Method for constructing chlorella expression vector, converting chlorella and breaking wall of chlorella
An expression vector, chlorella technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, to achieve the effect of reducing costs and steps, increasing wall breaking rate, and increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1. Expression vector construction method of Chlorella ellipsoides nitrate reductase mutant
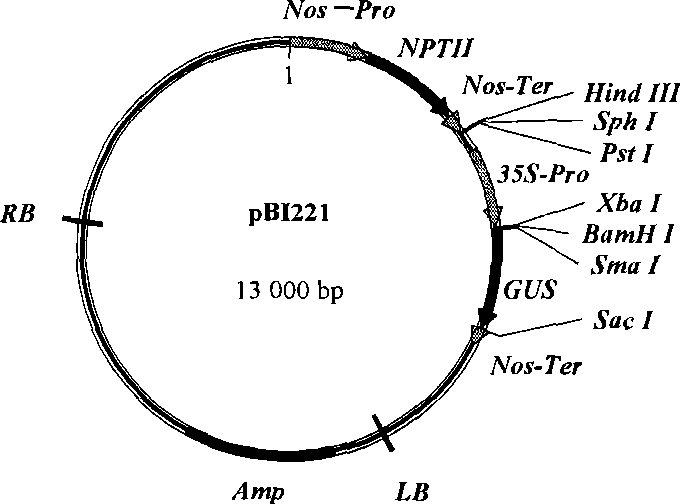
[0042] Primers were designed according to the Ubiquitin promoter sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1), upstream primer: 5'CCGGAAGCTTGTGCAGCGTGACCCG3' (SEQ ID NO: 2); downstream primer: 5'GCCCGGATCCCTGCAGAAGT3' (SEQ ID NO: 3), wherein in the upstream primer A Hind III restriction site was added, a BamHI restriction site was added to the downstream primers, and the Ubiquitin promoter was obtained from the maize genome by PCR. The sequencing results showed the Ubiquitin promoter sequence (SEQ ID NO: 4, which is in SEQ ID NO; A Hind III restriction site and a BamH I restriction site were added to the 5' end and 3' end of 1, respectively). The PCR product was double-digested with HindIII and BamHI endonucleases, plasmid pBI221 (Clontech) ( figure 1 ) was also digested with Hind III and BamH I endonucleases at 16°C overnight, and the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia co...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2. Using the pGreen0029 framework to construct an expression vector.
[0046] Primers were designed according to the Nos terminator sequence (SEQ ID NO: 7), upstream primer: 5'ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCGAATTTCCCCGATCGTTCAAAC3' (SEQ ID NO: 8) downstream primer: 5'CGAGCTCGCCCGATCTAGTAACATAGATGA3' (SEQ ID NO: 9), where Not was added to the upstream primer I enzyme cutting site, add the Sac I enzyme cutting site in the downstream primer, and obtain the Nos terminator from pBI221 (Clontech) by PCR method. The PCR product is double-digested with NotI and Sac I endonucleases, and the plasmid pGreen0029 (BBSRC)( Figure 5 ) was also digested with NotI and Sac I endonucleases at 16°C overnight, and the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, cultured upside down at 37°C overnight on LB medium containing 50 mg / L kanamycin, and the growth of resistant The plasmid was extracted from the colony and identified by enzyme digestion, and the plasmid that could obta...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3. Construction of the expression vector pbin-NR-UΩ-NP1 of Chlorella ellipsoides nitrate reductase mutant
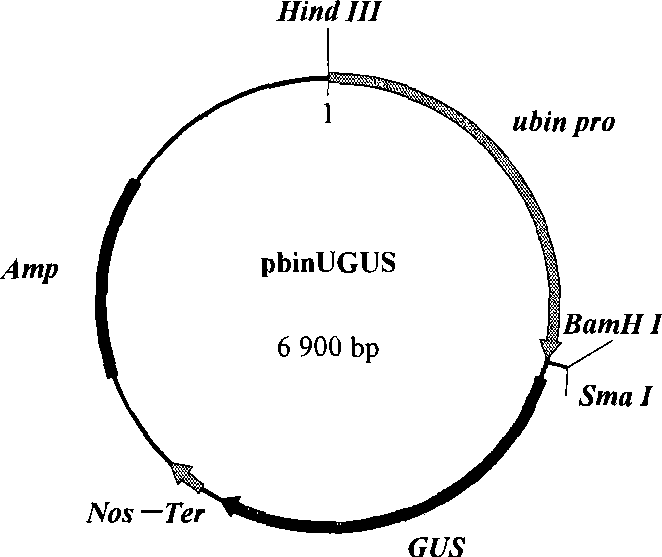
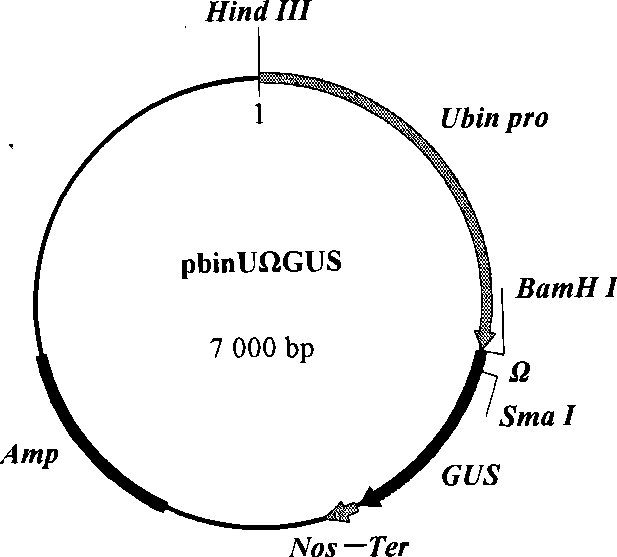
[0050] According to conventional techniques, the GUS gene on the pbin-NR-UΩGUS plasmid was partially digested with BamH I and SacI, and the vector was recovered. The target gene NP-1 (its sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 12) has the restriction sites of BamH I and Sac I at both ends. The NP-1 gene of about 200 bp is recovered by enzyme digestion, and then ligated with the above-mentioned recovered vector overnight at 16°C , the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, cultured upside down on LB medium containing 50mg / L ampicillin at 37°C overnight, and the resistant colony was identified by plasmid digestion, and a fragment of about 200bp (NP-1 gene) to construct the NP-1 plant expression vector pbin-NR-UΩ-NP1( Figure 9 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com