Escherichia coli strain for producing succinic acid with glycerol as well as construction method and use
A technology of Escherichia coli and succinic acid, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of limited flux and achieve the effects of accelerating the growth rate of bacteria, increasing the production rate, and increasing the density of bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
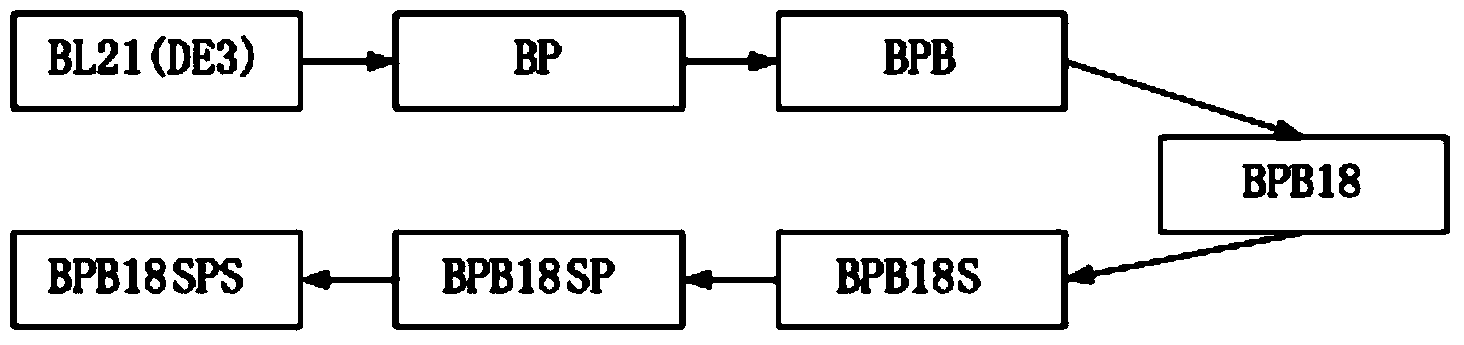
[0028] Construction of departure strains for directed pathway evolution
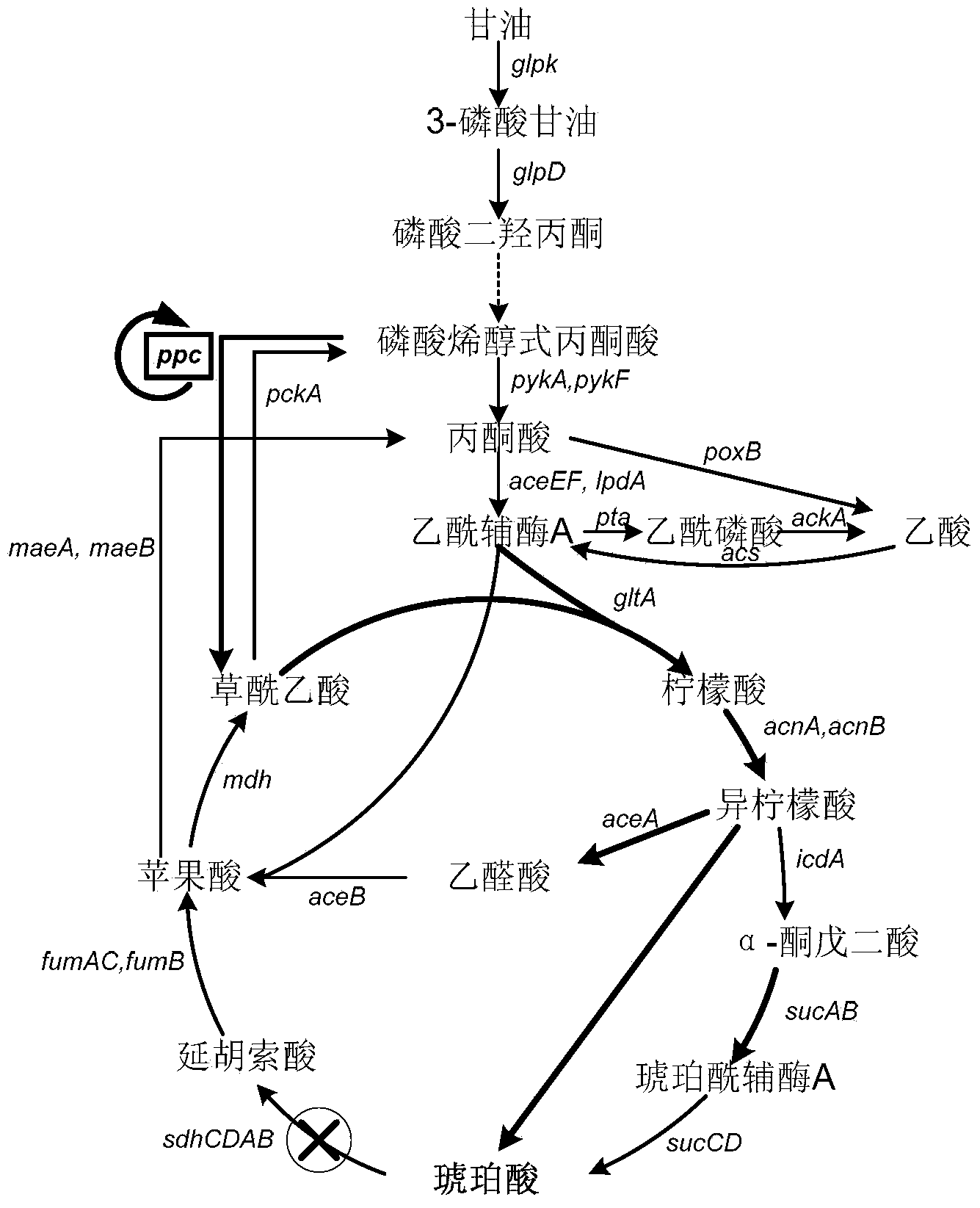
[0029] (1) Knockout the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (purchased from Novagen), and overexpress the key enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle, isocitrate lyase and malate synthase, to obtain The starting strain for evolution;
[0030] The specific operation of knocking out the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene ppc is as follows:
[0031] The chloramphenicol resistance gene was amplified using amplification primers Kan1 / Kan2 and plasmid pKD3 (purchased from CGSC) as a template, and cloned into plasmid pUC18 (purchased from Invitrogen) at the Hind III / Sal I site to obtain plasmid pCM01.
[0032] The upstream homology arm of the ppc gene was amplified using the amplification primers Pout1 / Pout2 and the genome of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) as a template, and cloned into the plasmid pCM01 at the HindⅢ site to obtain the plasmid pCMppcH.
[0033] Using ampl...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Enhancing glyoxylate cycle flux through directed pathway evolution
[0041] In order to improve the flux of glyoxylate cycle and reduce the accumulation of α-ketoglutarate, a byproduct of succinic acid production, the strain BPB was used as a starting point to enhance the flux of glyoxylate cycle by directed pathway evolution.
[0042] The specific operation is as follows: the bacterial strain BPB obtained in Example 1 is cultivated in the M9 basic salt medium with glycerol as the only carbon source, the culture conditions are 37 ° C, 220 rpm, and continuous transfer is carried out in the logarithmic phase of bacterial growth Culture, the time interval of transfer is 12 hours, and when cultured to 100 generations, isolate to the specific growth rate of 0.4h in the M9 basic salt medium with glycerol as the only carbon source -1 One of the strains grown was named BPB18. A single gene knockout was performed on the strain BPB18, and it was found that the glyoxylate cycle b...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Construction of high-yielding strains of succinic acid by genetic engineering
[0047] Taking the evolved strain BPB18 as the starting strain, through genetic engineering methods including knocking out the succinate dehydrogenase gene, overexpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase to construct a system that can use glycerol as Substrate strains that efficiently produce succinic acid. The overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is achieved by replacing their respective promoters with strong trc promoters.
[0048] (1) The specific operation of knocking out the succinate dehydrogenase gene sdhCDAB is as follows: transfer the plasmid pKD46 into the evolved strain BPB18 obtained in Example 2 and make it competent for electroporation; use the primer Sdh1 / Sdh2, using pKD4 as a template, amplified the fragment containing the kanamycin resistance gene and the upstream and downstream homology arms, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com