Doxorubicin hydrochloride-carrying natural polymer-poly(3-benzene acid acrylamide) composite nanospheres, manufacturing method and application thereof
A technology of acrylamidophenylboronic acid and natural polymers, which is applied in the direction of non-active ingredients of polymer compounds, preparation of microspheres, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., to achieve good biocompatibility, strong drug sustained release function, The effect of chemical stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Preparation of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres
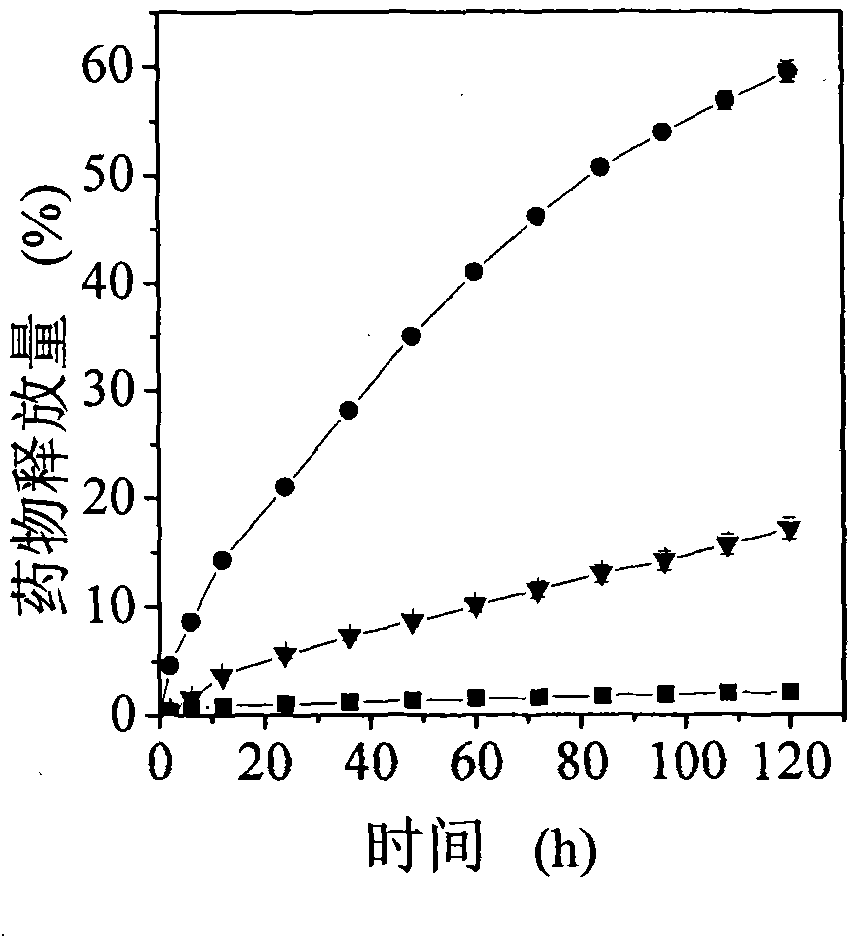
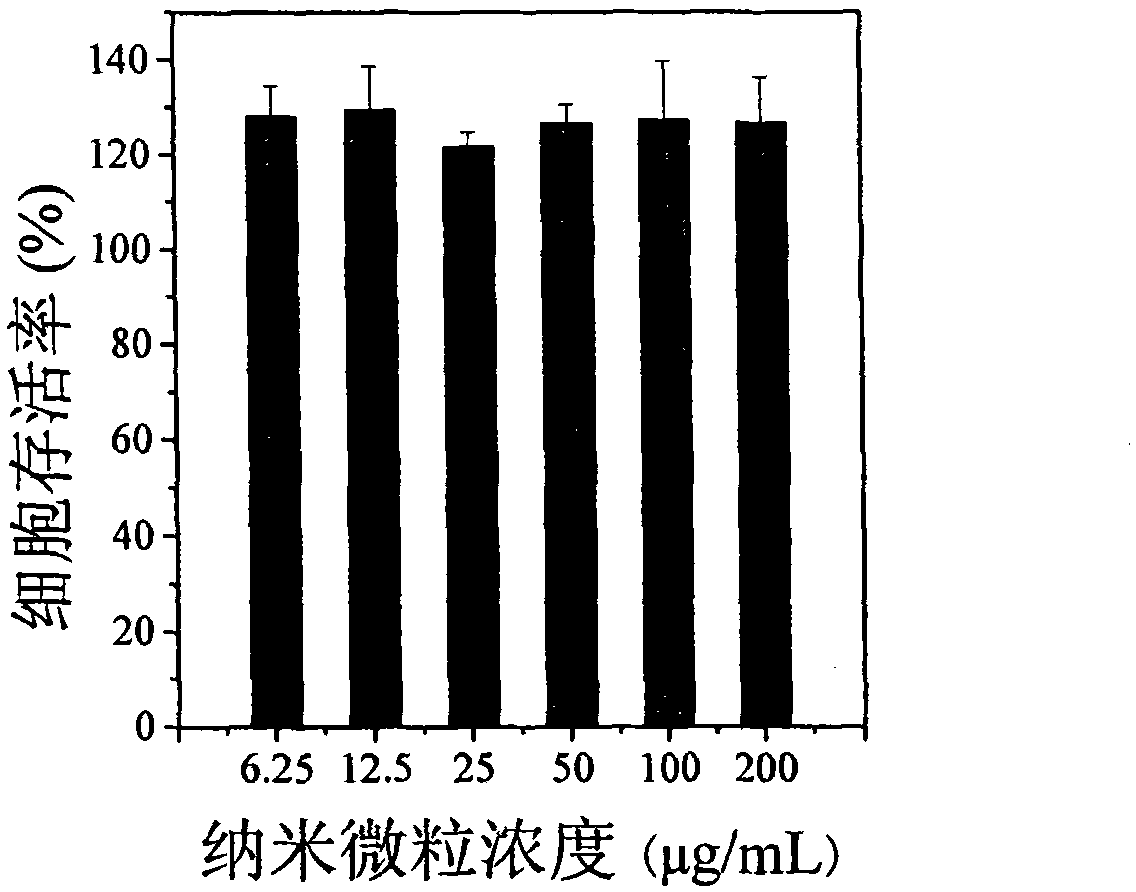
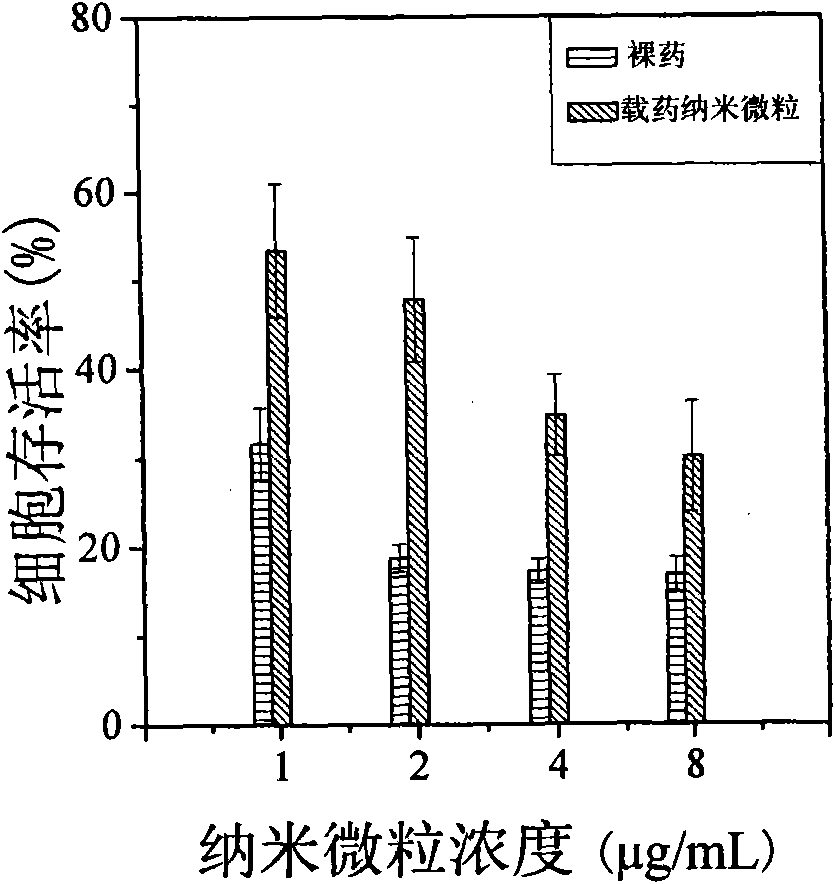
[0030] In a 25 ml stirred reactor, 90 mg of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid and 152 mg of dextran with a number average molecular weight of 3000 were dissolved in 12 ml of distilled water. After cooling to room temperature, 9.4 mg of 4,4'-azo(4-cyanovaleric acid) initiator was added. The temperature was raised to 80° C., and the polymerization reaction was initiated for 2 hours to obtain an aqueous solution of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres. Stop the reaction, lower the system temperature to room temperature, put the aqueous dispersion into a dialysis bag (Cut-off molecular weight: 12000) and dialyze for 24 hours to remove unreacted monomers in the system. The average particle size of the nanospheres measured by dynamic light scattering is 72.5±2.0 nm. Among them, natural polymer accounts for 9.1%, and poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: Preparation of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres
[0032]In a 25 ml stirred reactor, 90 mg of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid and 76 mg of dextran with a number average molecular weight of 3000 were dissolved in 12 ml of distilled water. After cooling to room temperature, 9.4 mg of 4,4'-azo(4-cyanovaleric acid) initiator was added. The temperature was raised to 80° C., and the polymerization reaction was initiated for 2 hours to obtain an aqueous solution of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres. Stop the reaction, lower the temperature of the system to room temperature and filter. After filtration, put the aqueous dispersion into a dialysis bag (cut-off molecular weight: 12000) and dialyze for 24 hours to remove unreacted monomers in the system. The average particle size of the nano-microspheres measured by dynamic light scattering is 77.4±2.1 nm, wherein natural polymer accounts for 4.2%, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: Preparation of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres
[0034] In a 25 ml stirred reactor, 90 mg of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid and 38 mg of dextran with a number average molecular weight of 3000 were dissolved in 12 ml of distilled water. After cooling to room temperature, 9.4 mg of 4,4'-azo(4-cyanovaleric acid) initiator was added. The temperature was raised to 80° C., and the polymerization reaction was initiated for 2 hours to obtain an aqueous solution of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres. Stop the reaction, lower the temperature of the system to room temperature and filter. After filtration, put the aqueous dispersion into a dialysis bag (cut-off molecular weight: 12000) and dialyze for 24 hours to remove unreacted monomers in the system. The average particle size of the nano-microspheres measured by dynamic light scattering is 65.1±0.1 nm, wherein natural polymer accounts for 2.5%, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com