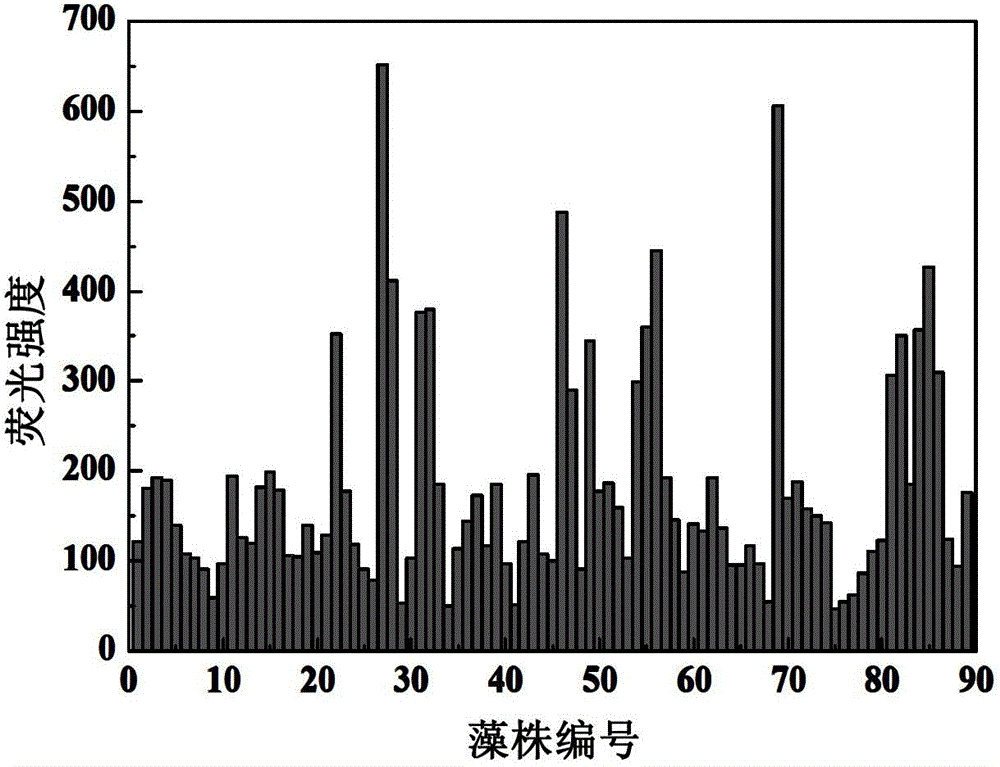
High-throughput screening method of oil-rich microalgae
A screening method and high-throughput technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of high-throughput determination of oil content, toxic reagents, human and environmental hazards, time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of avoiding traditional oil detection steps, fast measurement and less time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: A high-throughput screening method for oil-rich microalgae in this embodiment is achieved through the following steps:
[0020] 1. Take microalgae samples and add them to medium A for enrichment and culture for 15 to 30 days to obtain algae liquid; 2. Take the algae liquid obtained in step 1 and inoculate in medium A with an inoculation amount of 10% by volume , cultured in a light incubator at a temperature of 25°C for 7 to 14 days; 3. Repeat step 2 2 to 3 times to obtain algae liquid A; 4. Take the algae liquid A obtained in step 3, and the volume percentage is Inoculate 10% of the inoculum into medium B, and cultivate in an incubator at 25°C for 7 to 14 days to obtain algae liquid B; -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 and 10 -6 Dilute the multiple of 10 -5 ~10 -6 The algae liquid after multiple dilution is evenly spread on the solid medium C plate, and cultivated in a 25°C incubator until algal colonies appear; 6. In a sterile environment, pick a sin...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific embodiment two: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the microalgae samples described in step one are Chlorella, Scenedesmus, diatoms, Cryptodinoflagellates, Flatweed, Dunaliella, Spirulina, One or several types of golden algae are mixed in any ratio. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the culture medium A described in step one and step two is made of 1 part of sodium nitrate, 0.075 part of magnesium sulfate, 0.04 part of phosphoric acid in parts by weight Dipotassium hydrogen, 0.036 parts of calcium chloride, 0.02 parts of sodium carbonate, 0.006 parts of citric acid, 0.006 parts of ferric ammonium citrate, 0.001 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 0.00541 parts of trace elements. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com