Fermented soy-based beverage
A beverage and soybean technology, applied in food preparation, plant protein processing, milk substitutes, etc., to effectively remove the abnormal taste of soybeans
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Nine commercially available thermophilic LAB cultures were screened for their ability to metabolize n-hexanal during the fermentation of fresh soymilk products. The tested LAB cultures contained the following LAB species:
[0111] 1. Mixed culture of Streptococcus thermophilus strains
[0112] 2. Lactobacillus helveticus
[0113] 3. Mixed culture containing Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium animalis and Streptococcus thermophilus strains
[0114] 4. Lactobacillus bulgaricus
[0115] 5. Mixed culture containing Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Streptococcus thermophilus strains
[0116] 6. Mixed culture containing Lactobacillus helveticus and Streptococcus thermophilus strains
[0117] 7. Lactobacillus rhamnosus
[0118] 8. Lactobacillus acidophilus
[0119] 9. Lactobacillus plantarum
[0120] The analysis showed that two cultures, cultures 2 and 4, achieved a significant reduction in the hexanal concentration during the fermentation. Further experiments were...
Embodiment 2
[0122] A soy base was prepared by mixing 5.6% soy powder (Soy Supreme Fiber Reduced soy powder, available from SunOpta Grains and Food Group, Hope, MN, USA) in hot water (75-85°C). The powder had a lipoxygenase activity of less than 5 kU / mg soybean powder and was hydrated for at least 15 minutes before adding 2% sucrose, 1% glucose and 0.35% HM pectin. The mixture was then pasteurized at 72°C for 20 seconds and homogenized at 150 bar. The soy base was stored at 5°C until further use.
[0123] At 43°C, with 0.02% commercially available frozen yogurt culture concentrate T-071016 (defined mixed culture of Streptococcus thermophilus strains, by Chr Hansen, Denmark) was inoculated with 500 ml of soybean base. At the same temperature, the mixture was incubated for 4 hours, during which time the pH decreased from 6.7 to 5.3. The fermentation process was stopped by rapidly cooling the mixture to 4°C.
[0124] During the fermentation process, the viable count changed from 4.4x10 ...
Embodiment 3
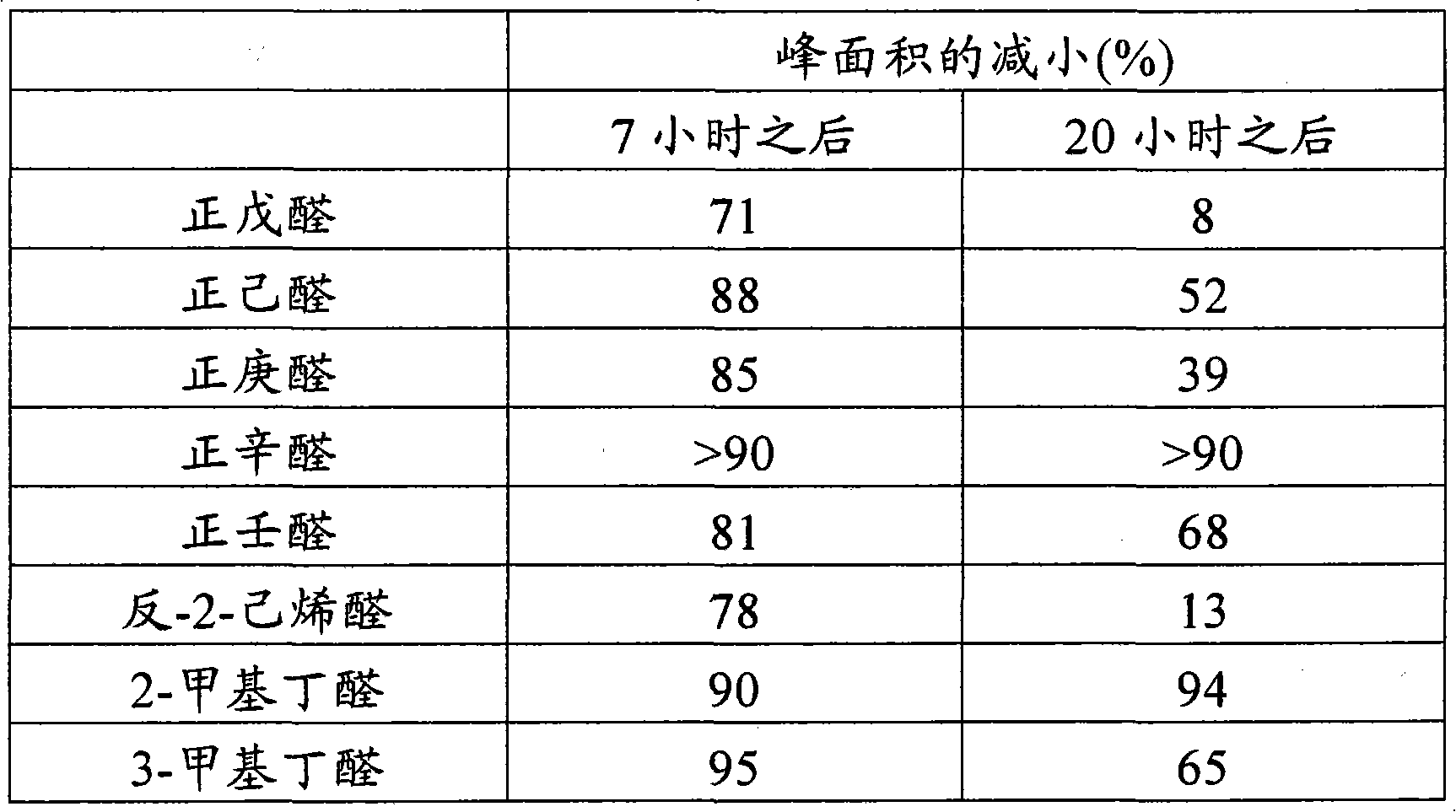
[0130] At 43°C, with 0.02% commercially available frozen yogurt culture concentrate T-071016 (defined mixed culture of Streptococcus thermophilus strains, by Chr Hansen, Denmark) was inoculated with 500 ml of soybean base prepared according to Example 2. At the same temperature, the mixture was incubated for 20 hours, during which time the pH decreased from 6.7 to 4.2. The fermentation process was stopped by rapidly cooling the mixture to 4°C. Over a 20 hour period, the viable count went from 4.4x10 7 increased to 1.2x10 8 Cfu / ml. During the same time period, lactate levels increased to 4.2 g / l.
[0131] Aliquots of the fermented samples and the initial soybean base were subjected to SPME followed by GC-MS analysis. It was found that the peak areas of pentanal, hexanal, heptanal, octanal, nonanal, trans-2-hexenal, 2-methylbutyraldehyde and 3-methylbutyraldehyde were greatly reduced during the fermentation process, as Table 2 shows:
[0132] Table 2
[0133] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com