Material and method for adsorbing heavy metals in aqueous solution
A technology for heavy metal ions and separation materials, applied in the direction of adsorption water/sewage treatment, solid adsorbent liquid separation, separation methods, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to remove or separate heavy metal ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068]
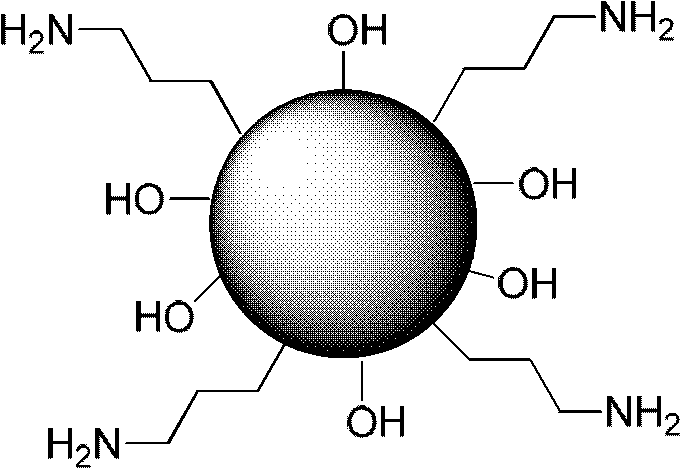
[0069] In a 250mL round-bottom flask, mix 0.83g NaOH (20.75mmol) and 1.52g cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 4.2mmol) in 80mL water, stir at 80℃ for 30min, until CTAB is completely dissolved In the water. Subsequently, 1.24g of 3-(triethoxysilane)propylamine (5.6mmol) was added, and after stirring for 2h at 80°C, 7mL (3.46mmol) of ethyl orthosilicate was added dropwise, and the addition was completed in 30min, at 80°C. After continuing to stir for 2 hours, the reaction was stopped, and hot suction filtration was performed to obtain a white filter cake. After the filter cake was dried at 90° C., it was evenly dispersed in methanol (200 mL) containing 10 mL of hydrochloric acid, stirred under reflux for 24 hours, filtered to obtain a white solid, and dried to obtain amino-functionalized mesoporous silica particles.
[0070]
[0071] Weigh 500 mg of ethylene glycol diethyl ether diamine tetraacetic acid (EGTA, 1.3 mmol) and mix in 50 mL of deionized water. Then prepar...
Embodiment 2
[0073]
[0074] Magnetic Fe 3 O 4 The particles were dispersed in chloroform, added to 10 mL of an aqueous solution containing 1.5 g of CTAB, stirred for 30 minutes to obtain an oil-water emulsion, and then heated to 60°C and stirred for 10 minutes to volatilize the chloroform. The above mixture was added to 60 mL of water and 0.6 mL of 2M sodium hydroxide solution, stirred and heated to 70°C. Then 1 mL (ethyl orthosilicate) TEOS was added. After 10 minutes, 100 μL of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) was added, and stirring was continued for 3 hours. Centrifugation, ethanol washing three times, adding the particles to a Ph=1.4 hydrochloric acid ethanol solution, stirring at 60°C for 3 hours, centrifuging, ethanol washing three times, and drying to obtain magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with surface amino groups.
[0075]
[0076] Weigh 500 mg of ethylene glycol diethyl ether diamine tetraacetic acid (EGTA, 1.3 mmol) and mix in 50 mL of deionized water...
Embodiment 3
[0078]
[0079] Weigh 500 mg of ethylene glycol diethyl ether diamine tetraacetic acid (EGTA, 1.3 mmol) and mix in 50 mL of deionized water. Then prepare a 2M NaOH solution, adjust the pH of the EGTA aqueous solution to about 5, and stir evenly until the solution becomes clear. Add 200 mg of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI, 1.0 mmol) and stir for 20 min. Then add 2.0 g of epoxy resin containing primary amine groups on the surface, and stir overnight at room temperature. After stopping the reaction, filter with suction and wash the resin particles with deionized water several times. The resin particles are taken out and dried at 90° C. to obtain an acceptor-modified epoxy resin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com