Application of micromolecular heat shock protein gene improving stress resistance of oryza sativa
A heat shock protein, rice stress resistance technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problem of short gene sequence, and achieve the effect of short coding sequence, high safety performance and easy access
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: Cloning of rice OsHSP18 gene
[0026] 1. Reagents
[0027] RNA extraction reagent Trizol was purchased from Invitrogen; reverse transcriptase ReverTraAce was purchased from Toyobo; high-fidelity DNA polymerase PrimeStar was purchased from TaKaRa; cloning vector pEASY TM -Blunt Simple Cloning Vector was purchased from Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; the primers were synthesized by Shanghai Yingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and the rest of the reagents were imported or domestic analytically pure products.
[0028] 2. E. coli strains and plant material
[0029] Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) strain DH5α was purchased from Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; rice japonica variety Nipponbare (Oryza sative L.ssp.japonica cv.Nipponbare) seeds were provided by Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
[0030] 3. Medium and solution
[0031] LB medium: tryptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L. Adjust the pH to 7.0 with NaOH and aut...
Embodiment 2
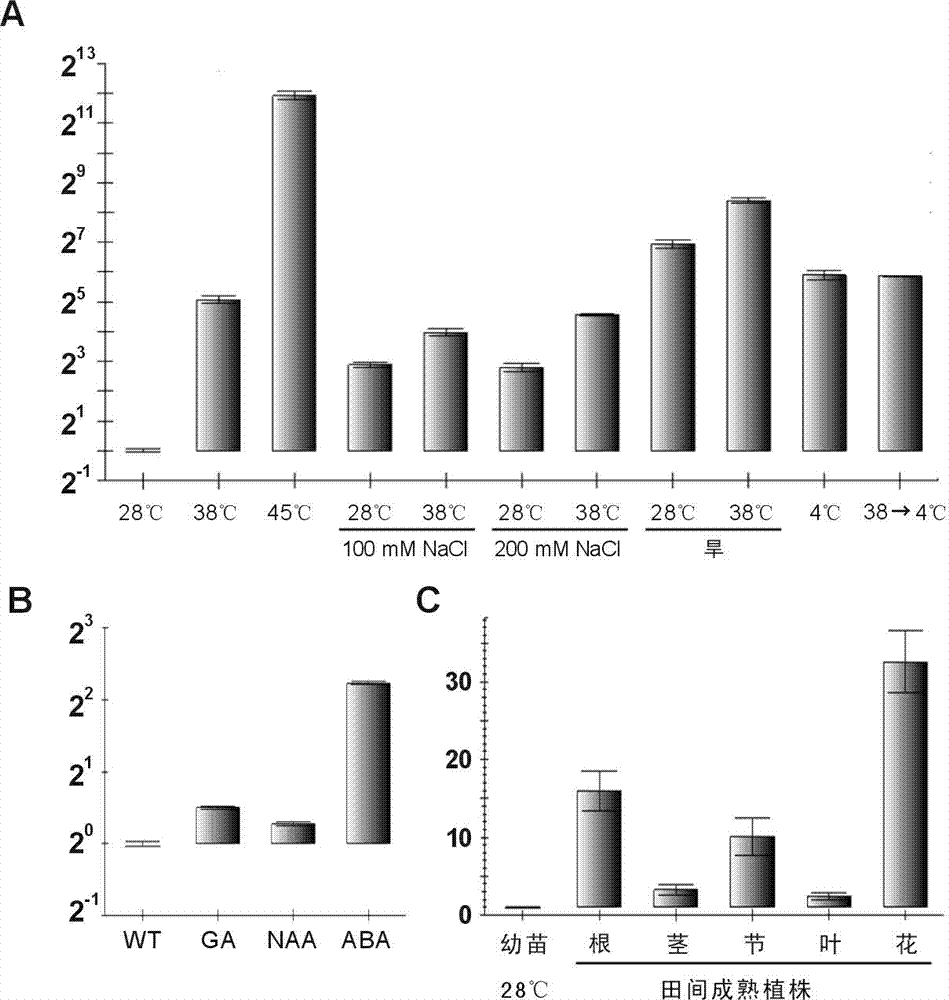
[0083] Example 2: Analysis of rice OsHSP18 gene expression pattern
[0084] 1. Reagents
[0085] RNA extraction reagent Trizol was purchased from Invitrogen; reverse transcriptase ReverTraAce was purchased from Toyobo; real-time quantitative PCR reagent TransStart TM Green qPCR SuperMix was purchased from Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; primers were synthesized by Shanghai Yingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0086] 2. Method
[0087] Tissue samples of wild-type Nipponbare seedlings and mature plants under various stress conditions and hormone induction were taken, ground with liquid nitrogen, RNA was extracted, and reverse transcription was performed. The operation steps were as described in Example 1.
[0088] Using rice reference gene (ACTIN, Genbank accession number X16280) as a control, the real-time quantitative PCR analysis of OsHSP18 gene expression level was carried out. OsHSP18 gene quantitative PCR primers are: RT18F and RT18R; ACTIN gene quantitative P...
Embodiment 3
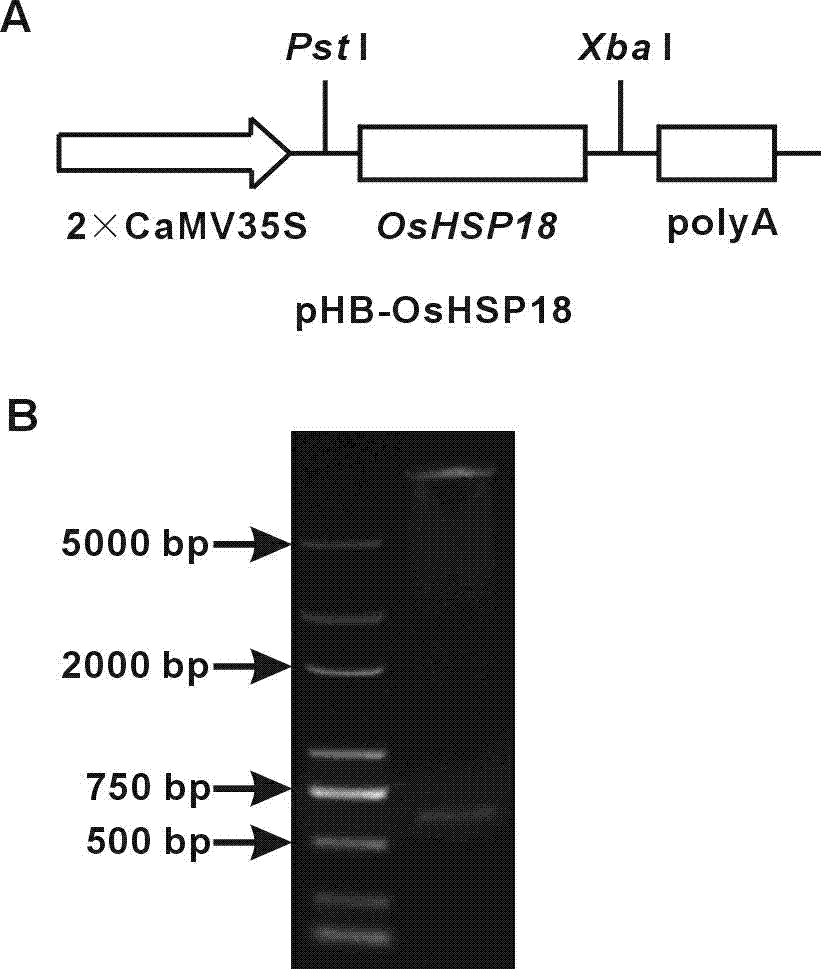
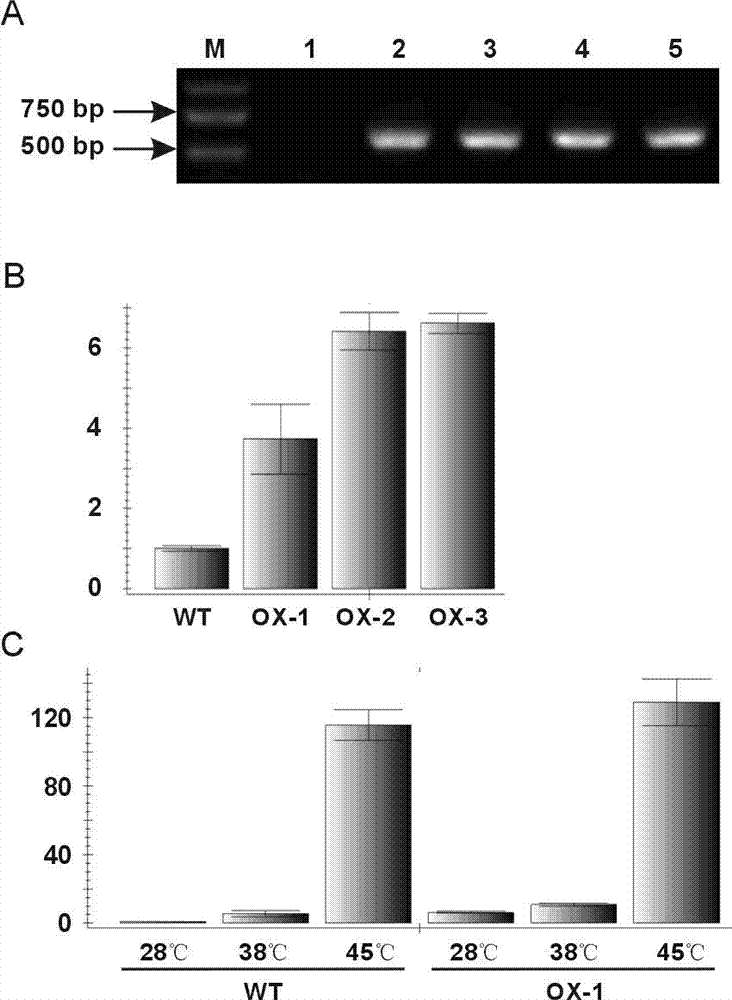
[0103] Example 3: Construction of OsHSP18 Gene Overexpression Recombinant Plasmid
[0104] 1. Reagents
[0105] Plasmid extraction kit EasyPure Plasmid MiniPrep Kit was purchased from Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; agarose gel recovery kit EasyPure Quick Gel Extraction Kit was purchased from Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; restriction enzymes Pst I, Xba I. T4 ligase was purchased from TaKaRa Company.
[0106] Other imported sub-packages and conventional reagents are the same as in Example 1.
[0107] 2. Agrobacterium strains and plant expression vectors
[0108] The Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) strain EHA105 used for transgenesis was purchased from Clontech Company; the eukaryotic expression vector pHB was constructed by the laboratory of Professor Yang Hongquan of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Mao et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , 2005) provided.
[0109] 3. Medium
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com