Strain of copper-resistant bacteria and application thereof
A technology of bacteria and copper pollution, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of short plants, low biomass, and long growth cycle of hyperaccumulative plants, and achieve the effects of improving phytoremediation efficiency, increasing total absorption, and increasing biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1.1 Strain isolation and purification
[0028] The soil samples were collected from the tailing vegetable garden soil of Funiushan Copper Mine in Tangshan Town, Nanjing City, the tailing soil of Anji Mountain, and the plant rhizosphere soil of the tailing soil of Fenghuang Mountain and Tongguan Mountain in Tongling. Within one week, the soil samples were separated and purified by dilution plate coating method (Shen Ping et al., 1999) and plate streaking method. Part of the soil samples were air-dried and stored for soil sample nutrient and heavy metal element analysis, mainly to determine the contents of water-soluble Cu, exchangeable Cu and total Cu in the soil. The specific steps of strain isolation and purification are as follows:
[0029] (1) Pour plate Prepare nitrogen medium, mix well, and pour plate after autoclaving. Nitrogenous medium formula is: sucrose 10g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.0g, K 2 HPO 4 2.0g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g, NaCl 0.1g, yeast extract 0.5g, disti...
Embodiment 2
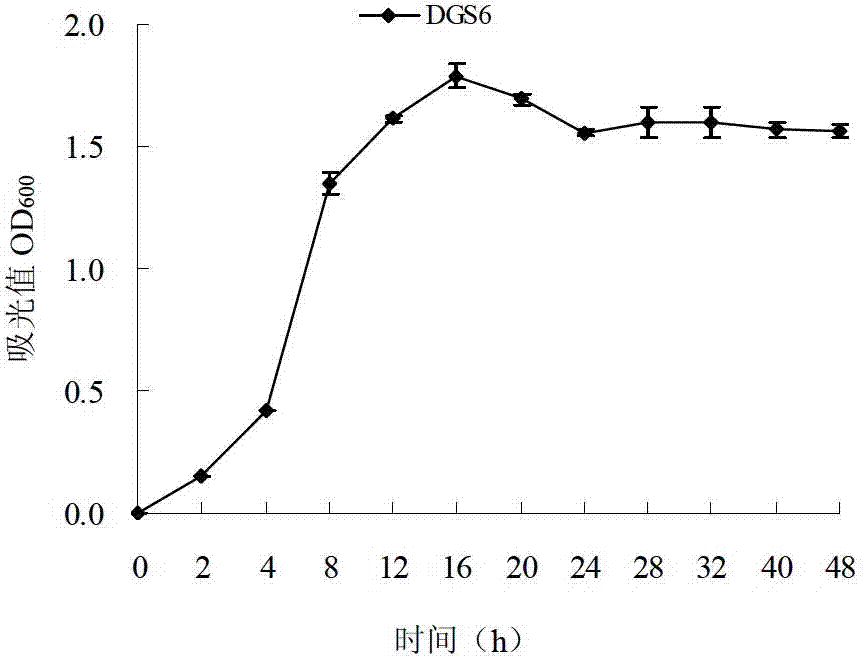
[0051] Activation of Cu by the bacterial strain DGS6 of embodiment 2
[0052] 2.1 Soil sample collection
[0053] The soil samples were collected from the polluted vegetable garden near the Funiushan Copper Mine in Tangshan Town, Nanjing City. After the soil samples were air-dried, stone particles and plant roots were removed, and passed through a 2mm sieve. For the analysis of soil sample nutrients and heavy metal elements, it mainly determines the water-soluble Cu and exchangeable Cu in the soil. Part of the samples were ground in an agate mortar and passed through a 100-mesh sieve for the determination of total Cu content.
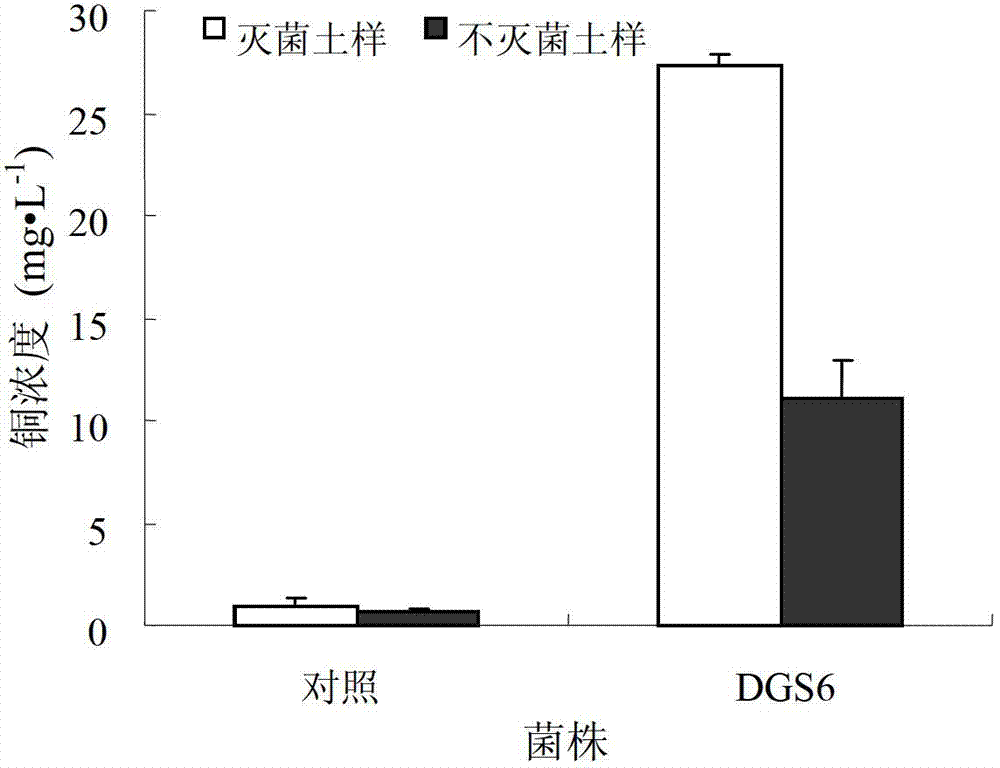
[0054] 2.2 Activation test of the tested strains on Cu in soil
[0055] Put 3.00g of sterilized and non-sterilized test soil into 50mL centrifuge tubes respectively. After the test strain was cultured in a liquid nitrogen medium for 16 hours, take 3.0 mL of the DGS6 bacterial solution (CGMCC NO.4817) in the logarithmic growth phase and pour it into a...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Effect of embodiment 3 bacterial strains on plant growth and absorbing Cu
[0061] 3.1 Effects of strain DGS6 on the elongation of the roots of A. haizhou, corn and oil sunflower
[0062] Cultivate the strain DGS6 (CGMCC NO.4817) in a nitrogenous medium for 24 hours, centrifuge the pure culture at 4°C, discard the supernatant, wash twice with sterile water, resuspend in sterile water, and measure at 600nm Adjust the optical density of the bacterial suspension to 0.5±0.02. Soak the seeds of Azalea, corn, and sunflower in 70% alcohol for 1 minute, then disinfect with 1% sodium hypochlorite for 10 minutes, and wash them with sterile water for more than 5 times immediately. Soak the seeds in bacterial suspension or sterile water for 3 hours at room temperature, then place them on a filter paper wetted with sterile water, Cu solution or bacterial solution in a petri dish, and place them on a slight inclination (to prevent water flooding and seeds). Root length was measured...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com