A method of producing lithium ion battery positive pole material fluorine Lithium Vanadium Phosphate by microwave rapid reaction
A lithium-ion battery, lithium vanadium phosphate technology, applied in the field of lithium vanadium phosphate, can solve the problems of poor conductivity and cycle performance, uneven particle size distribution of synthetic materials, uneven particle size distribution of materials, etc., and achieve easy control , Inhibit excessive growth, the method is simple and convenient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
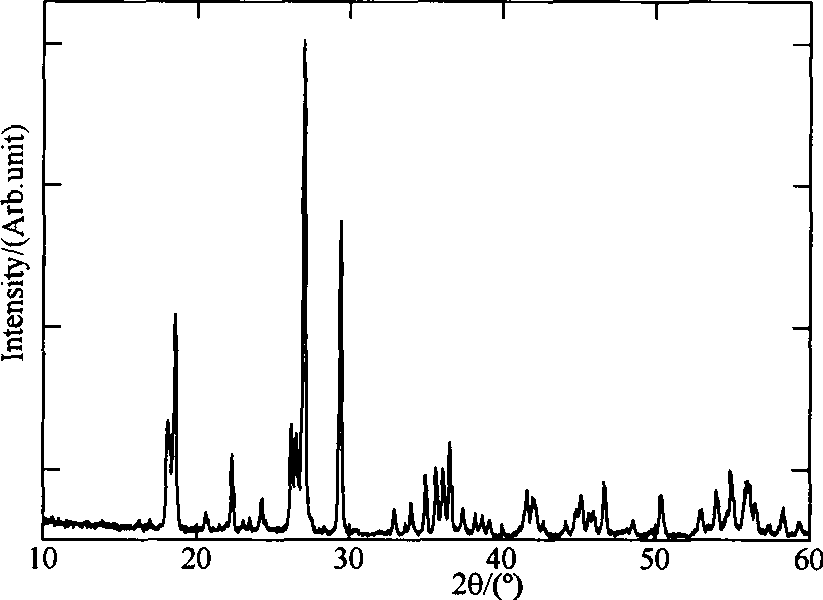
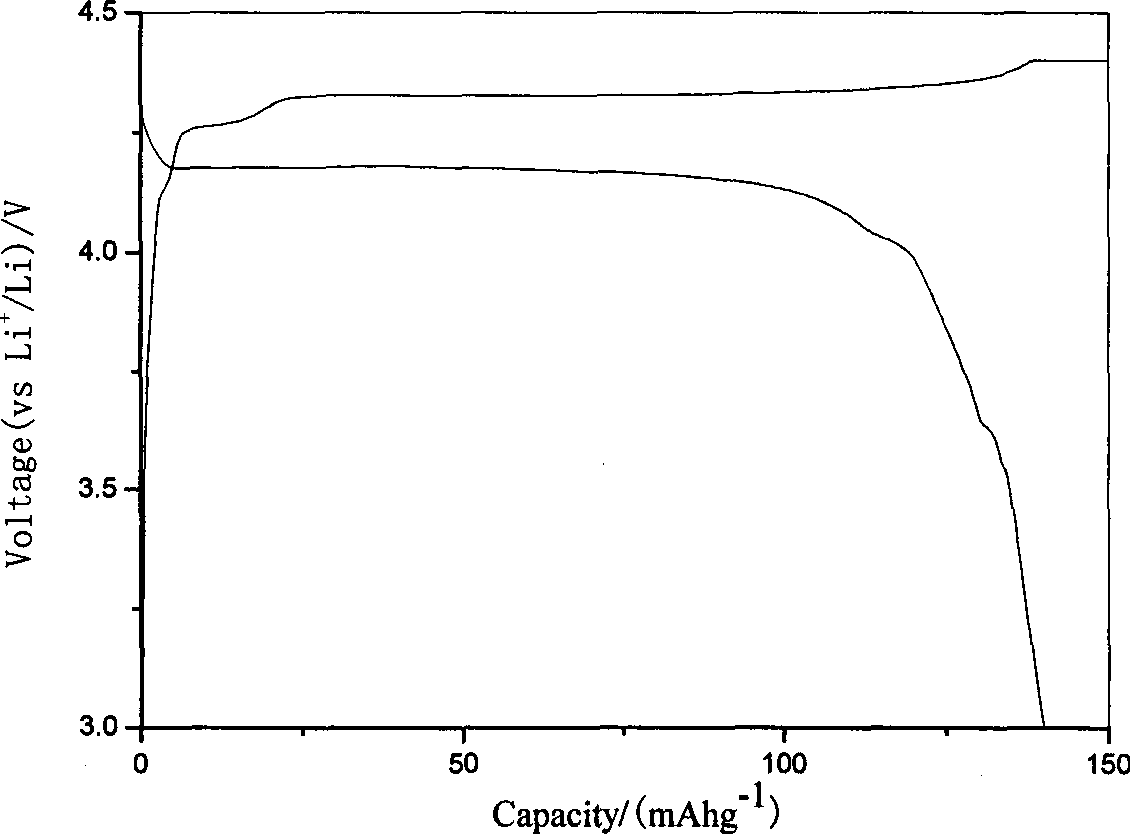
[0017] After mixing 0.095mol of vanadium pentoxide powder, 0.21mol of lithium acetate, 0.105mol of malic acid, 0.20mol of ammonium fluoride and 0.21mol of diammonium hydrogen phosphate, under the protection of nitrogen at 450°C, 550°C, 650°C, Sinter at 750°C for 10 minutes respectively, and the finished product LiVPO will be obtained after cooling 4 F. The obtained products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, showing that they were all LiVPO 4 F, without any impurity phase, the particle size of the product obtained by SEM is about 2 μm. The obtained product was assembled into an experimental button battery to measure its charge-discharge specific capacity and cycle performance. The charge-discharge was carried out at a rate of 1C. The initial discharge capacity and the discharge capacity after 30 cycles are shown in Table 1.
[0018] Table 1 Experimental conditions and results of Example 1
[0019] serial number Sintering temperature
Embodiment 2
[0021] After mixing 0.10mol of vanadium pentoxide powder with 0.20mol of lithium fluoride, 0.10mol of adipic acid, 0.21mol of sodium fluoride and 0.20mol of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, they were sintered at 650°C under the protection of argon for 10, 20, 30 and 40 minutes, after cooling, the finished LiVPO 4 F. The obtained products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, showing that they were all LiVPO 4 F, without any impurity phase, the particle size of the product obtained by SEM is about 2 μm. The obtained product was assembled into an experimental button battery to measure its charge-discharge specific capacity and cycle performance. The charge-discharge was carried out at a rate of 1C. The initial discharge capacity and the discharge capacity after 30 cycles are shown in Table 2.
[0022] Table 2 Experimental conditions and results of Example 2
[0023] serial number Sintering temperature
Embodiment 3
[0025] After mixing 0.105mol of vanadium pentoxide powder, 0.19mol of lithium chloride, 0.095mol of citric acid, 0.19mol of potassium fluoride and 0.19mol of potassium phosphate, under the protection of argon at 480°C, 580°C, 680°C, Sinter at 750°C for 40 minutes respectively, and the finished product LiVPO will be obtained after cooling 4 F. The obtained products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, showing that they were all LiVPO 4 F, without any impurity phase, the particle size of the product obtained by SEM is about 2 μm. The obtained product was assembled into an experimental button battery to measure its charge-discharge specific capacity and cycle performance. The charge-discharge was carried out at a rate of 1C. The initial discharge capacity and the discharge capacity after 30 cycles are shown in Table 3.
[0026] Table 3 Experimental conditions and results of Example 3
[0027] serial number Sintering temperature
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com