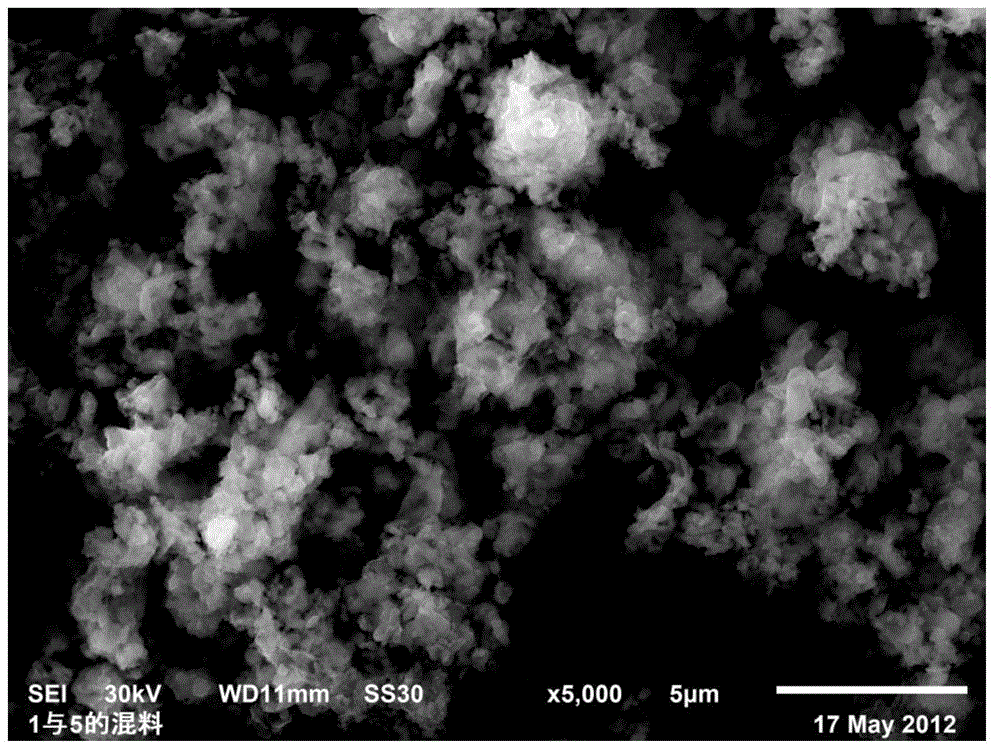
Method for preparing lithium iron phosphate material
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and raw materials, which is applied in the field of preparation of lithium iron phosphate material, a positive active material of lithium ion batteries, can solve the problems of large specific surface area, low tap density, low compaction density, etc., and achieves high specific capacity, high vibration Moderate solid density, the effect of reducing steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
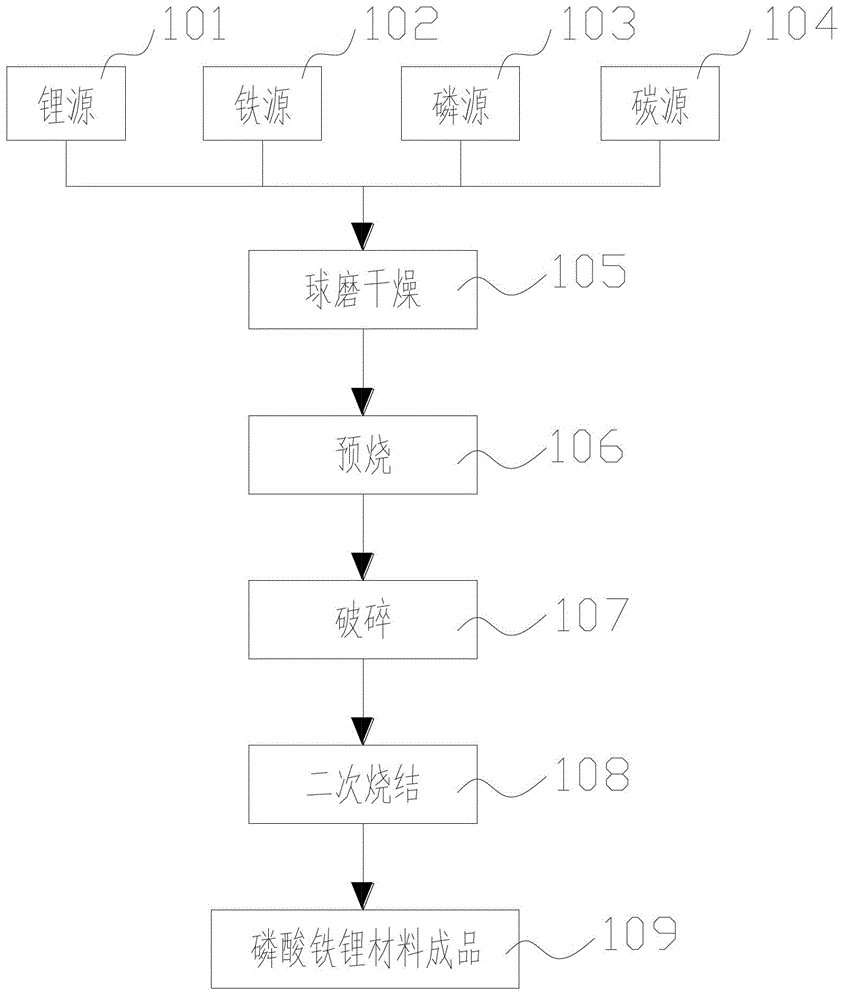
[0031] figure 1 A process flow diagram of a method for preparing a lithium iron phosphate material according to an embodiment of the present invention is shown. like figure 1 The process flow chart of the method for preparing lithium iron phosphate material shown, comprises the following steps:
[0032] Mixing raw materials for preparing lithium iron phosphate materials, including lithium source 101, iron source 102, phosphorus source 103 and carbon source 104;
[0033] Ball milling and drying 105 of the mixed raw materials, ball milling and drying 105 is to put the mixed raw materials into a ball mill for ball milling, and then carry out drying treatment;
[0034] Pre-burn the dried raw materials by 106 ball mill to obtain the precursor of lithium iron phosphate material;
[0035] The precursor of the lithium iron phosphate material obtained by crushing 107 and pre-burning 106;
[0036] The precursor of the lithium iron phosphate material after crushing 107 is subjected t...
Embodiment 1
[0044] The lithium source, the iron source and the phosphorus source are mixed with a mixture of lithium carbonate, ferrous oxalate and ferric oxide and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in a molar ratio Li:Fe:P=1:1:1, wherein ferrous oxalate and triferrous The mol ratio of ferric oxide is 4:1, adds the sucrose that accounts for all raw material gross mass 2.6% simultaneously;
[0045] Put the mixed raw materials into a ball mill for 3 hours at a speed of 80 rpm, and then put them into a vacuum dryer with a vacuum degree of -0.07MP at 140°C to dry;
[0046]Put the dried material into an atmosphere box furnace for pre-calcination, and pre-fire it at a rate of 8 °C / min in nitrogen atmosphere from room temperature to 350 °C, keep the temperature for 7 hours, and then at a rate of 8 °C / min Down to room temperature, obtain the precursor of lithium iron phosphate material;
[0047] The precursor of the lithium iron phosphate material obtained by pre-burning is crushed by a crusher;
...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The finished product of lithium iron phosphate material is prepared according to the method described in Example 1, the difference is: Lithium source, iron source and phosphorus source take lithium hydroxide, ferrous oxalate and three according to the molar ratio Li:Fe:P=1:1:1 The mixture of ferric oxide and diammonium hydrogen phosphate are mixed, the molar ratio of ferrous oxalate to ferric oxide is 1:1, the secondary sintering temperature is 710°C, and the constant temperature time is 14h.
[0055] The method for preparing a half-cell described in Example 1 was used to make a half-cell from the finished lithium iron phosphate material prepared in this example, and the half-cell was tested, and the results are shown in the following table:
[0056]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com