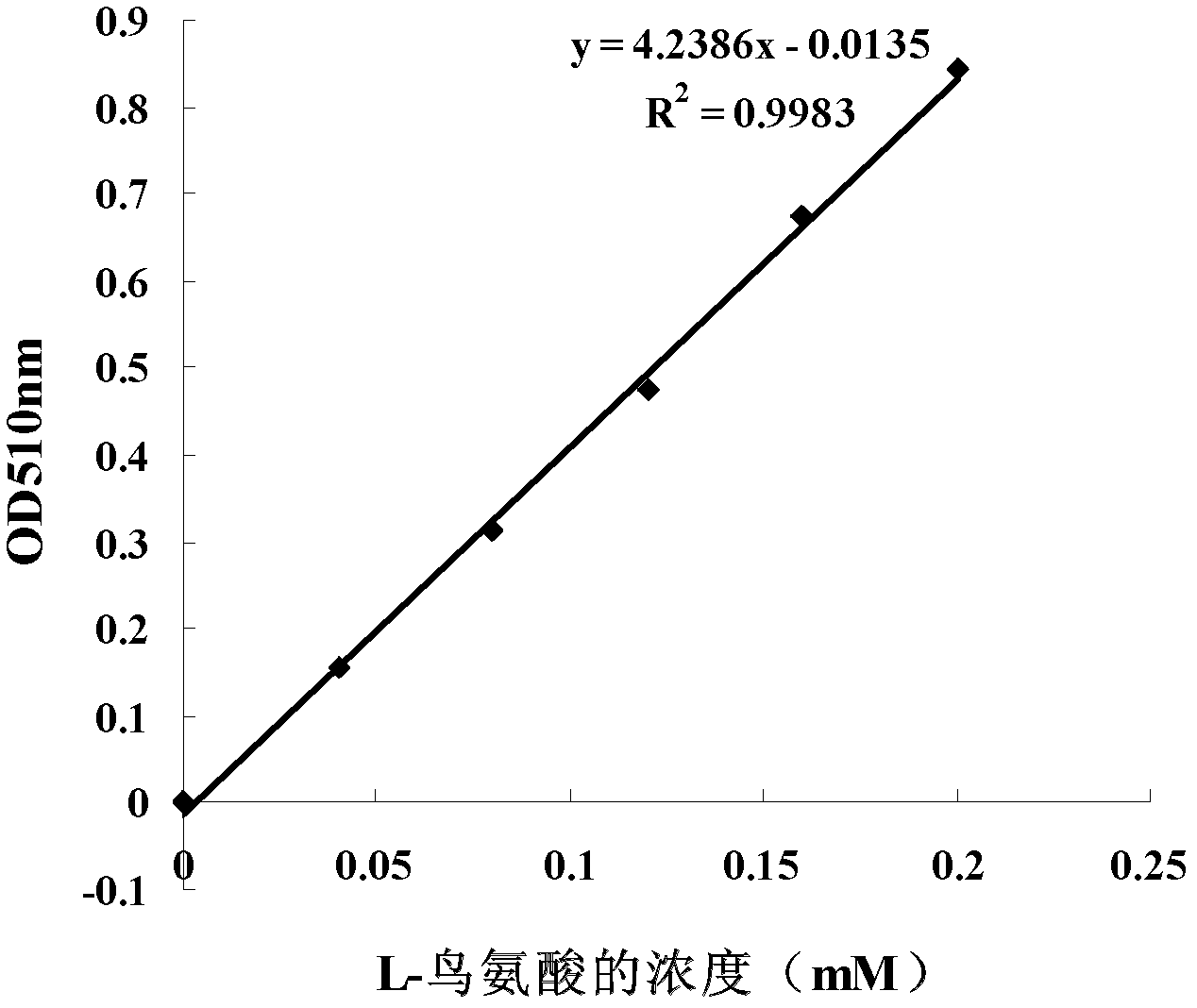
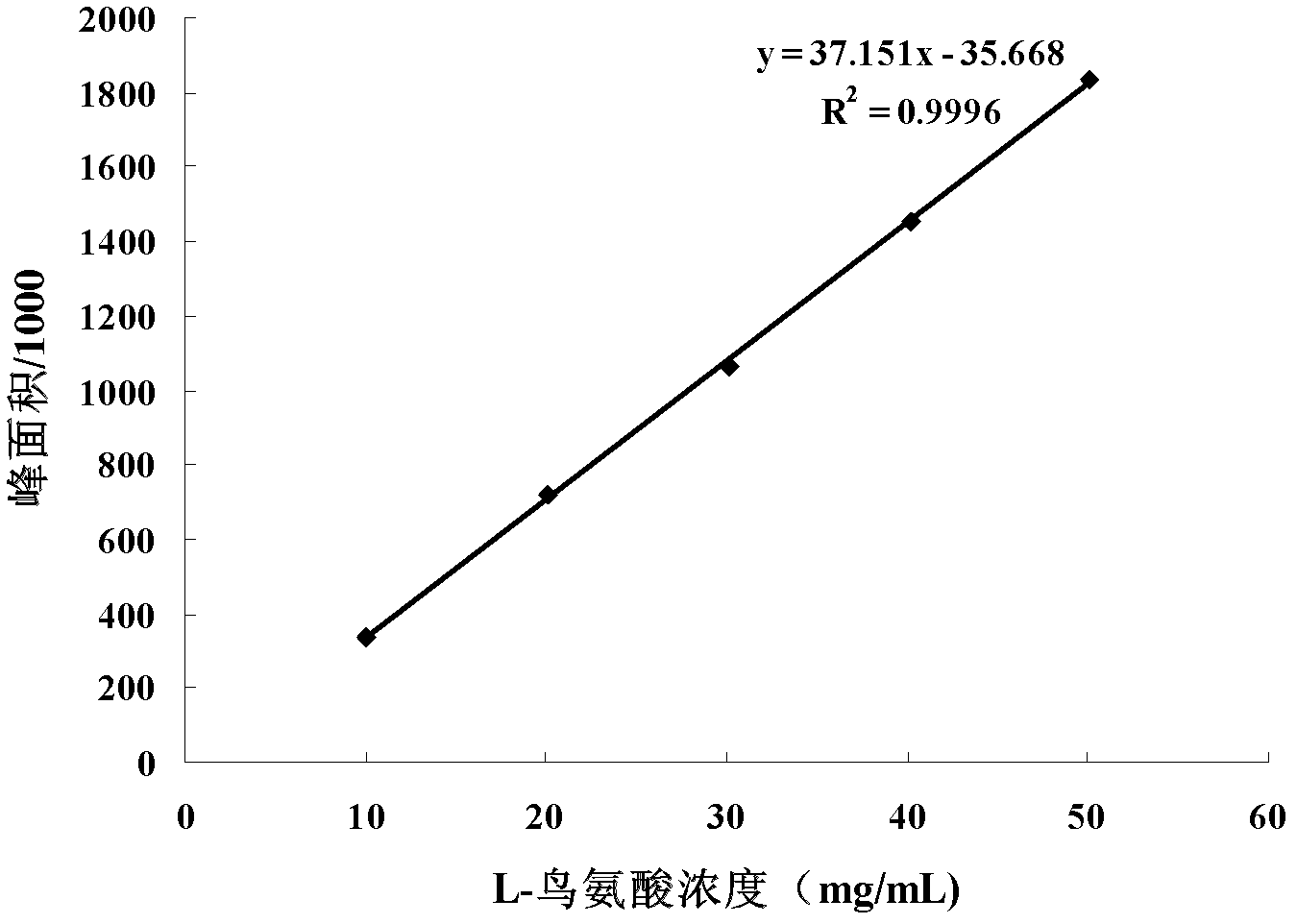
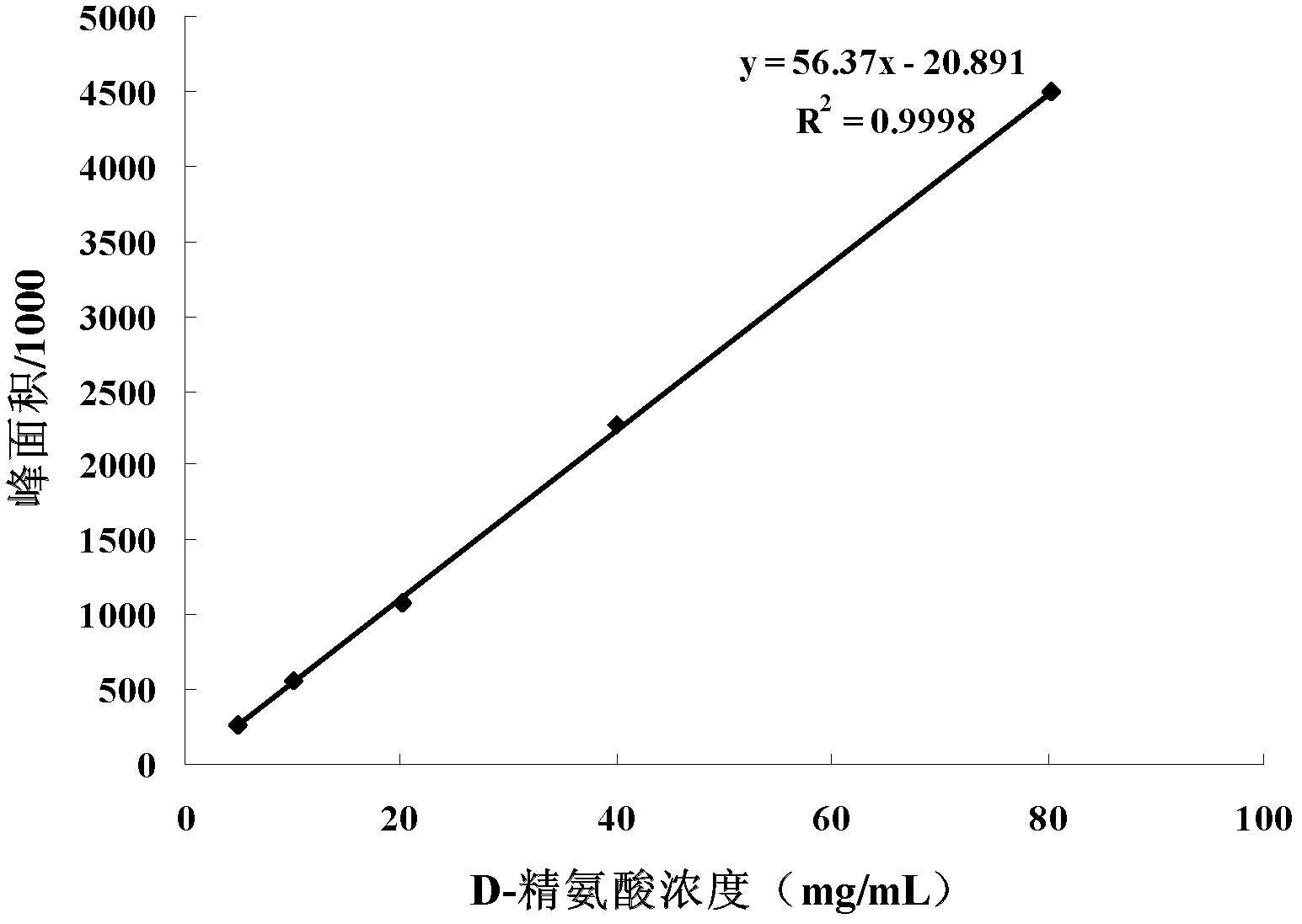
Method for preparing d-arginine hydrochloride and l-ornithine hydrochloride by splitting dl-arginine by microbial enzymatic method
A technology of arginine hydrochloride and ornithine hydrochloride, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the cumbersome separation and extraction process, limited expression enzyme activity level, extraction process cumbersome and other problems, to achieve the effect of simple process steps, less enzyme input and safe operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1, the construction of genetically engineered bacteria Escherichia coli and the expression of recombinant L-arginase
[0038] According to the rat arginase gene sequence recorded in the NCBI database, the upstream primer arg1: 5'-GCGGGATCC ATG AGC TCC AAG CCA AAG CC-3' and the downstream primer arg2: 5'-GCC GTCGAC TTATTT CGG TGG TTT A- 3'. Rat liver total RNA was extracted, and cDNA was prepared by reverse transcription. Using rat liver cDNA as a template, arginase gene was amplified by PCR. The recombinant expression plasmid pET-21a(+)-Arg was constructed by genetic engineering method. The recombinant expression vector pET-21a(+)-Arg was transformed into E.coli BL21(DE3) to obtain the genetic engineering strain Arg5.
[0039] The positive recombinant strain was inoculated into 4 ml of LB medium containing 100 μg / mL of ampicillin for overnight culture, and then inserted into 100 mL of fresh LB medium containing 100 μg / mL of ampicillin at a transfer rate of...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2, fermentation of recombinant L-arginase genetically engineered recombinant bacteria
[0042] The recombinant Escherichia coli in Example 1 was inoculated in 4 mL of LB medium containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin and cultivated overnight as a primary seed liquid; then inserted into 100 mL of LB culture containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin with 1% transfer amount culture medium at 37°C and 200rpm for 8h-12h as the secondary seed liquid; the secondary seed liquid was transferred to a 100L fermenter with 1% inoculum, the fermentation medium was fresh LB medium, and the culture temperature was 37°C. The initial rotation speed is 300rpm, and the initial pH is 7.2. Samples were taken regularly, and when the OD600nm of the bacterial solution reached 1.0-1.2, IPTG induction solution with a final concentration of 1 mM was added for induction. The fermented liquid in the lower tank was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C to collect the bacterial cells to obtain the ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3, the investigation of spray-drying condition and the preparation of solid enzyme preparation
[0044] To the bacterial suspension obtained in Example 2, add 20 g / L sugars, polymers, polyols, proteins, surfactants, salts, etc. as investigation objects, and after fully dissolving, preheat in a 50°C water bath After 30 minutes, the remaining enzyme activity of the blank sample was regarded as 100%, and the relative remaining enzyme activity was compared. The results are shown in Table 1. Skimmed milk powder, sodium glutamate, and gum arabic all have good protective effects. Among them, skimmed milk powder has the best protective effect. If cost is considered, sodium glutamate or gum arabic can be preferred.
[0045] The influence of table 1 protective agent on temperature stability
[0046]
[0047] Add a certain amount of skimmed milk powder, sodium glutamate or gum arabic to the bacterial suspension with a concentration of 100-200g / L as a protective agen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com