Disease-preventing bio-organic fertilizer prepared from straw and its preparation method
A bio-organic fertilizer and straw technology, which is applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, the treatment of bio-organic parts, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient use, high cost of pesticide production, affecting the improvement of yield and economic benefits, and achieves the goal of improving Efficiency, good effect of preventing soil-borne diseases, and improved effect of disease prevention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
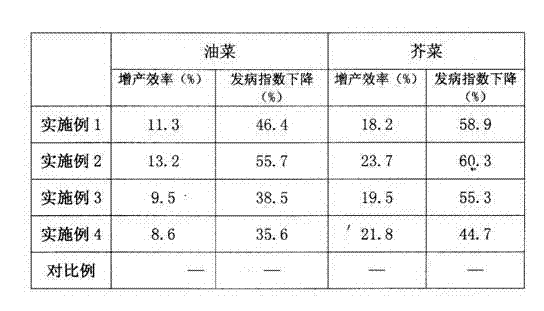
Embodiment 1
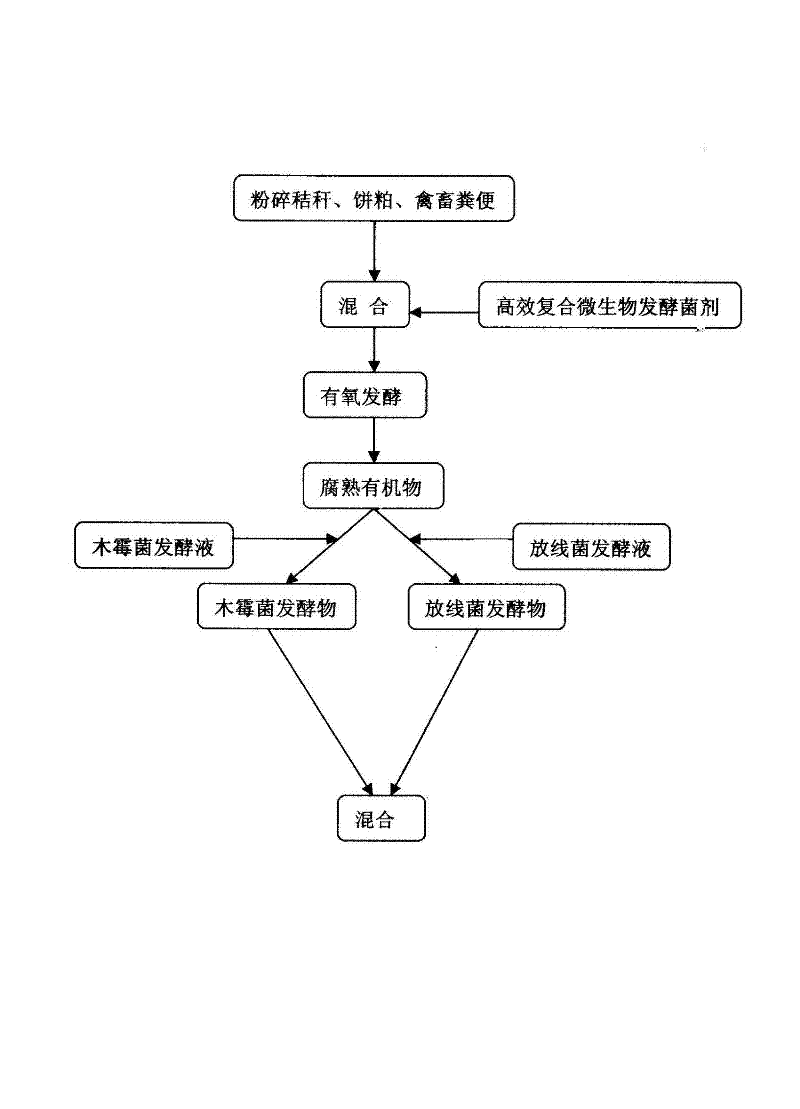
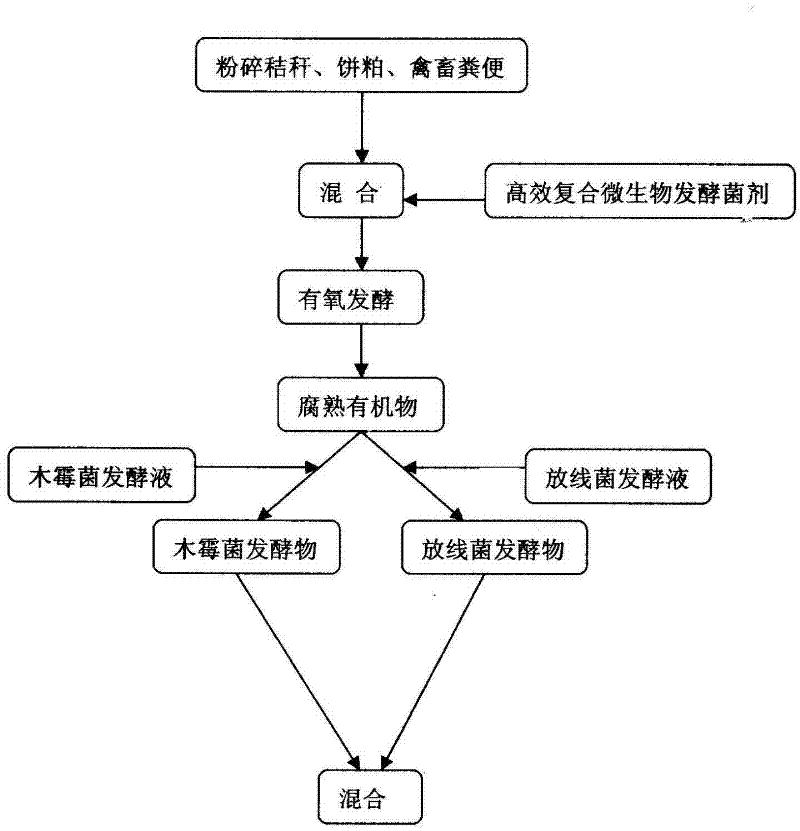
[0044] (1) Preparation of high-efficiency compound microbial fermentation inoculant
[0045] Trichoderma konii, white rot fungus, Trametes versicolor, EM bacteria, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria, and potassium-solubilizing bacteria were expanded and cultivated on the corresponding medium. Shake well in a sterile Erlenmeyer flask to form a bacterial suspension; ② Inoculate the slant culture in a seed bottle, and incubate at 30°C, 200r / min for 24 hours to obtain a seed liquid; ③ Inoculate 10% of the seed liquid into a fermentation bottle and expand the culture for 44 hours to obtain a fermentation Liquid, according to the ratio of 15:15:15:25:10:10:10 to prepare high-efficiency compound microbial fermentation broth.
[0046] (2) Preparation of decomposed organic matter:
[0047] In terms of parts by mass (the same below), 74 parts of crushed air-dried cotton stalks, 15 parts of soybean meal, 10 parts of chicken manure, and 1 part of high-efficiency...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The preparation of high-efficiency composite microbial fermentation inoculant, decomposed organic matter, Trichoderma fermented liquid and actinomycetes fermented liquid is the same as embodiment 1. The difference is that the preparation of disease-preventing biological organic fertilizer is as follows:
[0058] Add 2 parts of Trichoderma fermented liquid to 98 parts of decomposed edible fungus slag, adjust the moisture content to 68%, pH 6.8, fully mix, pile up into a strip-shaped stock pile with a height of 0.5 meters, cover the sack, and control the stock pile. The temperature is 25-30°C, the compost is turned once a day, and the co-fermentation is carried out for 7 days. In addition, 2 parts of actinomycetes fermented liquid were added to 98 parts of decomposed edible fungus residues, the moisture content was adjusted to 60%, the pH was 7.3, fully mixed, piled up into a 0.5-meter-high strip-shaped pile, covered with a plastic film, Control the temperature of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] (1) The preparation of the high-efficiency composite microbial fermentation inoculant is the same as in Example 1;
[0061] (2) Preparation of decomposed organic matter:
[0062] In terms of parts by mass (the same below), 55 parts of pulverized air-dried cotton stalks, 28 parts of soybean meal, 15 parts of chicken manure, and 2 parts of high-efficiency composite microbial fermentation inoculum were fully mixed evenly. Adjust the water content of the mixture to 58%, C / N to 25, and pH to 7.5.
[0063] Pile the above-mentioned mixed materials into a trapezoidal pile with a height of 1.5 meters, punch holes from the top down, the number of holes per square meter is 15, cover with sacks, and carry out aerobic fermentation. When the temperature of the heap rises to 50°C, start counting and ferment for 7 days. When the temperature of the stockpile starts to drop, turn the pile and ferment for another 7 days, then turn the pile every 7 days for a total of 35 days of fermenta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com