A protein regulating leaf color at low temperature and its gene and application
A technology of leaf color and protein, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of unclear nuclear-cytoplasmic interaction mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
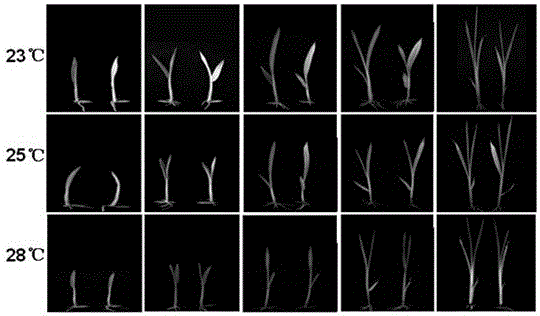
[0036] Example 1: Phenotypic analysis of ywl1 mutants
[0037] a) Rice material
[0038] Rice (Oryza sativa L) mutant ywl1, the original wild-type material is indica variety 93-11.
[0039] b) Determination of chlorophyll content and photosynthetic characteristics
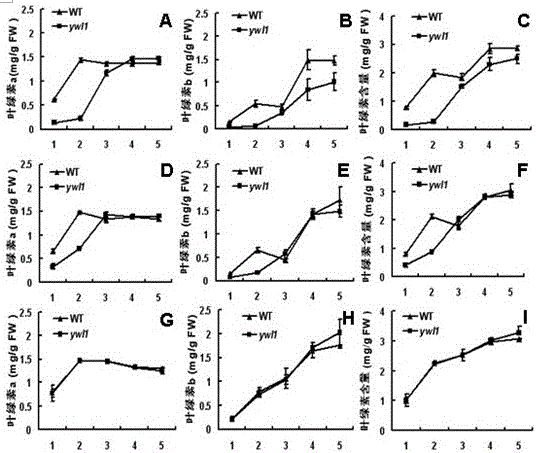
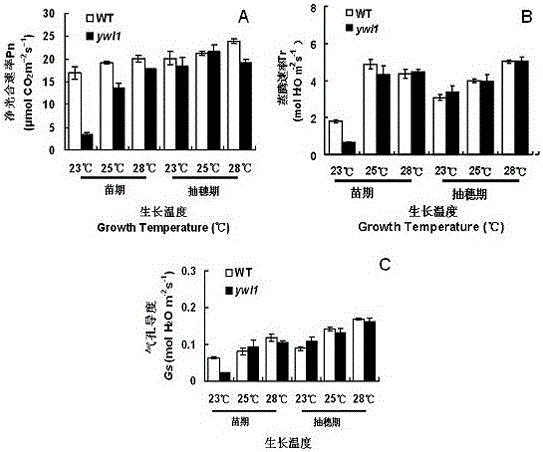
[0040] Select plump mutant and wild-type seeds to soak and accelerate germination, plant the germinated mutant and wild-type 93-11 seeds in pots, and set the daily constant temperature in the artificial climate box to 23°C, 25°C and 28°C respectively , the light length was 12h, the dark treatment was 12h, and the light intensity was 5Lax. Observe and record mutant phenotypes. The chlorophyll content of leaves was measured at five stages (one-leaf stage, two-leaf stage, three-leaf stage, four-leaf stage and five-leaf stage) before and after greening.
[0041] Determination of chlorophyll content: Take 0.1g-0.2g of the sample to be tested and soak it in 10ml of 95% ethanol, and place it in a refrigerator at 4°C t...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: Cloning of YWL1 gene
[0054] a) Genetic analysis and mapping populations
[0055] The positive and negative hybridization was used to confirm that ywl1 was a recessive mutant, and the mutant was selected for hybridization with japonica rice 02428, the F1 generation was self-crossed, and a single plant was harvested to plant the F2 population, and 4391 recessive individuals were selected from the segregated population as the positioning population . At the three-leaf stage, about 1 gram of young leaves were taken from each plant to extract total DNA for gene mapping.
[0056] b) Preliminary and fine mapping of the YWL1 gene
[0057] Genomic DNA for gene localization was extracted from rice leaves using the rapid extraction method of rice micro-DNA. The DNA extraction method was SDS method (Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version Ⅱ. Plant Mol Bio Rep 1:19-21). Take about 100mg of rice leaves, cut them into pieces and ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: Chloroplast localization experiment of YWL1 (SEQ ID NO.3)
[0072] According to the full-length CDS sequence of YWL1 (SEQ ID NO.2), a restriction recognition site containing BamHI was designed, and recombinant primers were designed. The sequence is:
[0073] PGXhF: TTTCTCGAGATAAACCCCCTCCCACTCTCCAC (SEQ ID NO. 14)
[0074] PGSalR: TTTGTCGAGCCAAATTTGATATTGCACAATGGGA (SEQ ID NO. 15)
[0075] Using the wild-type cDNA as a template, the CDS sequence (SEQ ID NO.2) of the YWL1 gene was amplified with PrimeSTAR high-fidelity enzymes. After the amplified product was sequenced and verified to be correct, it was ligated with the PAN580-GFP vector to obtain the fusion expression vector 35S ::YWL1::GFP.
[0076] Extract and construct the fusion expression vector 35S::YWL1::GFP plasmid and the 35S::GFP control plasmid without gene fusion respectively wrapped with gold powder, and use the PDS-1000 / He type gene gun of Bio-rad company under the helium pressure of 1100psi B...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com