Universal primers for identifying bacillus and classification method using same
A technology of bacillus and universal primers, which is applied in the field of universal primers for identifying bacillus, can solve problems such as inaccurate classification results, complicated operations, and difficulty in distinguishing bacillus species, and achieve simple classification and identification methods, accurate classification results, and polymorphic sexual enrichment effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
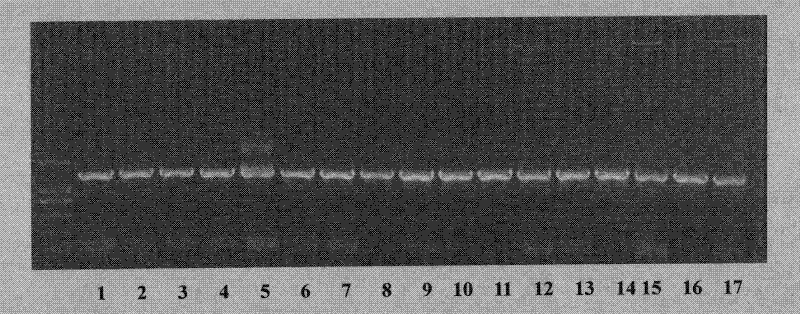
[0044] Embodiment 1: Comparison test of phoPR and gyrB gene polymorphism between different species of Bacillus
[0045] The 9 representative bacillus standard bacterial strains involved in this test are respectively: bacterial strain Bacillus subtilis (B.subtilis) 168, amyloliquefaciens (B.amyloliquefaciens) FZB42, licheniformis (B.licheniformis) 14580, B. pumilus SAFR-032, B. weihenstephanensis KBAB4, B. cereus 03BB102, B. clausii KSM-K16, Bacillus megaterium B. megaterium DSM319 and B. thuringiensis BMB171.
[0046] In this experiment, nine standard strains of different species of Bacillus were amplified by PCR with phoPR-F / phoPR-R primers and gyrB-F / gyrB-R primers respectively, and then sequenced and compared.
[0047] Proceed as follows:
[0048] (1) Strain activation: activate the Bacillus strain on LB medium (the composition and ratio of LB medium are: tryptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, NaCl 5g, agar powder 10g, and the rest are water) per 1000ml .
[0049] (2) Extracti...
Embodiment 2
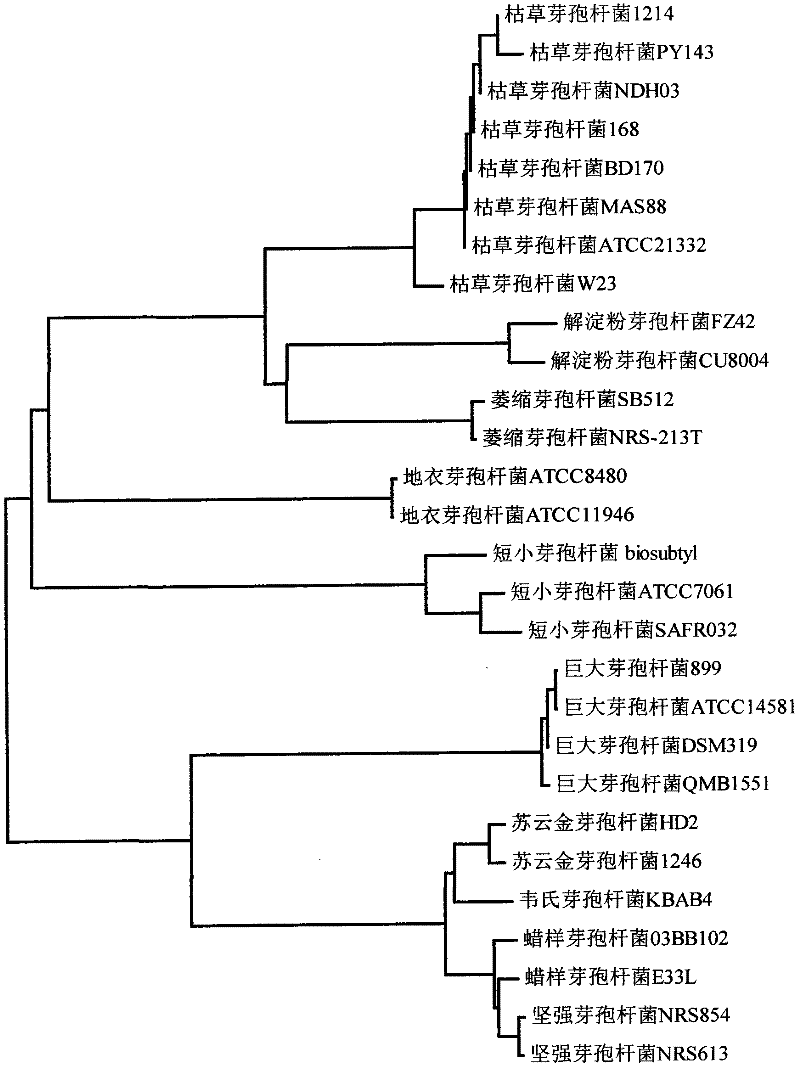
[0060] Embodiment 2: Verification test that the classified bacillus is classified with universal primers of the present invention
[0061] The 28 standard strains of Bacillus involved in this test (see Table 3) were respectively purchased from the Bacillus Genetics Stock Center (BGSC), China Agricultural University and TaKaRa Company.
[0062] Table 3 The strain code, classification and source used in the classification identification test
[0063] Strain code
Strain Classification
source
Strain code
Strain Classification
source
W23
BGCS
NRS-123T
BGCS
SAFR-032
BGCS
899
BGCS
DSM319
Bacillus megaterium
BGCS
ATCC14581
Bacillus megaterium
BGCS
QMB1551
Bacillus megaterium
BGCS
NRS854
BGCS
KBAB4
Bacillus welcheei
BGCS
NRS613
Bacillus f...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3 Utilize the universal primers of the present invention to classify and identify Bacillus strains with unknown taxonomic status
[0073] The source of the strains to be tested: The Institute of Plant Protection, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences isolated and screened 36 strains of biocontrol bacteria with strong antagonistic activity against Verticillium dahliae from cotton rhizosphere soil (see Table 4).
[0074] The strain name, source and 16S rDNA sequence registration number table used in Table 4 Example 3
[0075] Numbering
strain name
Strain Classification
source
16S rDNA sequence accession number
1
70A-7
unknown
HAAFS
GU269571
2
BDT-14
unknown
HAAFS
GU269574
3
BZT-34
unknown
HAAFS
GU269577
4
CJT-2
unknown
HAAFS
GU269578
5
DHT-12
unknown
HAAFS
GU269579
6
DHT-13
unknown
HAAFS ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com