Method and device for separating oil and sand
A separation method and oil sand technology, which are applied in the petroleum industry, the preparation of liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, etc., can solve the problems that solid processing is not well solved, solvents are not easy to obtain, and solvent recovery is difficult, so as to save intermediate operating costs. , good stability, continuous operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
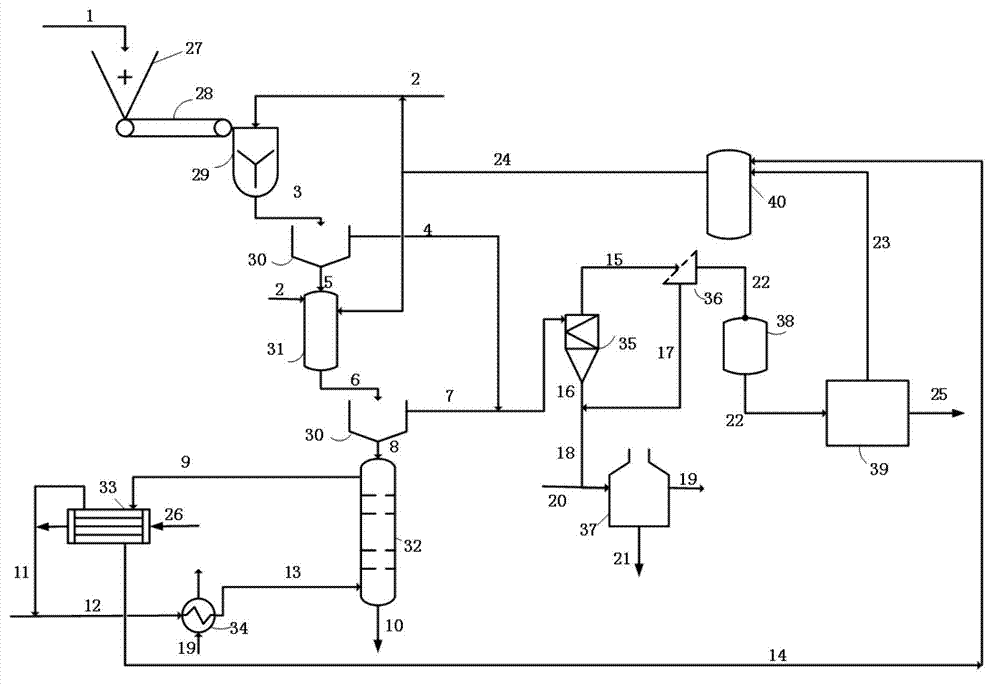
[0046] 5 kg of oil sand pulverized by the pulverizer 27 is sent to the mixed solvent of the mixing tank 29 and n-heptane / toluene (n-heptane:toluene=5:1) according to the liquid-solid ratio (mass ratio) of 2: 1. At 25°C, carry out mixing and stirring extraction for 2 minutes, reduce the stirring speed, and send the upper liquid phase to the suspension separator 35 after liquid-solid separation in the mechanized clarification tank for liquid-solid separation again. The residual sand is sent to the secondary extraction tank 31, and 0.2 times the mass of the solid is added to the circulating solvent at 25°C for washing and extraction for 2 minutes, and then enters the mechanized clarification tank, and the liquid phase is sent to the hydrocyclone 35 for liquid-solid separation. The residual coarse solids are sent to the fluidized drying tower 32 for desolvation treatment; after the fluidized gas nitrogen is preheated to 50°C by the preheater 34, it is sent from the bottom of the to...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 5 kg of oil sand pulverized by the pulverizer 27 is sent to the mixed solvent of the mixing tank 29 and n-heptane and toluene (n-heptane:toluene=3:1) according to the liquid-solid ratio (mass ratio) of 2: 1. At 55°C, carry out mixing and stirring extraction for 5 minutes. After the oil sand is extracted, the mixture enters the mechanized clarification tank, and the upper liquid phase is sent to the suspension separator 35 for liquid-solid separation again, and at the same time, the residual sand containing solvent at the bottom is sent to the In the secondary extraction tank 31, add 0.5 times of the mass of solids and other circulating solvents at 25°C for washing and extraction for 5 minutes. After the liquid-solid separation in the mechanized clarification tank, the extract is also sent to the hydrocyclone 35 for liquid-solid separation. The residual coarse particle solid 8 is sent to the fluidized drying tower 32 for desolvation treatment; after the fluidized gas nitr...
Embodiment 3
[0052] 5 kg of oil sand pulverized by the pulverizer 27 is sent to the mixed solvent of the mixing tank 29 and n-heptane and toluene (n-heptane:toluene=2:1) according to the liquid-solid ratio (mass ratio) of 10: 1. At 55°C, carry out mixing and stirring extraction for 30 minutes. After the oil sand is extracted, the mixture enters the mechanized clarification tank 30, and the upper liquid phase is sent to the suspension separator 35 for liquid-solid separation again. At the same time, the primary treatment residual sand + solvent 5. Send it to the secondary extraction tank 31, add a circulating solvent equal to the mass of 1 times the solid at 50°C, carry out washing and extraction for 10 minutes, and then send it to the mechanized clarification tank 30, and send the extract to the hydrocyclone 35 for liquid-solid separation , the residual coarse solids 8 are sent to the fluidized drying tower 32 for desolvation treatment; after the fluidized gas carbon dioxide is preheated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com