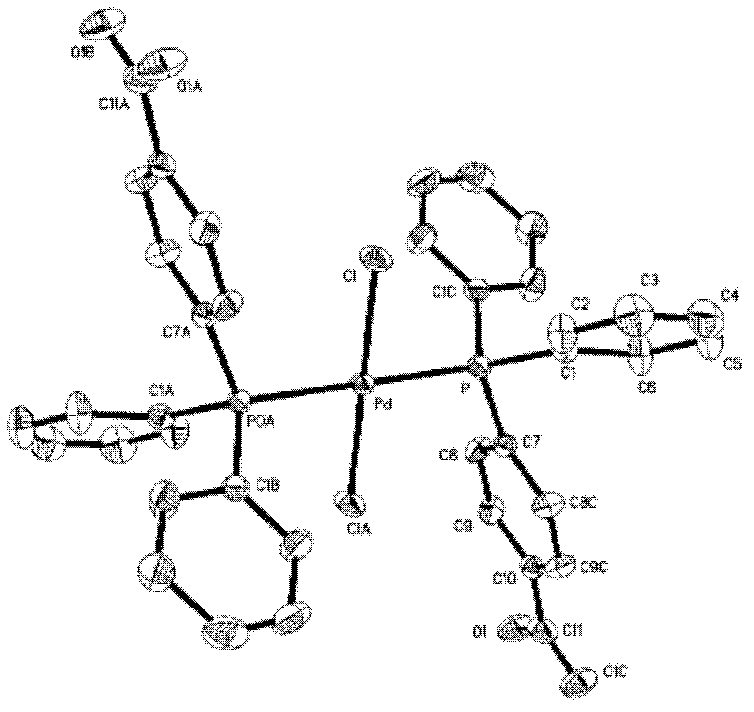
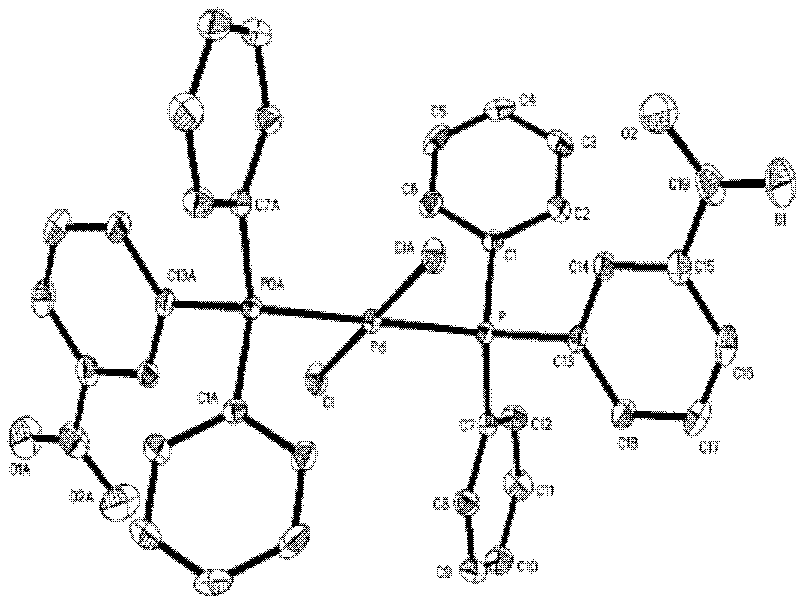
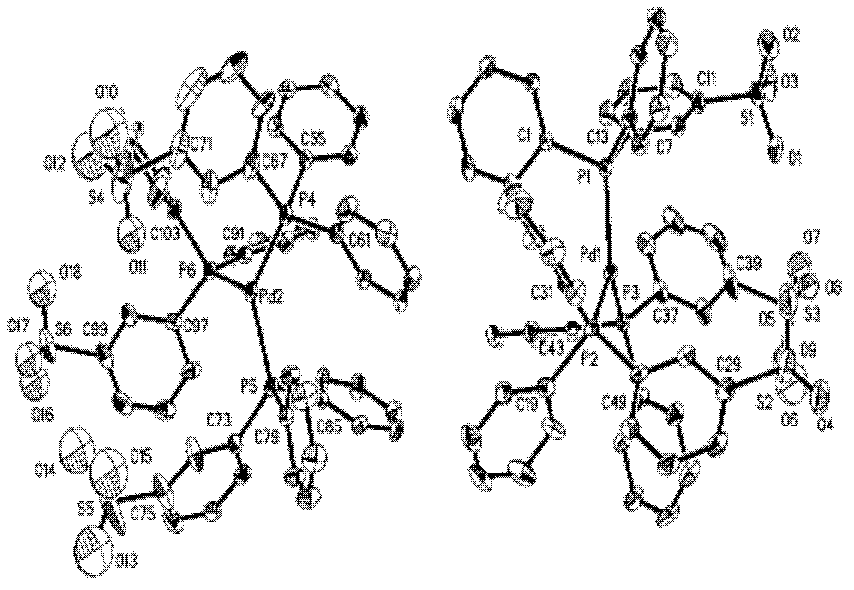
Preparation method of palladium complex and conjugated aromatic polymer
A technology of palladium complexes and conjugated aromatics, which is applied in the field of preparation of palladium complexes and conjugated aromatics polymers, can solve the problems of unfavorable oxidative addition, difficult coordination, poor oil solubility, etc., and achieve good catalytic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of 3-(diphenylphosphine) benzenesulfonic acid (3-TPPMSH)
[0079] In a 250ml three-neck round bottom flask, add 20ml of fuming sulfuric acid (Oleum), and add 10g of triphenylphosphine (PPh) in batches in an ice-water bath under an argon atmosphere. 3 ), stirred until completely dissolved, then raised the temperature to 93°C and stirred for 2h. After cooling to room temperature, add 20 g of ice and 100 ml of distilled water, add NaOH aqueous solution to adjust the reaction solution to neutral, and precipitate a white solid, which is recrystallized twice from distilled water after filtration to obtain 3 g of bright white crystalline powder sodium sulfonate ligand, sulfonic acid The yield of sodium ligand was 20%. Sodium sulfonate ligand is dissolved in hydrochloric acid methanol solution to obtain 3-TPPMSH, and the reaction formula is shown in the following formula:
[0080]
[0081] Carry out nuclear magnetic resonance analysis to interme...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of 4-(diphenylphosphine) benzoic acid (4-TPPMC)
[0083] In a 500ml three-necked round-bottomed flask, 6g of KOH and 300ml of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were added under the protection of argon. After adding 10.4ml of diphenylphosphine, a red reaction solution was obtained. Stir at room temperature for 2h, add 7.26 g p-fluorobenzonitrile, the reaction solution immediately produces a white precipitate, and after stirring for 0.5h, the precipitate is filtered and recrystallized twice with methanol to obtain 13.75g bright white crystal 4-(diphenylphosphine)benzonitrile, 4-(diphenylphosphine) The yield of phenylphosphine)benzonitrile was 80%. Product 4-(diphenylphosphine) benzonitrile is carried out nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, and characterizing result is as follows: 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 300MHz): δ=7.30-7.39(m, 12H), 7.57ppm(d, J=6.9Hz, 2H); 31 P { 1 H}NMR (CDCl 3 , 161.9Hz): δ=-4.67ppm(s). It can be seen that 4-(diphenylphosphine)benzo...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of 3-(diphenylphosphine) benzoic acid (3-TPPMC)
[0088] In a 500ml three-neck round bottom flask, add 6gKOH and 300ml dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) under the protection of argon, after adding 10.4ml diphenylphosphine, a red reaction solution is obtained, stir at room temperature for 2h, add 7.26g Fluorobenzonitrile, the reaction solution produced white precipitate immediately, after stirring for 0.5h, the precipitate was filtered and recrystallized twice with methanol to obtain 12g bright white crystal 3-(diphenylphosphine)benzonitrile, 3-(diphenylphosphine) ) Benzonitrile productive rate is 70%. Product 3-(diphenylphosphine) benzonitrile is carried out nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, and characterizing result is as follows: 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 400MHz): δ=7.27-7.31(m, 4H), 7.375(d, J=5.2Hz, 6H), 7.44(d, J=7.6Hz, 1H), 7.48-7.55(m, 2H), 7.60ppm (d, J=7.6Hz, 1H); 31 P { 1 H}NMR (CDCl 3 , 161.9Hz): δ=-5.83ppm(s). It can be seen that 3-(diphen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com