Near-beta titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high strength and preparation method of near-beta titanium alloy
A β-titanium alloy, high-purity technology, applied in the field of titanium alloys, can solve the problems of difficult control of metallurgical quality of ingots, inability to meet low modulus, high strength, and increased preparation costs at the same time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] The method for preparing the low elastic modulus and high strength near-β titanium alloy according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a vacuum melting step and a thermomechanical treatment step. The vacuum smelting step includes: high-purity titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), molybdenum (Mo) and tin (Sn) metals and titanium dioxide (TiO 2) powder is prepared according to the ratio of 15-35% niobium, 1-8% molybdenum, 1-8% tin, 0-1.2% titanium dioxide powder, and the rest is titanium, and the prepared raw materials are placed in In a magnetically stirred vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace, the ingot is repeatedly turned and smelted under the condition of an inert gas protective atmosphere, and the ingot is formed after solidification; the so-called thermomechanical treatment steps include: hot forging the ingot to a predetermined thickness; sealing the forged ingot In the quartz tube, after vacuuming the quartz tube, seal the quartz tube, put the sealed ...
Embodiment 1
[0051] Get the composition described in Table 1, high-purity titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), molybdenum (Mo) and tin (Sn) metal are based on the niobium of 15~35% by weight, the molybdenum of 1~8%, 1~ The ratio of 8% tin and the rest is titanium, and the prepared raw materials are placed in a magnetically stirred vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace, repeatedly turned and smelted under the condition of an inert gas protective atmosphere, and formed into an ingot after solidification; Hot forge the ingot to a thickness of 5mm; seal the forged ingot in a quartz tube, vacuumize the quartz tube and seal the quartz tube, put the sealed quartz tube into a heat treatment furnace to heat up to a temperature range of 900°C After 5 hours of internal heat preservation, the quartz tube is taken out, the quartz tube is crushed, and the spindle is directly dropped into water for water cooling, and the homogenized annealed spindle is cold-rolled into a 1mm thick plate (referred to as cold-...
Embodiment 2
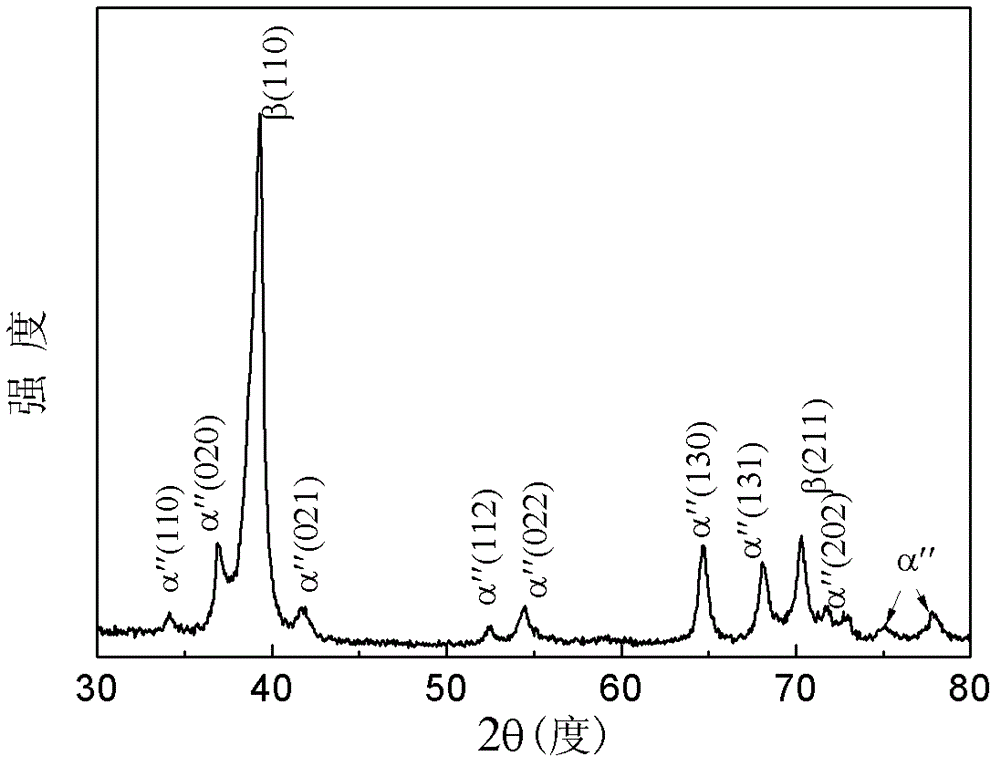
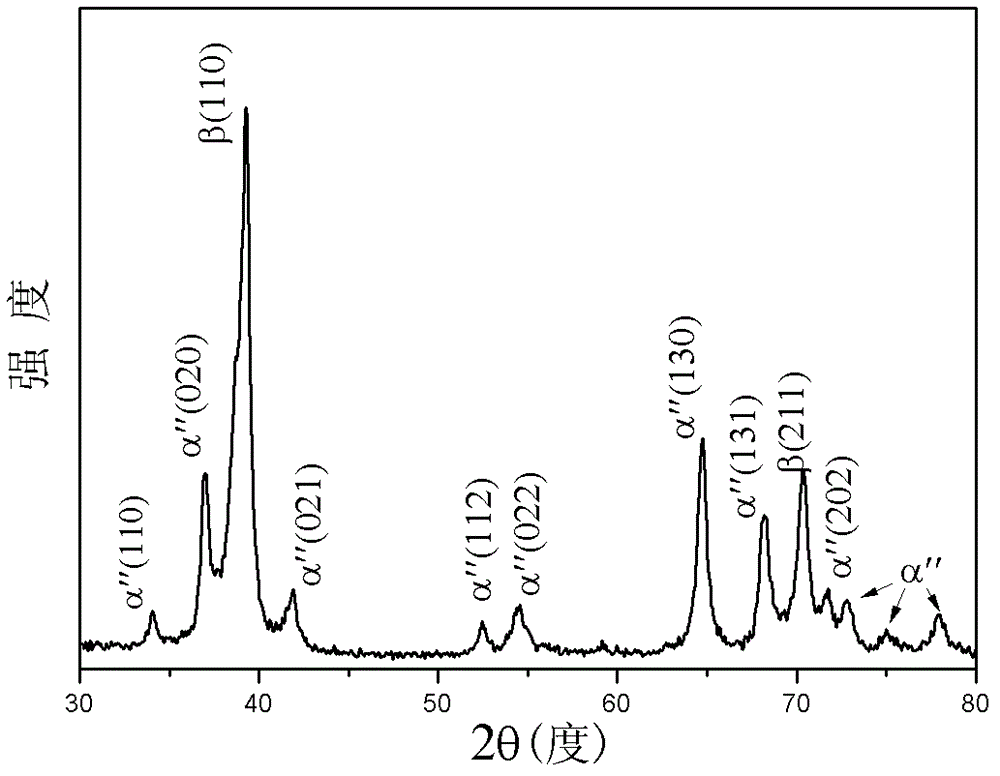
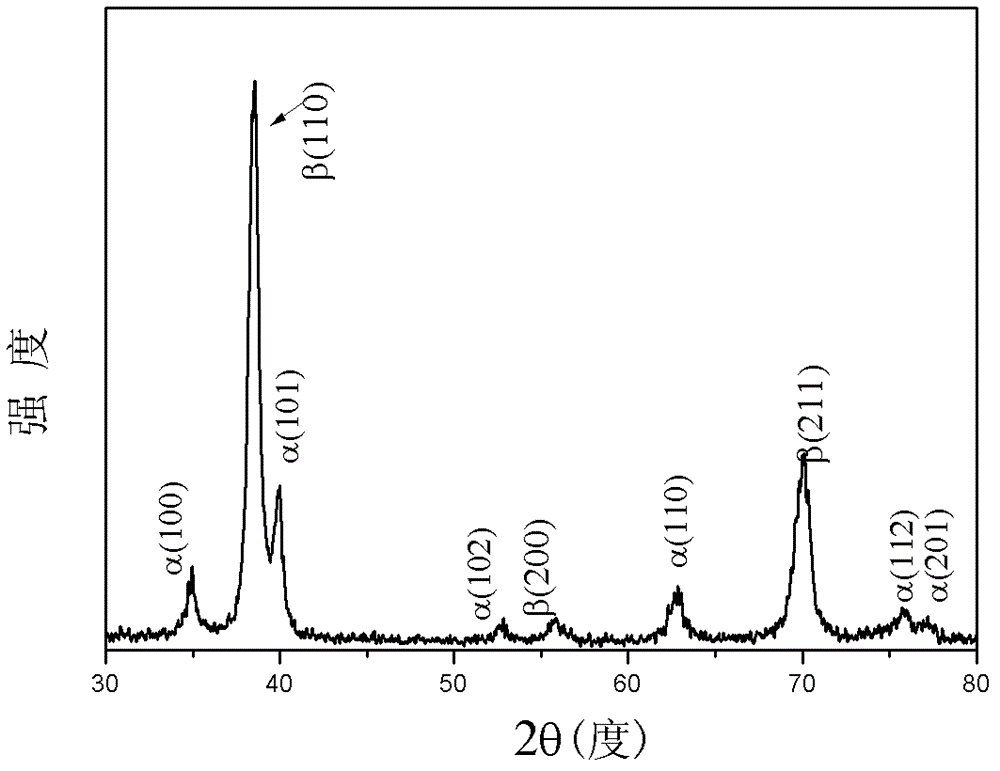
[0059] The difference from Example 1 is that this example studies the influence of the alloy phase composition on the mechanical properties of the alloy, and characterizes the phase composition characteristics of the low modulus and high strength titanium alloy.
[0060] Get the composition described in Table 2, high-purity titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), molybdenum (Mo) and tin (Sn) metal are based on the niobium of 15~35% by weight, the molybdenum of 1~8%, 1~ The ratio of 8% tin and the rest is titanium, and the prepared raw materials are placed in a magnetically stirred vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace, repeatedly turned and smelted under the condition of an inert gas protective atmosphere, and formed into an ingot after solidification; Hot forge the ingot to a thickness of 4mm; seal the forged ingot in a quartz tube, vacuumize the quartz tube and seal the quartz tube, put the sealed quartz tube into a heat treatment furnace to heat up to a temperature range of 850°C ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com