Quick high-sensitivity microbiological identification method based on micromolecular metabolic substance spectral analysis
A technology for small molecule metabolites and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of rapid and high-sensitivity microbial identification, achieving the effects of less sample consumption, rapid microbial identification, and rapid cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
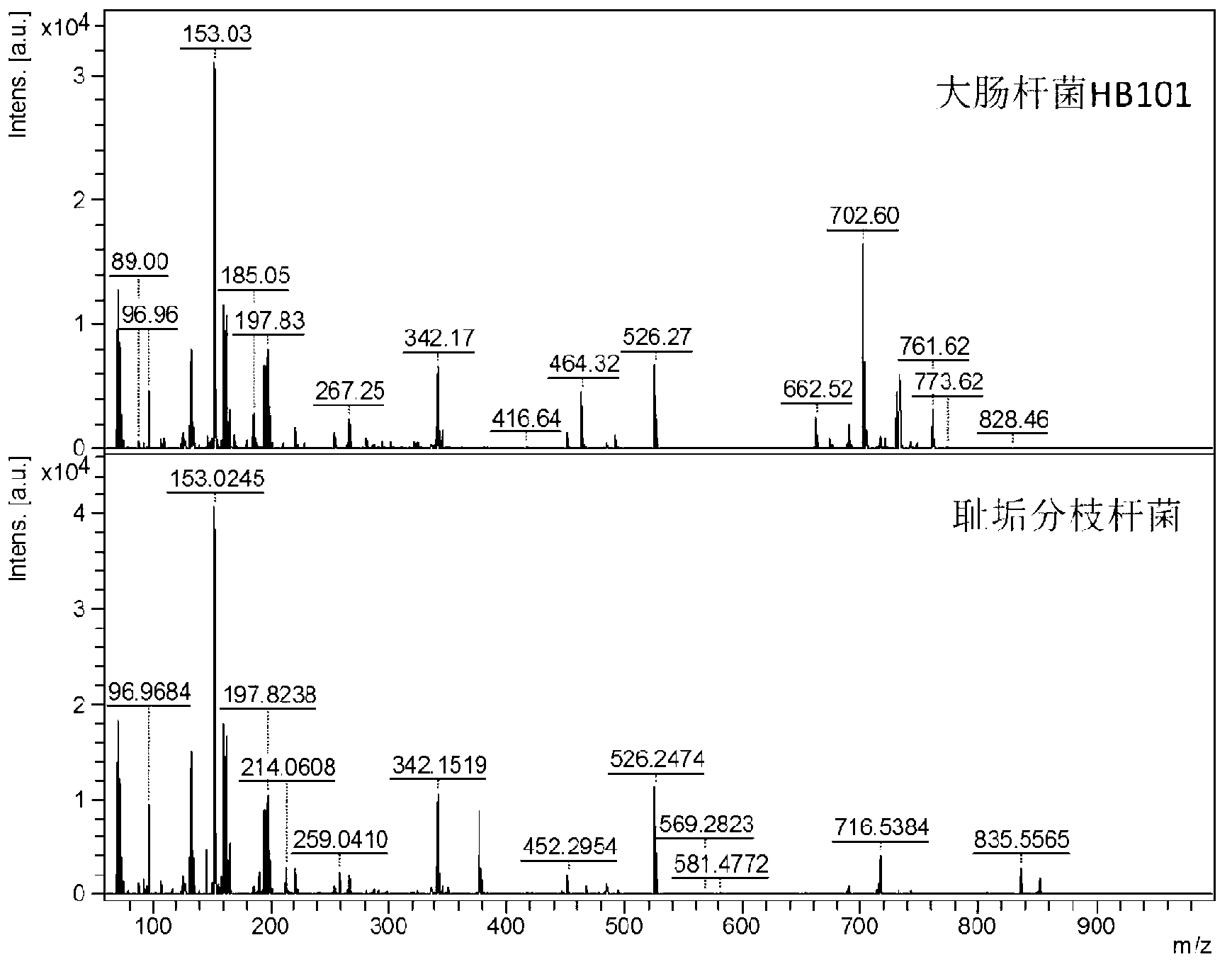
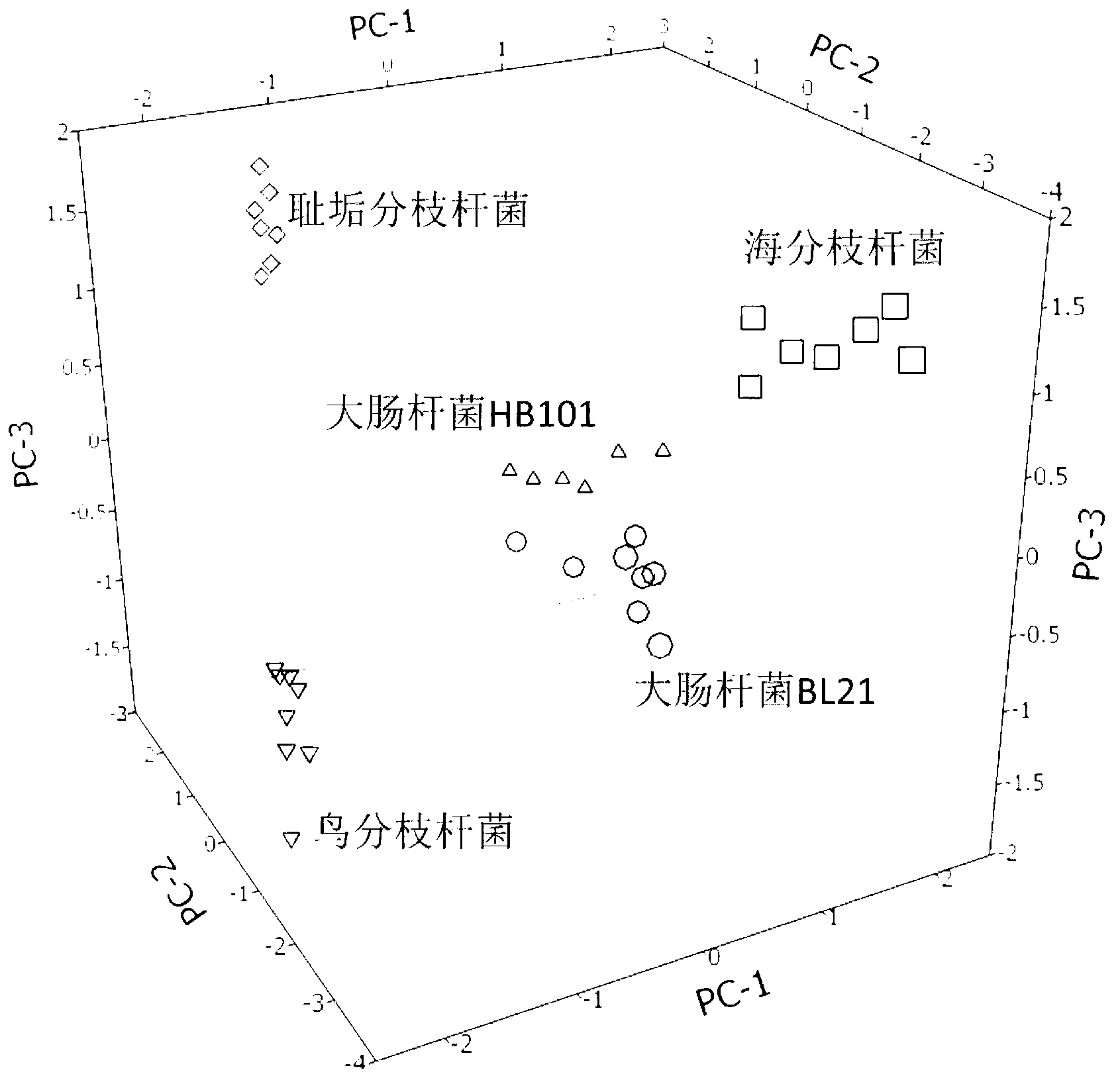
[0053] Embodiment 1, identify and distinguish different species-genus microorganisms (bacteria)
[0054] Cultured three mycobacteria (Mycobacterium smegmatis, Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium marinum), and two subspecies of Escherichia coli K12 (DH5α and HB101) bacteria grew to greater than OD 600 = 0.8-1.0 after collection. The collected cells were washed with 50-fold phosphate buffer saline with a pH value of 7.4, and then frozen at -20°C or directly used for further processing. The bacteria suspended in the phosphate buffer were replaced with deionized water, centrifuged at 5000 rpm to retain the precipitate, 3 times (ie 30 ul) volume fraction of 80% ethanol aqueous solution was added to the 10 mg precipitate, suspended and allowed to stand for 5 min. After centrifugation at 5000 rpm, the supernatant was taken, or an appropriate amount of sample was taken directly without centrifugation for mass spectrometry analysis.
[0055] Take the sample and matrix (naphthalene eth...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2, identification distinguishes different mutant strain microorganisms (bacteria) of the same species
[0058] Cultured Mycobacterium smegmatis (wild type, strain is mc 2 155) and five single-gene mutant strains (Msmeg2415KO, Msmeg1640KO, Msmeg1641KO, Msmeg1804KO and Msmeg_3312KO) (Msmeg_2415KO is Hemerythrin HHE cation binding region gene knockout (starting site 2497580, end site 2498158), Msmeg_1640pK gene knockout (Start site 1732495, end site 1733076); Msmeg_1641KO is mfpA gene knockout (start site 1733082, end site 1733657); Msmeg_1804KO is Mycobacterium tuberculosis SigF homologous gene knockout (start site 1881660 , ending point 1882412); Msmeg_3312KO is Hemerythrin HHE cation binding domain subfamily gene knockout (starting point 3391207, ending point 3391764). All gene information can be checked through the website after entering the gene name in MSMEG_XXXX format http: / / mycobrowser.epfl.ch / smegmalist.html . ) grow to OD 600 = 0.8-1.0 after colle...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com