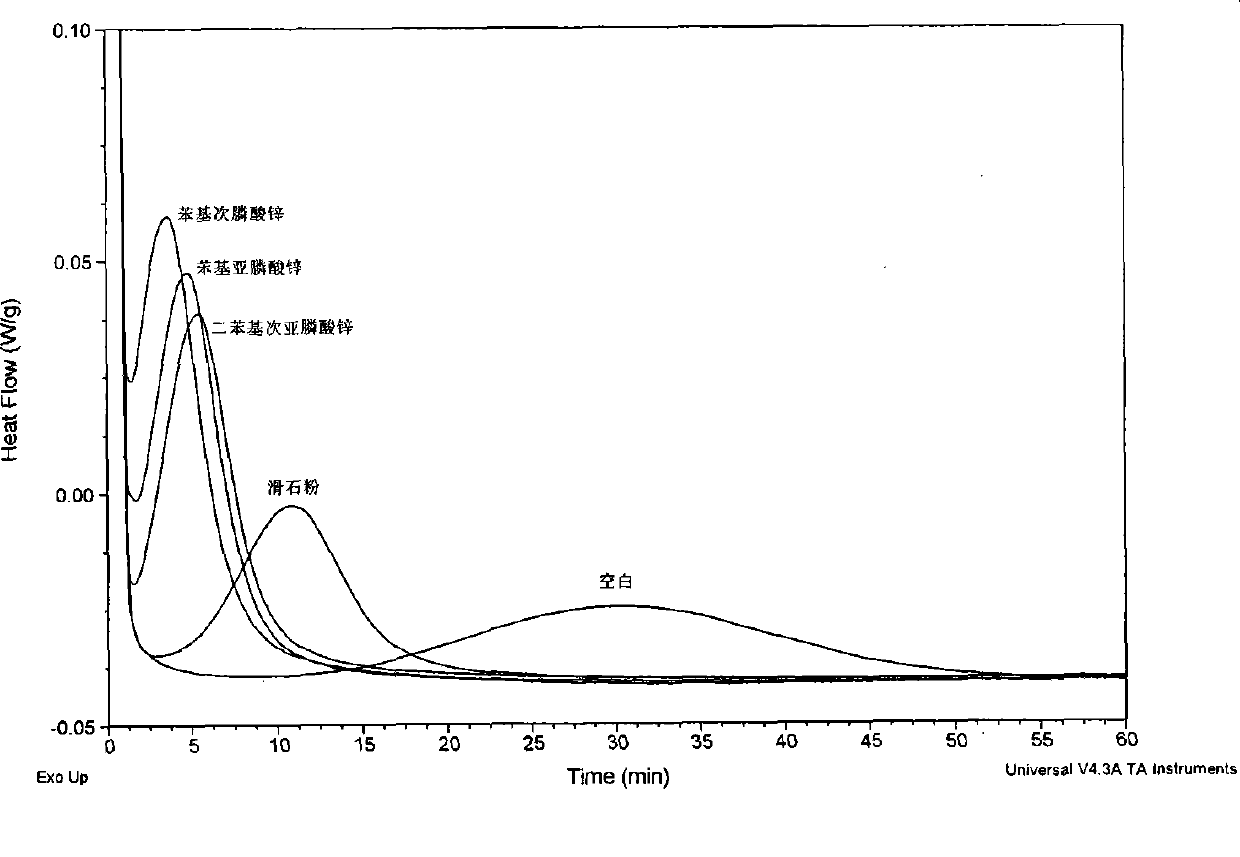
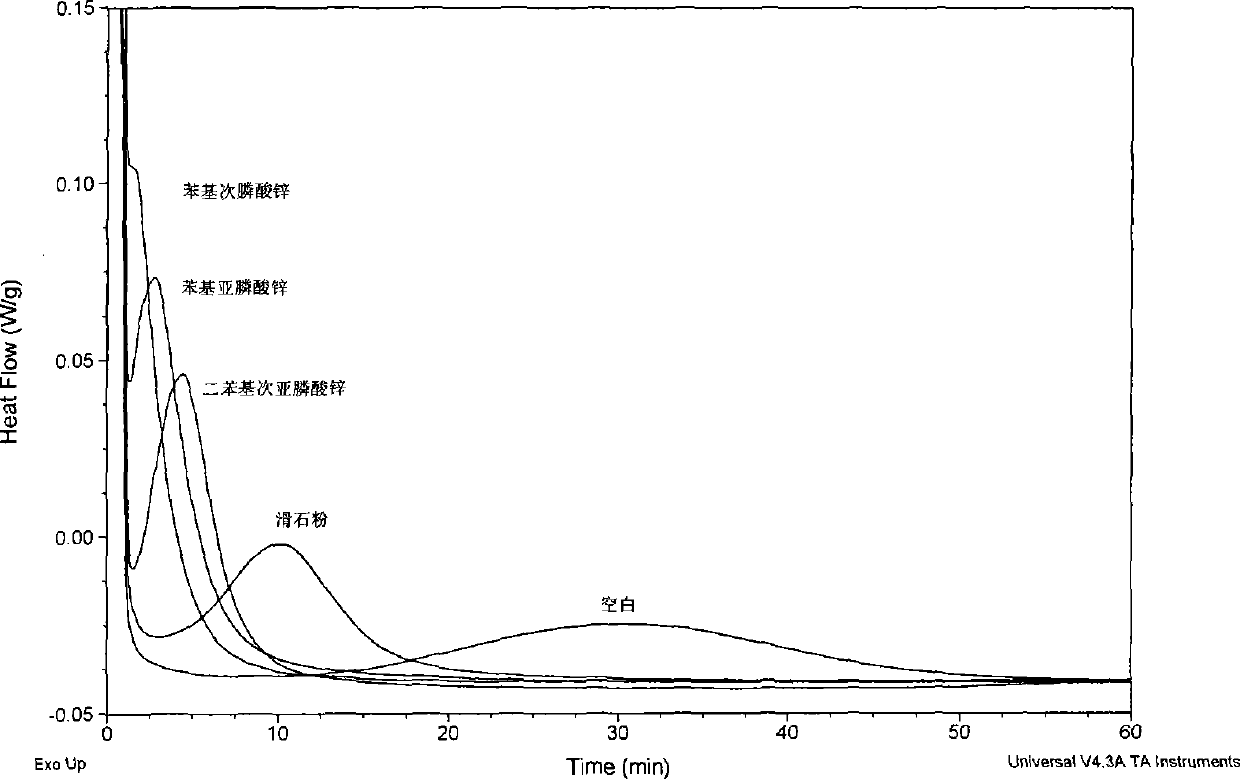
[0042] Test of crystallization speed: the blended resin is tested by DSC. Under the protection of nitrogen, heat up from 20°C to 190°C at 10°C / min, stay for 4 minutes to eliminate heat history, then rapidly cool down to 0°C at 45°C / min, and finally raise the temperature twice from 0°C at 10°C / min to 190°C. This test records the ΔH of polylactic acid during the second heating m (J / g). The secondary temperature rise process to eliminate the heat loss history is...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Polylactic acid resin S330 (provided by Hisun Biomaterials Co., Ltd., containing about 7.1% poly-L-lactic acid in D configuration, with a viscosity average molecular weight of 46,000) and a nucleating agent in a certain proportion, using the method in Example 1 Be prepared into mixed resin, adopt the DSC method test of embodiment 1, the result is shown in table 2.
[0048] Table 2. Melting endothermic enthalpy of polylactic acid resin S330 with different nucleating agents
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Talcum powder is the commonly used nucleating agent of reported polylactic acid, as can be seen from Table 2, compared with adding sodium stearate, sodium benzoate and blank sample, the nucleating effect of talcum powder is good, but adding phenyl The exothermic enthalpy of melting of zinc phosphinate and zinc phenylphosphinate resins is significantly higher than that of talcum powder, indicating that zinc phenylphosphinate and zinc phenylphosphinate have better nucleat...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Polylactic acid resin S401 (provided by Hisun Biomaterials Co., Ltd., containing about 5.5% of D-configuration poly-L-lactic acid, with a viscosity-average molecular weight of 46,000) and a nucleating agent in a certain proportion, using the method in Example 1 Prepare mixed resin, adopt the DSC method test of embodiment 1, the result is shown in table 3.
[0054] Table 3 Melting exothermic enthalpy of polylactic acid resin S401 with different nucleating agents
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] In Table 3, the exothermic enthalpy of melting of the resin added with zinc phenylphosphinate is higher than that of the resin added with calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide, zinc stearate, and zinc benzoate, indicating that the nucleation rate of zinc phenylphosphinate is faster.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com