Energy storage energy-efficient foam gypsum cement composite material and preparation method thereof
A cement composite material and composite cementitious material technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of foam gypsum water resistance, high temperature brittleness, etc., and achieve the effects of short molding and curing time, low energy consumption, and energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Step 1: Take by weight percentage: 36% of hemihydrate gypsum, 24% of cement, 2% of silica fume, 1% of lime, 2% of expanded perlite (light aggregate), 2% of microcapsule-coated paraffin (phase transition temperature 26°C ) 3%, polyvinyl alcohol emulsion 3.2%, foam 2.8%, glass fiber 1.2%, surfactant 0.1%, magnesium hydroxide (flame retardant) 2.5%, sodium naphthalenesulfonate (water reducer) 0.2%, water twenty two%;
[0041] Wherein, the foam is prepared as follows: prepare a blowing agent solution with a concentration of polyoxyethylene ether of 0.2% and a concentration of polyvinyl alcohol emulsion of 0.1%. Then the blowing agent solution is sent to the compressed air foaming machine to produce a foam with a cell diameter of about 0.3mm and a foam density of 80kg / m3;
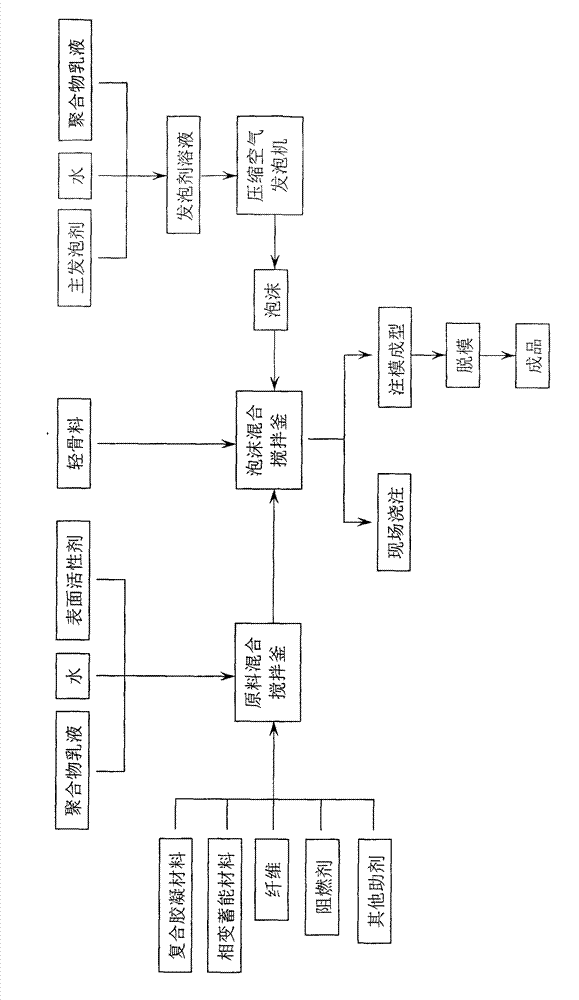
[0042] Step 2: Add liquid components such as water, polymer emulsion and surfactant into the raw material mixing tank. Premix solid components such as hemihydrate gypsum, cement and other composite ceme...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Weighing by weight percentage: 36% of hemihydrate gypsum, 24% of cement, 2% of silica fume, 1% of lime, 2% of polystyrene foam particles (light aggregate), 2% of microcapsule-coated paraffin (phase transition temperature 26oC)3 %, acrylic emulsion 3.2%, foam 2.8%, glass fiber 1.2%, surfactant 0.1%, magnesium hydroxide 2.5%, sodium naphthalenesulfonate 0.2%, water 22%;
[0048] Wherein, the foam is prepared as follows: a foaming agent solution with a concentration of 0.3% of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and a concentration of acrylic acid emulsion of 0.06% is prepared. Then the blowing agent solution is sent to the compressed air foaming machine to produce a foam with a cell diameter of about 0.5 mm and a foam density of 50 kg / m3; other preparation process steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3-8
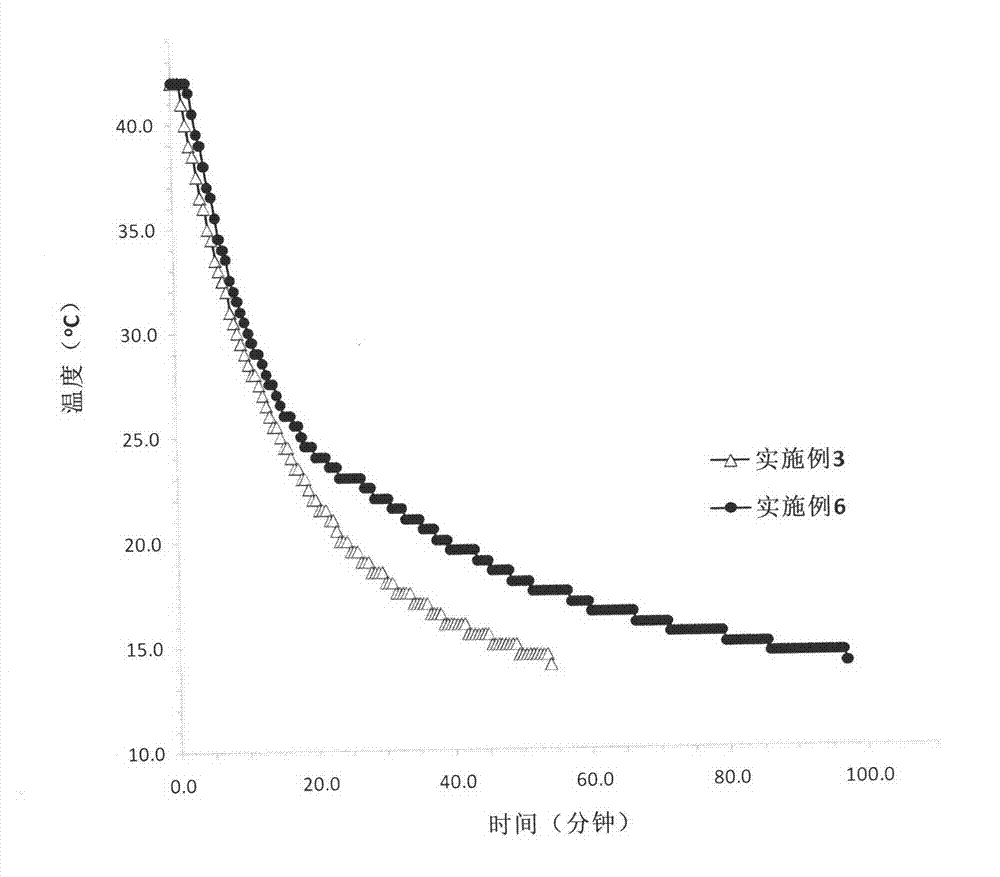
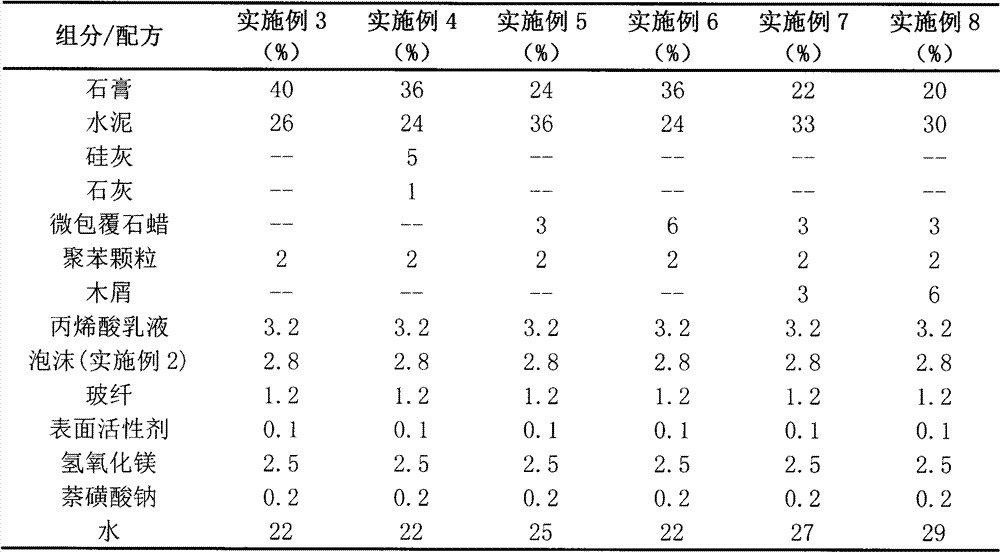
[0050] Embodiment 3-8 is the comparative test of six different formulations. The six formulations are listed in Table 1. The foam prepared in Example 2 is used, and the process method of Example 1 is used to make plates with a thickness, length and width of about 50x305x305mm.
[0051] Table 1. Weight percent formulations of syntactic foam examples 3-8
[0052]
[0053] The compressive strength is tested according to ASTM C109, and the fire resistance is tested according to GB 9978-88. Table 2 lists the main properties of the syntactic foam prepared by the formulations of Examples 3-8. From the compressive strength of Examples 3 and 4, it can be seen that under the similar density, silica fume and lime are not as obvious as phase change materials in improving the mechanical properties of the foam, and the addition of micro-encapsulated paraffin phase change materials makes the embodiment 6 The compressive strength of the foam material is increased by more than 70% compare...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com