Fluorescent probe for detecting histidine, precursor thereof and preparation methods of fluorescent probe and precursor
A technology of fluorescent probes and precursors, applied in chemical instruments and methods, fluorescence/phosphorescence, luminescent materials, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the wide application of probes, short fluorescence emission wavelengths, and difficult probe synthesis, and achieve good water solubility. high sensitivity, low anti-interference effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The preparation of compound shown in formula Ia
[0033] (1) Synthesis of Compound A1
[0034] Dissolve 0.5 g (1.6 mmol) of 4-bromo-5-nitro-1,8-naphthalic anhydride in 20 ml of ethanol, and stir well. Add 0.096g n-butylamine (1.6mmol), heat to reflux for three hours, track with TCL spot plate, until the point of raw material disappears or no longer diminishes, it is the end of the reaction. Cool, filter, and recrystallize with ethanol to obtain a brown solid. Melting point: 175.8-176.2°C. Yield: 77.8%.
[0035] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 , 20°C): δ8.71(d, J=7.6Hz, 1H), 8.52(d, J=8.0Hz, 1H), 8.22(d, J=8.0Hz, 1H), 7.94(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 4.18(t, J=7.6Hz, 2H), 1.76-1.68(m, 2H), 1.50-1.41(m, 2H), 0.99(t, J=7.2Hz, 3H).
[0036] 13 C NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 , 20°C): δ162.79, 162.02, 151.25, 135.96, 132.32, 131.20, 130.52, 125.77, 124.07, 123.54, 122.48, 121.19, 40.74, 30.02, 20.31, 13.79.
[0037] (2) Synthesis of compound A2
[0038] 1.0 g (2.6 mmol) of compound A1 was di...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The preparation of compound shown in formula IIb
[0050] (1) Synthesis of compound B1
[0051] In a 100 mL round bottom flask, 7-hydroxycoumarin (3.1 g, 19.1 mmol) was added to 50 mL of dichloromethane to form a suspension, then 2 mL of acetic anhydride and a drop of pyridine were added. The above reaction solution was stirred overnight at room temperature to obtain a light yellow clear solution. The solvent dichloromethane was spin-dried under reduced pressure to obtain a light yellow crude product solid. It was then added to 100 mL of water, extracted with ethyl acetate, the organic layer was taken, the water layer was discarded, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the ethyl acetate was removed by a rotary evaporator to obtain a light yellow solid. It was separated by column chromatography (petroleum ether:ethyl acetate=2:1, (v / v)) to obtain 3.8 g (yield 97%) of a white solid.
[0052] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ7.71(d, 1H, J=4.8Hz), 7.51(d, J=4.2Hz, 1H), ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] The UV and Fluorescence Spectrum Properties of Compounds Ia and IIb
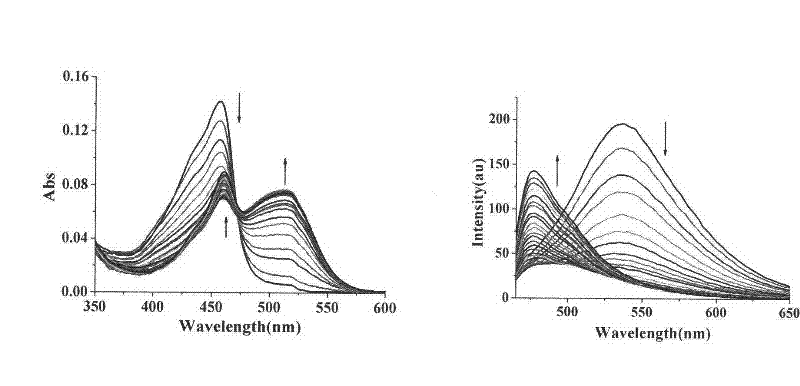
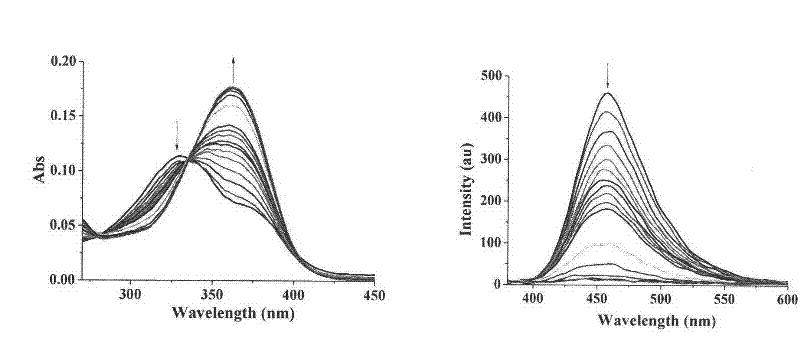
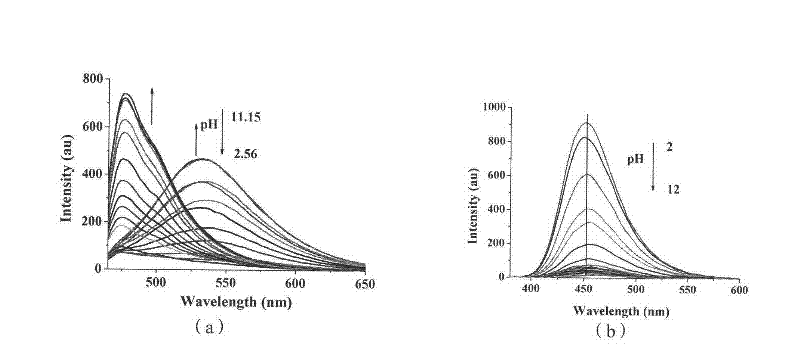
[0066] Compound Ia and Compound IIb are configured into 10 -3 mol / L DMSO stock solution, and then diluted 10 with the corresponding buffer solution -5 mol / L concentration of the test solution, and then add different concentrations of metal ions to test the ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission of the metal complex. like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, compound I complex metal Cu 2+ After that, the maximum ultraviolet absorption is at 460nm, and the maximum fluorescence emission is 472nm; Compound II is complexed with metal Ni 2+ Finally, the maximum UV absorption is at 350nm, and the maximum fluorescence emission is at 454nm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com