Method for increasing entrapment rate of polylactic acid microspheres to water soluble protein
A technology of water-soluble protein and polylactic acid, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein components, pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of increased drug diffusion, reduced encapsulation rate, and drug loss, and achieves improved Stability, improving encapsulation efficiency, inhibiting the effect of burst release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This embodiment is an experiment of the influence of O-CMC on the stability of protein lysozyme. Take 1 mL of 50 mg / mL (active concentration) lysozyme aqueous solution, add 0.2% and 0.4% O-CMC in mass fraction respectively, and take the solution without O-CMC as a comparison. In the above solution, add 3mL of dichloromethane, ultrasonically shake in a water bath for 1min, after standing for 5min, then ultrasonically shake for 1min, after standing for 5min, transfer the water phase, and extract the oil phase with aqueous solution for 5 times, and combine the extracts into the water phase , The active concentration of lysozyme was determined by the Schugach method, and the results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen that after adding O-CMC, the content of active lysozyme in the solution is higher.
[0031] Table 1 The active concentration of lysozyme
[0032] O-CMC / %
Embodiment 2
[0034]In this example, the method of the present invention was used to prepare microspheres whose carrier materials were PLGA-mPEG and the model drug lysozyme, and compared with the conventional method. The carrier material is PLGA (50:50, M w =200k)-mPEG(M w =5k), the mass ratio of medicine and material is 1: 6; The oil phase adopts dichloromethane, and wherein the content of PLGA-mPEG is 0.1g / mL; The molecular weight of carboxymethyl chitosan is 250k, and the carboxymethyl substitution degree 0.8; NaCl is used as the osmotically active substance, the volume ratio of the external aqueous phase to colostrum is 1:20, and ultrasonic emulsification is used. The main properties of the lysozyme microspheres obtained under the three formulations with different mass fractions of NaCl and O-CMC are listed in Table 2. Other conditions are the same, but the main properties of lysozyme microspheres obtained under the condition of not adding O-CMC and NaCl are also listed in Table 2. I...
Embodiment 3
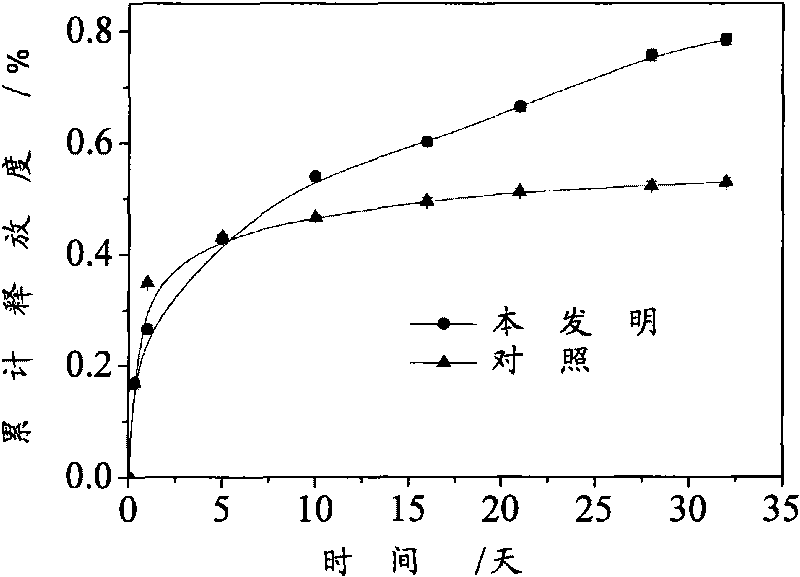
[0038] This implementation is the release characteristics of the microspheres prepared by the method of the present invention. The microspheres are: 1) the lysozyme microspheres prepared by the method in Example 1 according to prescription A, 2) the comparison microspheres in Example 1; the conditions for in vitro release are: release medium PBS, temperature 37°C, stirring speed 100rpm; the release rate is represented by the active concentration of lysozyme, and the activity of lysozyme is determined by the Schugard method. The cumulative drug release curve of the microspheres is attached figure 1 shown. The initial "burst release" is suppressed to a certain extent, and the cumulative release time reaches more than 30 days, which can be used as long-acting release particles. At the same time, the microspheres prepared by the present invention can release more active lysozyme, and the cumulative amount of active lysozyme released is significantly higher than that of the contr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com