High-yield succinic acid strain and its application
A succinic acid and strain technology, applied in the directions of bacteria, electricity/wave energy treatment of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the effective conversion efficiency of carbon, the high cost of succinic acid production, and hindering the biological process of succinic acid. industrialization process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Rational design to obtain engineering strains for succinic acid production
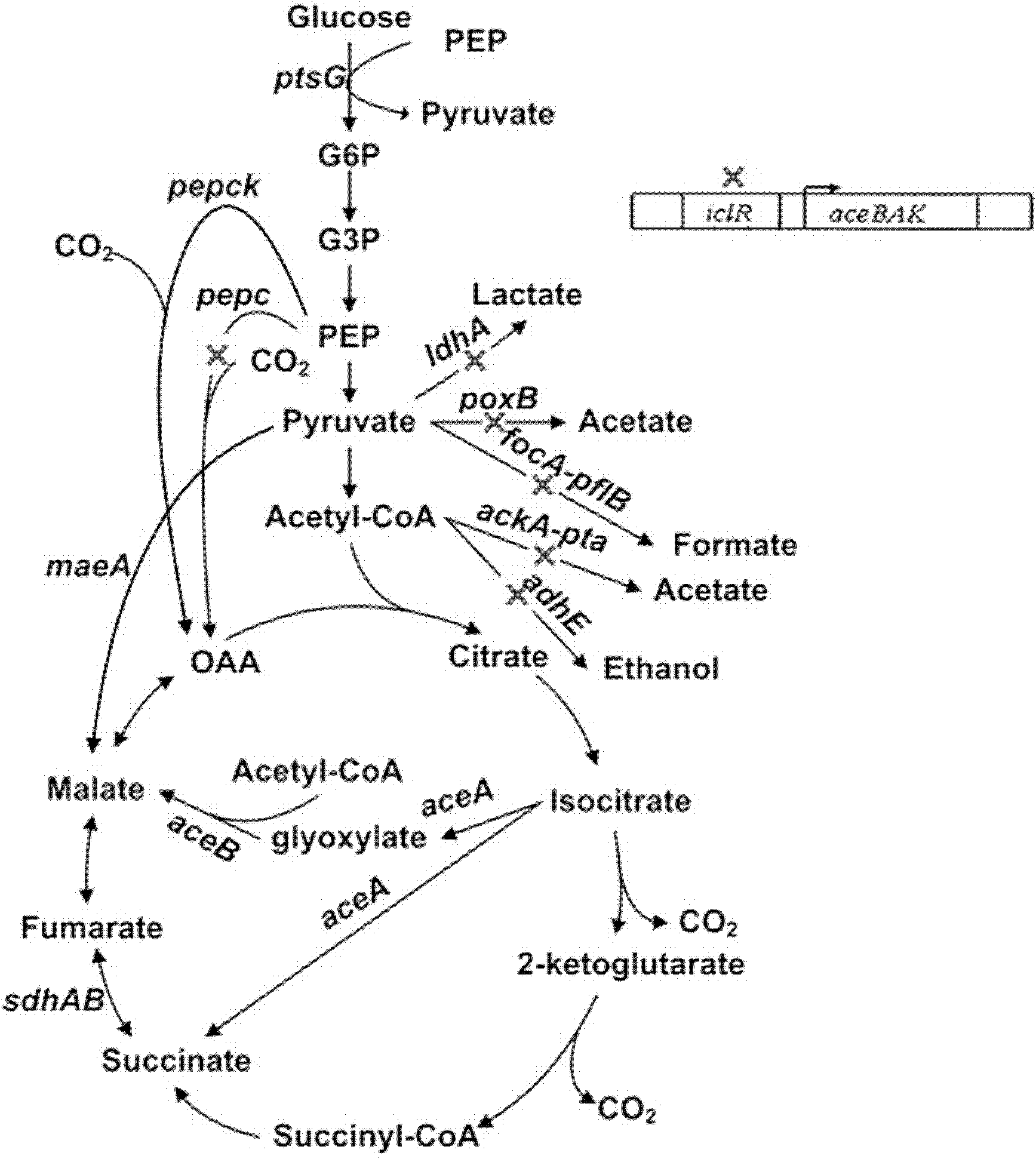
[0021] The following 9 genes in Escherichia coli MG1655 were sequentially knocked out by pDS132 traceless knockout system: adhE, ackA, pta, focA, pflB, iclR, ldhA, poxB, pepc.
[0022] Refer to the literature of the pDS132 traceless knockout system, the knockout and screening methods and steps of each gene are the same. The specific operation is as follows:
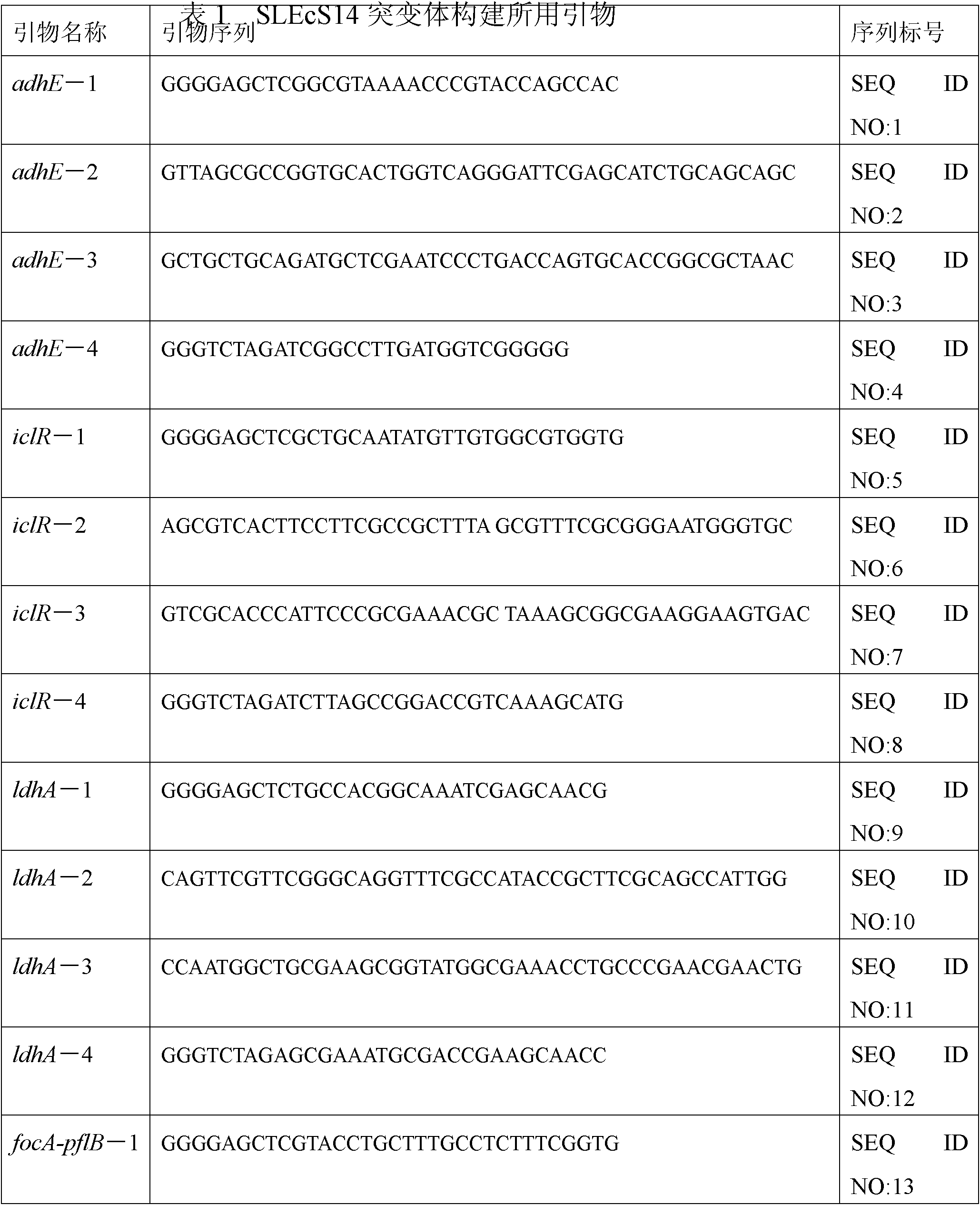
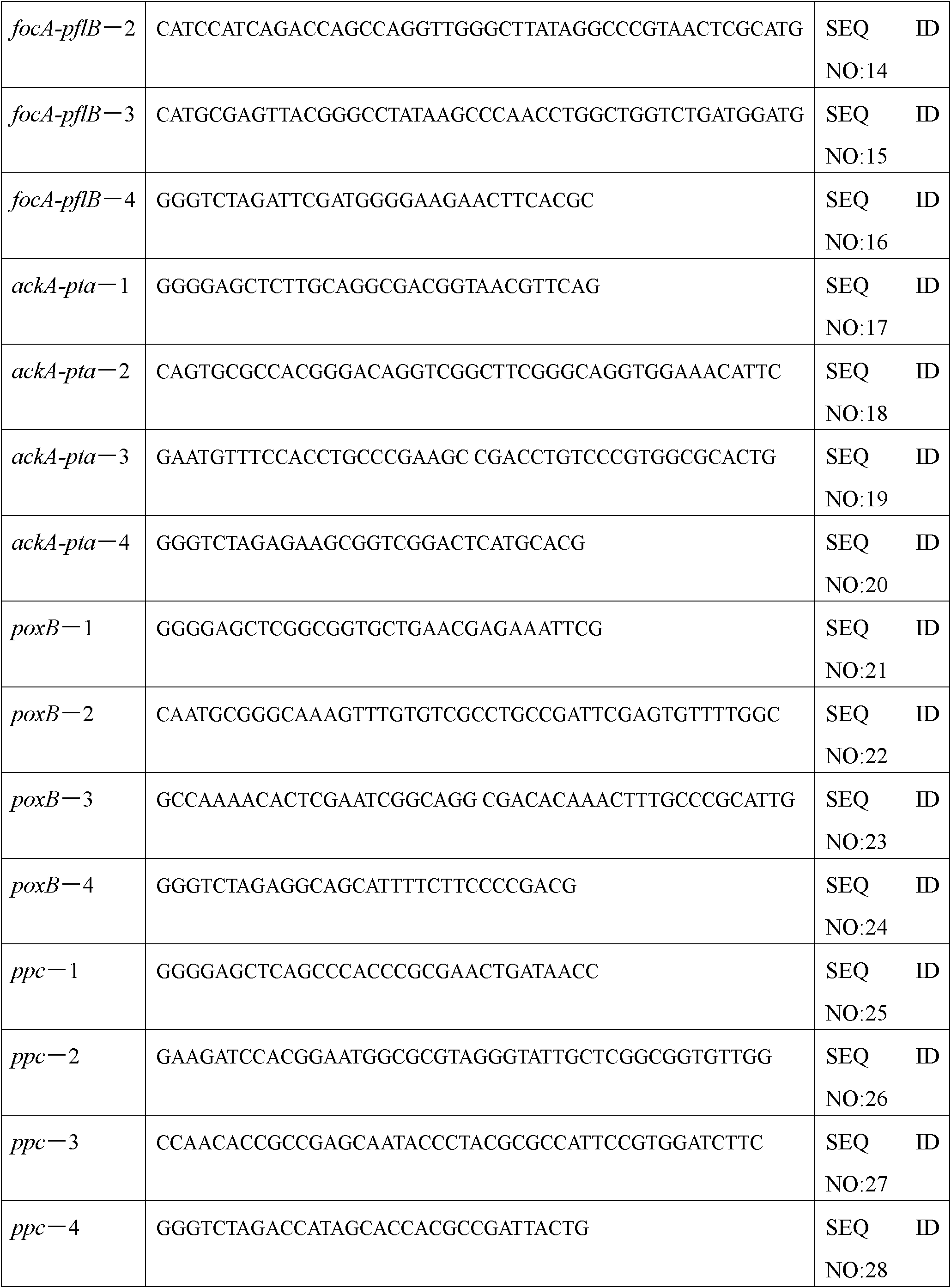
[0023]For the knockout of the adhE gene, first use the sequence as the primer 1 (adhE-1) of SEQ ID NO: 1 and the sequence as the primer 2 of SEQ ID NO: 2 (adhE-2); the sequence is the primer 2 of SEQ ID NO: 3 Primer 3 (adhE-3) and primer 4 (adhE-4) whose sequence is SEQ ID NO: 4 amplify two homologous arms of about 1 kb respectively from the genomic DNA of Escherichia coli MG1655, and then pass primer 1 and primer 4. Using the left and right homology arms as a template, obtain a fusion fragment of about 2 kb through fusion PCR...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: High-yielding succinic acid mutant strain obtained through irrational mutagenesis screening
[0033] Through genome analysis and metabolic pathway analysis, the SLEcS14 mutant strain has the potential to re-mutate and adjust itself to improve cell growth and succinic acid synthesis ability. The present invention uses ultraviolet mutagenesis combined with culture conditions to screen succinic acid high-yielding bacteria.
[0034] The SLEcS14 strain was used as the initial strain for mutagenesis, cultured in LB liquid medium (10g / L tryptone, 5g / L yeast extract, 5g / L NaCl) at 37°C to obtain a mid-log phase bacterial liquid, centrifuged the bacterial liquid, and precipitated After washing twice with normal saline, adjust the OD550 to 0.3 with LB liquid medium, select the irradiation time with a lethal rate of 70-80% as the irradiation time for mutagenesis, and then transfer the mutated bacterial solution into a 100ml anaerobic bottle containing 20ml of NBS basic ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: SLEcS16 mutant strain anaerobic fermentation
[0040] Because the pH of fermentation acid production in the anaerobic bottle is not well controlled, the growth of bacteria and the production of succinic acid are affected. Fill 3L of liquid in a 5L fermenter for sealed fermentation, the medium is NBS, the temperature is 37°C, 200rpm, feed 1.2MKOH and 2.6MK 2 CO 3 Lye controls pH7.0. The fermentation results are shown in the table below. At the end of 188 hours, the succinic acid fermentation process produced 19.62 g / L of succinic acid, almost no by-products, only a very small amount of acetic acid and lactic acid, and no ethanol and formic acid. The ratio of succinic acid to by-products was 15.45: 1.
[0041] Fermentation time (h) OD 550 Succinic acid (g / L) Lactic acid (g / L) Acetic acid(g / L) 0 0.15 0.12 0.00 0.00 24 0.52 0.56 0.00 0.04 48 0.82 1.66 0.06 0.09 72 1.27 3.80...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com