Epitaxial structure of high-brightness light emitting diode and implementation method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and epitaxial structures, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the technical difficulties of theoretically feasible epitaxial growth, increase non-radiative recombination of quantum wells, and low quantum efficiency in LEDs, and achieve improved radiation recombination Efficiency, enhanced radiative recombination probability, improved luminous efficiency and the effect of comprehensive device performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] Using MOCVD equipment (CCS model Crius I 31 pieces commercial machine of Aixtron Company), the source of group V used is ammonia (NH3), and the organic source material of group III used to grow GaN and its alloys except the quantum well light-emitting region is Trimethylgallium (TMGa), trimethylaluminum (TMAl), the organic raw materials used to grow the quantum well active region are triethylgallium (TEGa), trimethylindium (TMIn), P-type doping using metal organics The source diphenocene magnesium (Cp2Mg) provides Mg impurity atoms, and N-type doping uses gaseous silane (SiH4) diluted with H2 to provide Si impurity atoms.
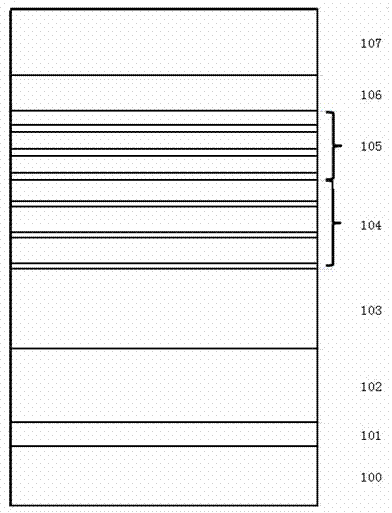
[0032] Combine below figure 1 , 2 Further illustrate the present invention:
[0033] 1. Grow a layer of GaN low-temperature buffer layer 101 on the sapphire substrate 100: the growth temperature is 580°C, the pressure is 65000Pa, the thickness is 30nm, and the growth atmosphere is H 2 .
[0034] 2. A layer of unintentionally doped GaN layer 102 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com