Technology for preparing microcrystal glass by utilizing blast furnace water granulated slag and coal ash
A technology of glass-ceramics and blast furnace slag, which is applied in the technical field of preparing glass-ceramics by using blast furnace slag and fly ash, which can solve the problems of complex process procedures, low utilization rate of waste slag, and addition of crystal nucleating agents, and achieve simplification Process flow, reduce production cost, reduce the effect of sintering temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
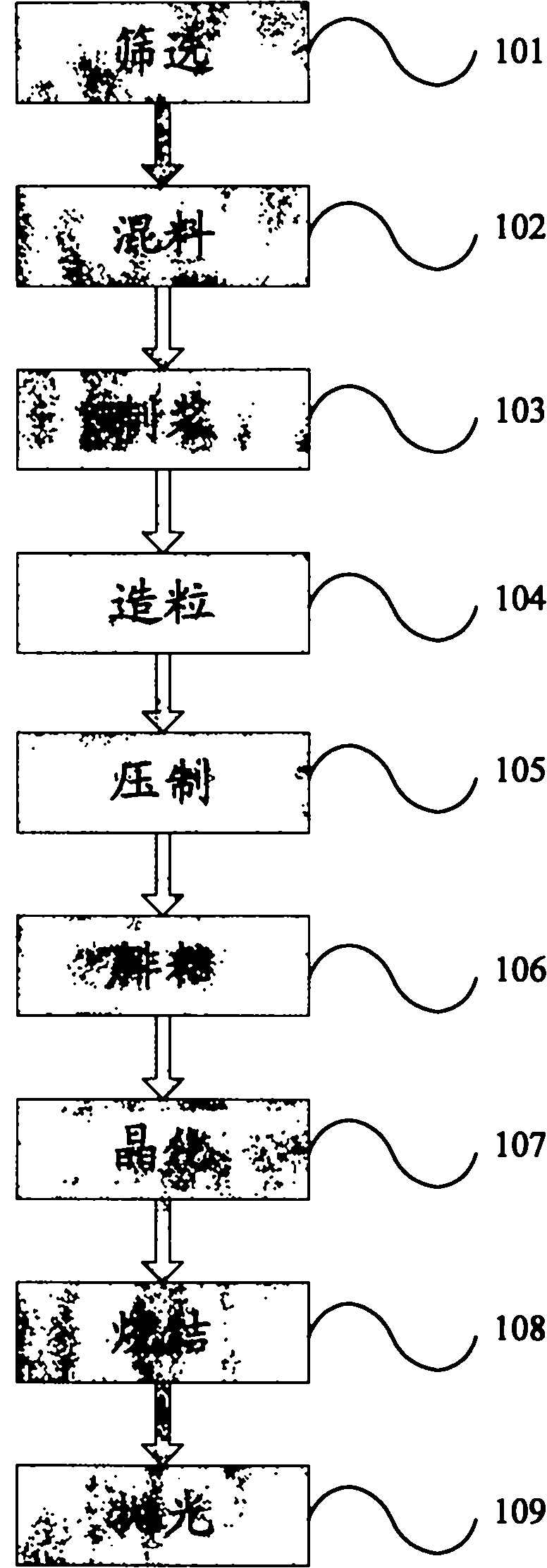
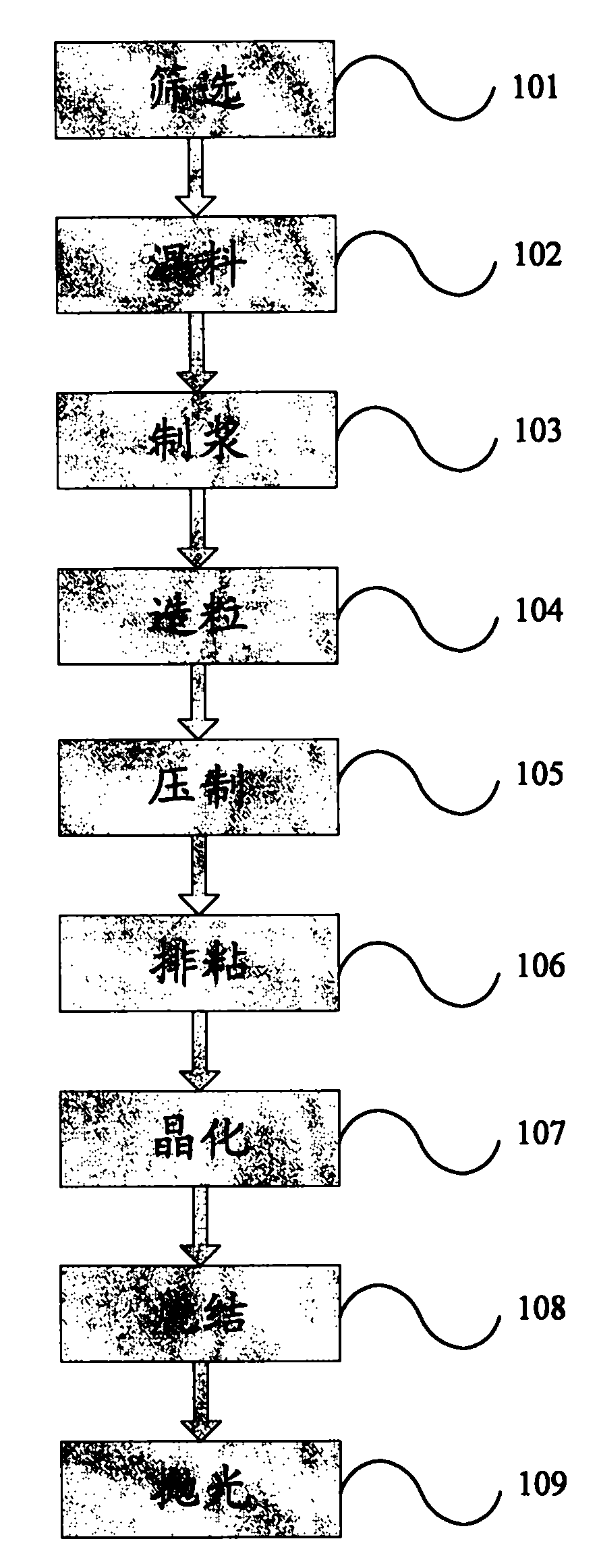
[0053] Screening The blast furnace slag is milled in a ball mill for 24 hours, passed through a 200-mesh sieve, and the water slag powder of <200 mesh is obtained;
[0054] The mixture is mixed with 91% water slag powder, 5% fly ash and 4% sodium carbonate by weight to make a mixed powder;
[0055] Slurry mixing the mixed material with balls and water at a ratio of 1:1.5:1.5, ball milling for 2 hours to make a slurry, drying at 80°C to obtain a wet material with a moisture content of ≤5%;
[0056] Granulation: adding 5% glycerin by weight of the wet material to the wet material for granulation to obtain pellets;
[0057] Press and press the pellets under 25MPa to obtain green body;
[0058] Crystallization: Crystallize the green body at 840°C for 40 minutes to precipitate the crystal phase of the glass powder;
[0059] Sintering The crystallized green body was sintered at 1200° C. for 1 hour at a heating rate of 5° C. / min to obtain glass ceramics.
[0060] Polishing the sur...
Embodiment 2
[0063] In this embodiment, the process and parameters are substantially the same as those in Embodiment 1, and the same parts will not be repeated, and only the differences will be described below:
[0064] In the mixing process, the raw materials consist of 86% water slag powder, 10% fly ash and 4% sodium carbonate by weight;
[0065] In the pulping process, the ratio of the mixed material to the ball and water is 1:2:2, and a wet material with a moisture content of ≤4% is obtained;
[0066] In the granulation process, adding liquid paraffin to the wet material for granulation;
[0067] In the pressing process, the pressing strength is 30MPa;
[0068] In the crystallization process, the green body is crystallized at 900° C. for 1 hour;
[0069] In the sintering process, the crystal is sintered at 1150° C. for 2 hours, and the heating rate is 8° C. / minute.
[0070] The waste slag glass-ceramics produced by the embodiment of the present invention has a density of 2.55g / cm 3...
Embodiment 3
[0072] In this embodiment, the process and parameters are substantially the same as those in Embodiment 1, and the same parts will not be repeated, and only the differences will be described below:
[0073] In the mixing process, the raw materials consist of 76% water slag powder, 20% fly ash and 4% sodium carbonate by weight;
[0074] In the pulping process, the ratio of the mixed material to balls and water is 2:1:1, and dried at 90°C to obtain a wet material with a moisture content of ≤2%;
[0075] In the granulation process, adding water to the wet material for granulation;
[0076] In the pressing process, the pressing strength is 100MPa;
[0077] In the crystallization process, the green body is crystallized at 800°C for 2 hours;
[0078] In the sintering process, the crystal is sintered at 1200° C. for 40 minutes, and the heating rate is 10° C. / minute.
[0079] The waste slag glass-ceramics produced by the embodiment of the present invention has a density of 2.26g / cm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| microhardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com