Smelting method of high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate
A smelting method and technology of zinc concentrate, which is applied in the field of smelting high-iron polymetallic zinc ore, can solve the problems of affecting efficiency, consuming large coal coke, and high production cost, so as to reduce energy consumption and production cost, and reduce metal loss in the process , the effect of reducing smoke emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
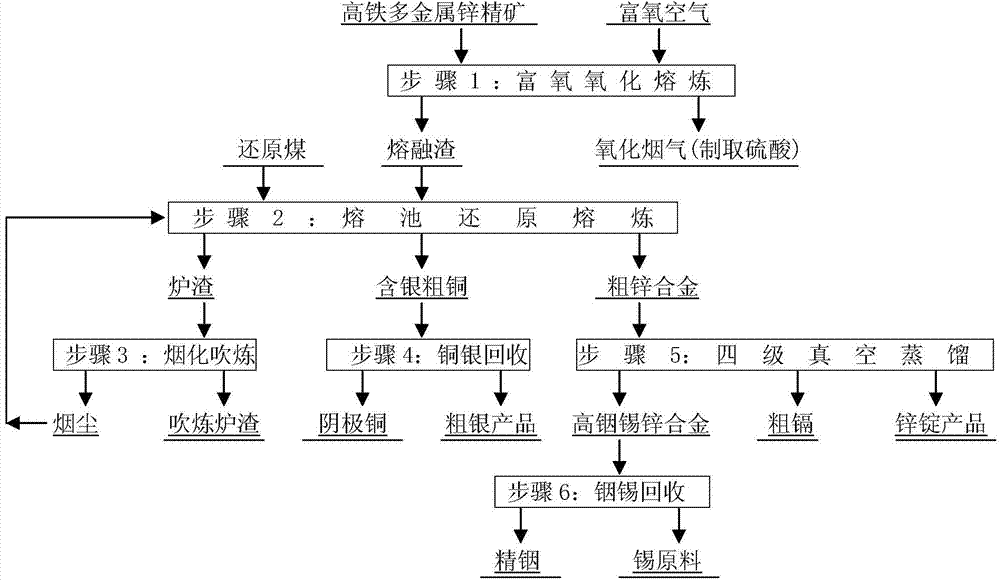
[0024] This embodiment is the first example of a method for smelting high-iron polymetallic zinc concentrate according to the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0025] (1) Oxygen-enriched oxidation smelting: the zinc concentrate containing Fe14%, In0.03%, Cu0.2%, Cd0.2%, Ag0.01%, Sn0.1%, Zn40%, S28% is used as 11t / h speed added to 21m 2 In the side blowing furnace, at the same time with 18000Nm 3 The speed of / h is sent to O 2 Oxygen-enriched air with a concentration of 32% is used for oxygen-enriched oxidation melting at a temperature of 1200°C, and the temperature is 17500Nm 3 / h speed output containing SO 2 13%, O 2 12% oxidized flue gas and molten slag produced at a rate of 10t / h, oxidized flue gas to produce sulfuric acid;
[0026] (2) Melting pool reduction smelting: The molten slag is fed into an Ausmelt furnace with an inner diameter of 4400mm and equipped with 2 lead rain condensers at a rate of 10t / h for molten pool reduction smelting. During ...
no. 2 example
[0032] This embodiment is the second example of a method for smelting high-iron polymetallic zinc concentrate according to the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) Oxygen-enriched oxidation smelting: the zinc concentrate containing Fe17%, In0.07%, Cu0.4%, Cd0.4%, Ag0.015%, Sn0.15%, Zn45%, S30% is mixed with 10t / h speed added to 20m 2 In the bottom blowing furnace, at the same time, with 14000Nm 3 The speed of / h is sent to O 2 Oxygen-enriched air with a concentration of 40% is smelted with oxygen-enriched oxidation at a temperature of 1250 ° C, and the temperature is 13500 Nm 3 / h speed output containing SO 2 17%, O 2 16% oxidized flue gas and molten slag produced at a rate of 9t / h, oxidized flue gas to produce sulfuric acid;
[0034] (2) Reduction smelting in the molten pool: The molten slag is fed into the Isa furnace with an inner diameter of 4500 mm and equipped with two lead rain condensers at a rate of 9 t / h for reduction smelting in the ...
no. 3 example
[0040] This embodiment is the third example of the smelting method of a high-iron polymetallic zinc concentrate according to the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) Oxygen-enriched oxidation smelting: the zinc concentrate containing Fe20%, In0.10%, Cu0.6%, Cd0.6%, Ag0.02%, Sn0.2%, Zn50%, S32% is mixed with 6.25% The speed of t / h is fed into the ISA furnace with an inner diameter of 4500mm, and at the same time, it is fed at a speed of 8000Nm 3 The speed of / h is sent to O 2 Oxygen-enriched air with a concentration of 48% is smelted with oxygen-enriched oxidation at a temperature of 1300 ° C, and the temperature is 7800 Nm 3 / h speed output containing SO 2 19%, O 2 18% oxidized flue gas and molten slag produced at a rate of 5.5t / h, oxidized flue gas to produce sulfuric acid;
[0042] (2) Reduction smelting in molten pool: Molten slag is added to the 15m m tank with lead rain condenser at a rate of 5.5t / h 2 Bottom-blown furnaces are used for molt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com