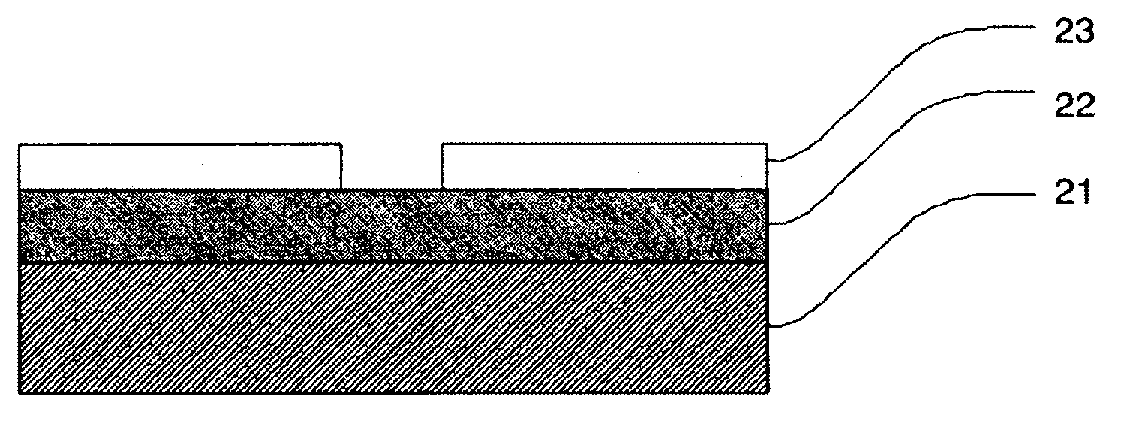
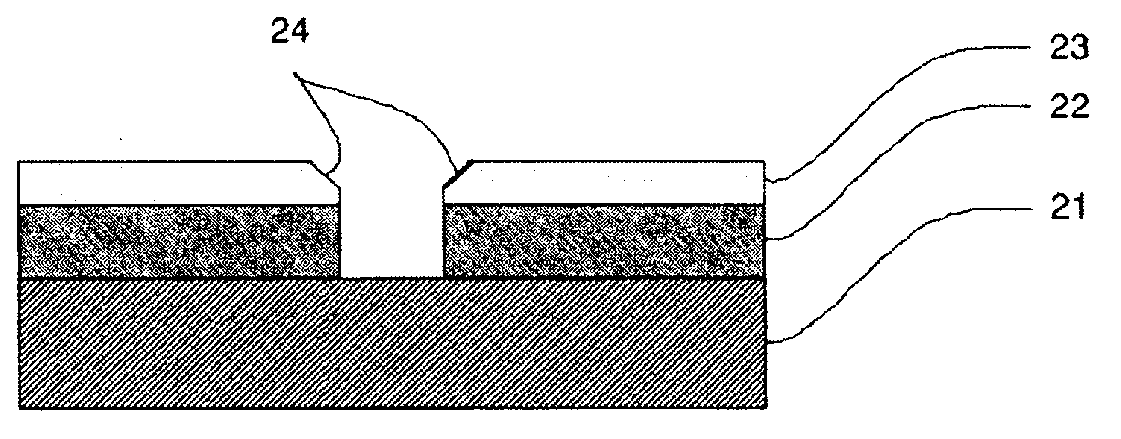
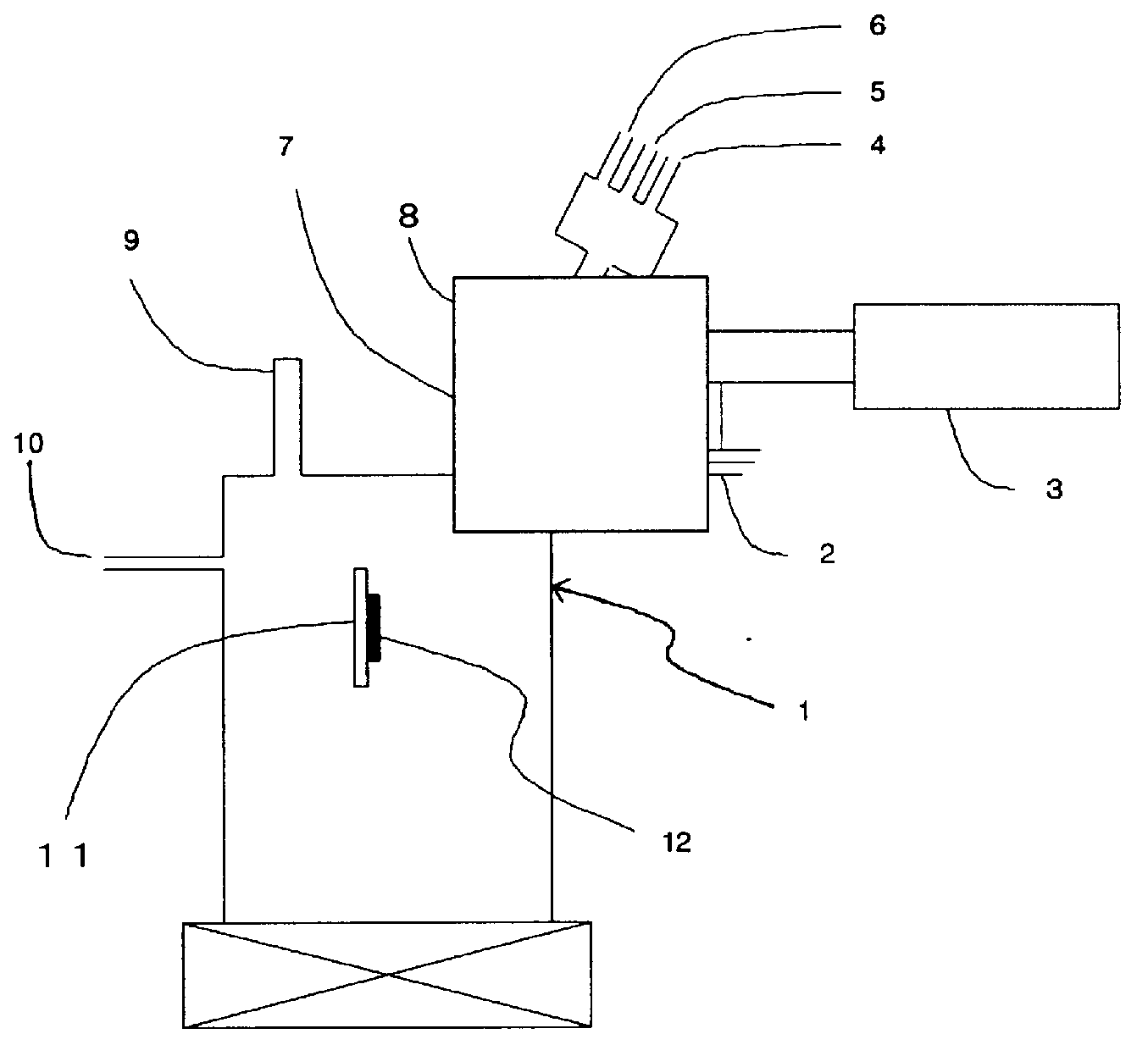
Method for producing semiconductor gas
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, organic chemistry methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of difficult distillation and separation, difficulty in obtaining starting materials, and difficult and efficient production methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0061] The preparation method of the phosphate catalyst is not particularly limited, and a commercially available phosphate can be directly used, or can be prepared by a common precipitation method. As a specific preparation method of the precipitation method, for example, dilute ammonia water is added dropwise to a mixed aqueous solution of metal nitrates (in case of multiple metals) and phosphoric acid, pH is adjusted, precipitated, and aged as necessary. Thereafter, water washing is performed, and whether the water washing is sufficient is confirmed by the electric conductivity of the washing water or the like. Depending on the situation, take out a portion of the slurry and measure the cations contained therein for confirmation. Next, filter and dry. The drying temperature is not particularly limited. Preferably it is 80°C to 150°C. More preferably, it is 100°C to 130°C. The obtained dried body is pulverized to have a uniform particle size, or further pulverized to for...
preparation example 1
[0137] Dilute 30g of 85% phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4 ) into the phosphoric acid aqueous solution obtained by immersing 100g of granular activated carbon G2X manufactured by Japan EnviroChemicals, Ltd., stirring well, and then standing still for 3 days. Thereafter, it was dried with a rotary evaporator, and then calcined in an electric furnace at 350° C. for 5 hours in a nitrogen stream, thereby preparing a phosphoric acid-carrying activated carbon catalyst.
preparation example 2
[0139] 1000g (2.666mol) aluminum nitrate nonahydrate (Al (NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O) and 128.6g (0.296mol) of cerium nitrate hexahydrate (Ce(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O) Dissolved in 5300 cc of pure water, 306 g (3.12 mol) of 85% phosphoric acid was further added and stirred. In this state, it is a transparent solution. Use a 1L large dropping funnel to add 10% ammonia (about 3000cc) dropwise over 10 hours to make it alkaline. Since the concentration of the solid content was high, stirring with a stirrer became impossible during the dropping process, so manual stirring was performed with a stainless steel shovel. After the generated white precipitate was left to stand overnight, it was suction-filtered and washed with water five times.
[0140] This white solid was transferred to a stainless steel pad, and dried overnight in a 180° C. drier. Grind with a mortar, sieve, and form into The particles were calcined at 700°C for 5 hours in a nitrogen stream to prepare the aluminum phosphate / ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com