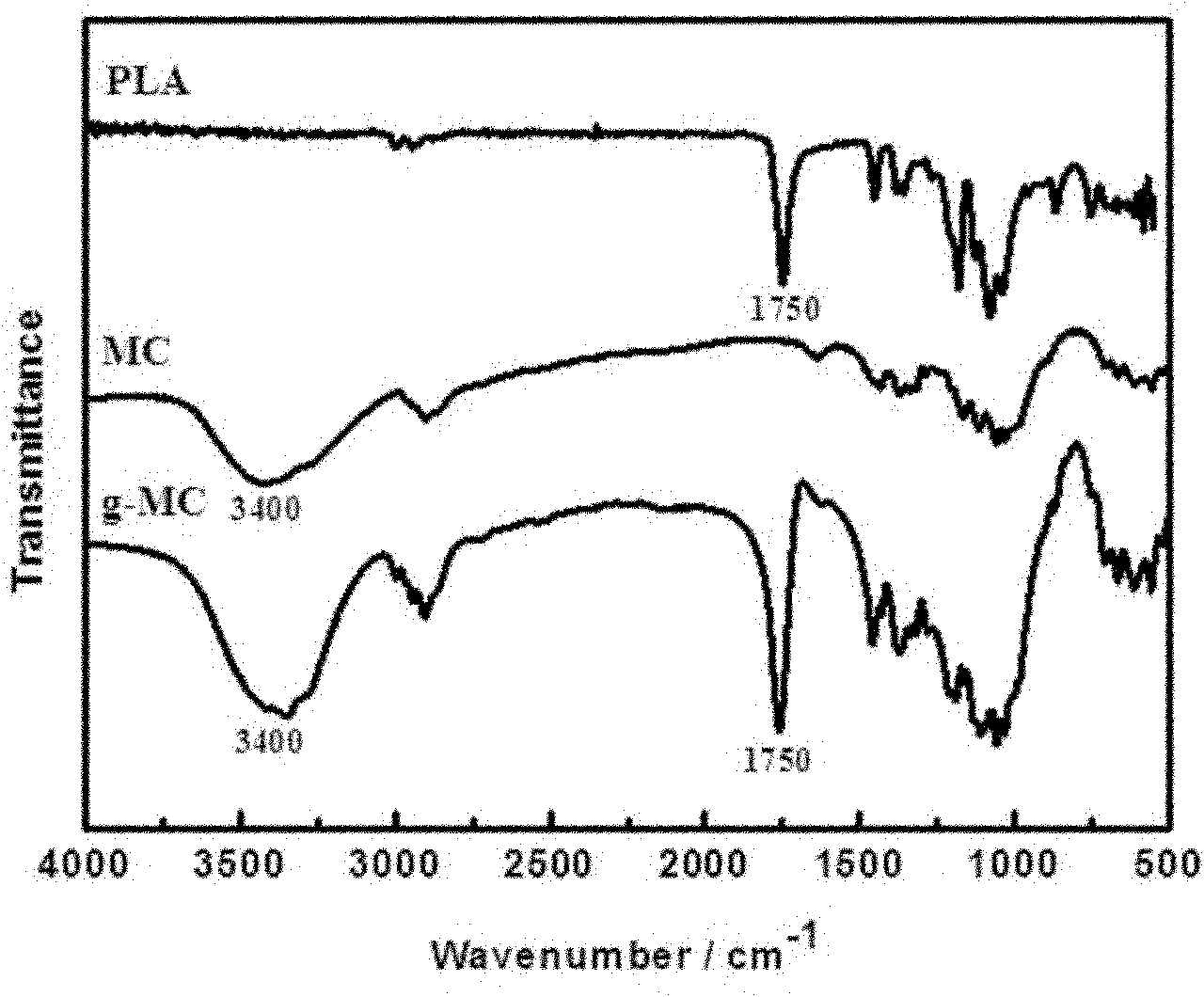
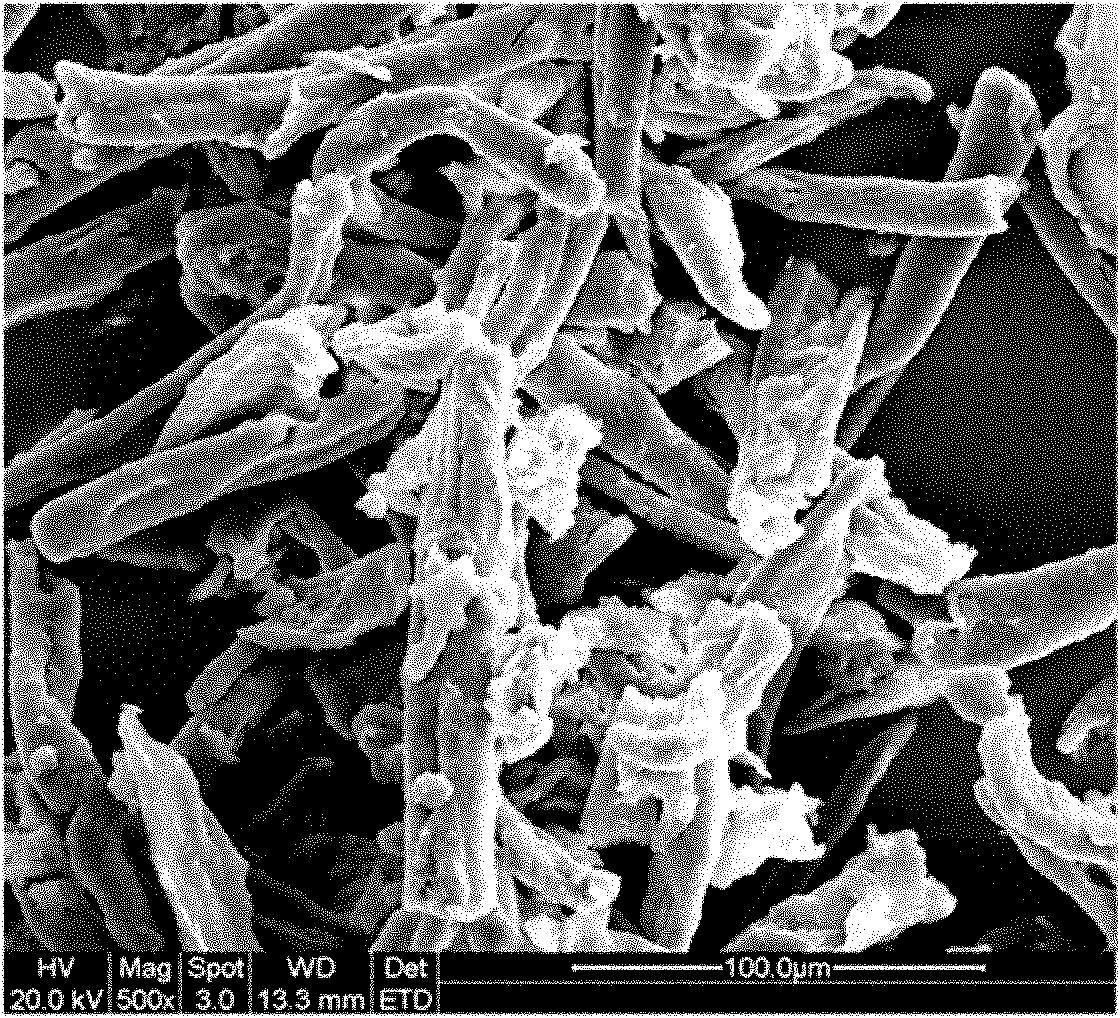Modified biopolymer fiber reinforced polylactic acid composite material and preparation method thereof
A biomass fiber and composite material technology, which is applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems that the interface between biomass fiber and polylactic acid has not been well resolved, the flexibility cannot be greatly improved at the same time, and the tensile strength has not been significantly improved. , to achieve the effect of maintaining full degradability, excellent mechanical properties, and easy control of reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
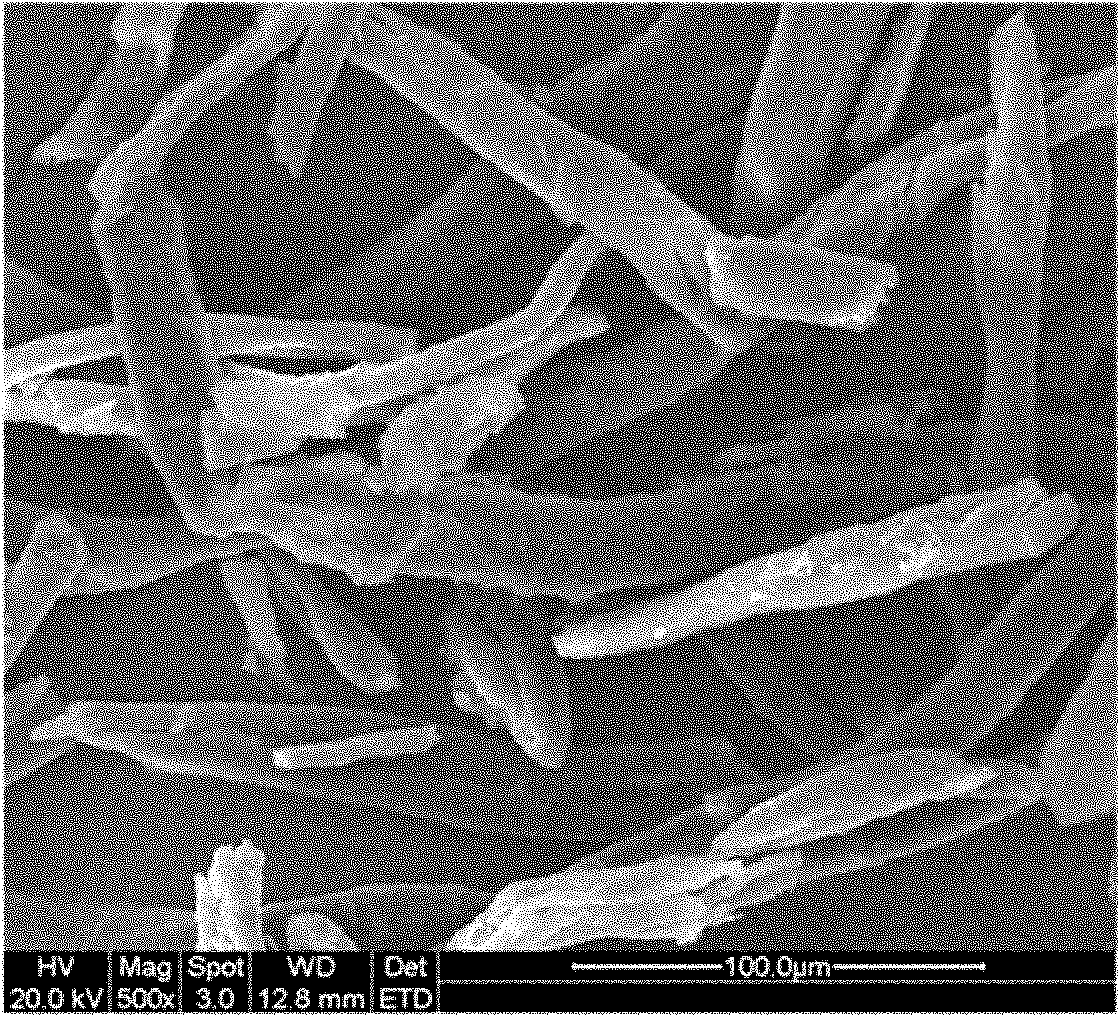
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1 Preparation of modified microcrystalline cellulose reinforced polylactic acid composite (g-MC / PLA)
[0055] The preparation of modified microcrystalline cellulose reinforced polylactic acid composite (g-MC / PLA) is carried out in the following steps:
[0056] (1) Preparation of modified microcrystalline cellulose (g-MC):
[0057] Put dehydrated L-lactic acid and dry microcrystalline cellulose (MC) in the reactor at a weight ratio of 5:1, raise the temperature to 60°C and stir and mix evenly, then press dehydrated L-lactic acid and dried microcrystalline cellulose (MC) 0.3% of the total weight of stannous chloride was added as a catalyst, and the reaction was stirred for 4 hours; then the temperature was raised to 100° C., and the reaction was continued for 4 hours; finally, the temperature was raised to 150° C., and the reaction was stopped for 4 hours, and the reaction was stopped to obtain crude modified microcrystalline cellulose. The vacuum degree of th...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2 Preparation of modified starch reinforced polylactic acid composite material
[0062] The preparation of modified starch reinforced polylactic acid composite material is carried out in the following steps:
[0063](1) Preparation of modified starch: put dehydrated L-lactic acid and dried cornstarch in a reaction bottle at a weight ratio of 5:1, heat up to 65°C and mix evenly, then press dehydrated L-lactic acid and dried cornstarch 0.5% of the total weight of crystalline cellulose (MC) was added with stannous chloride as a catalyst, and stirred for 3 hours; then the temperature was raised to 100° C., and the reaction was continued for 4 hours; finally, the temperature was raised to 150° C., and the reaction was stopped for 4 hours, and the reaction was stopped to obtain crude modified starch . The vacuum degree of the system is maintained at -0.09~-0.1MPa throughout the reaction process. The crude modified starch was taken out, washed 3 times with absolut...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3 Preparation of modified microcrystalline cellulose reinforced polylactic acid composite material (g-MC / PLA)
[0067] Based on Example 1, the difference is that the input weight ratio of L-lactic acid and microcrystalline cellulose in step (1) is changed to 8:1, and the others are the same as in Example 1. In this example, a modified microcrystalline cellulose reinforced polylactic acid composite material (g-MC / PLA) was obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com