Preparation method of electrolyte used for lithium manganate power battery at high temperature
A power battery and electrolyte technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of high-temperature electrolyte for lithium manganate power batteries, can solve the problems of poor cycle performance of lithium manganate batteries, loss of activity of the positive electrode, and low manganese dissolution, etc., to improve the high-temperature cycle Performance, improved safety, reduced dissolution effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0018] The preparation method of this specific embodiment is as follows: at room temperature, weigh film-forming additives, non-aqueous organic solvents, high-temperature additives, anti-overfilling additives, flame-retardant additives, stabilizers, and lithium salts in a glove box filled with argon; Pour the above-mentioned various raw materials into a beaker and place it on a magnetic stirrer, control the stirring rate until the lithium salt is completely dissolved, and mix various solvents evenly to obtain a non-aqueous electrolyte.
[0019] In this specific embodiment, by adding a film-forming additive with excellent performance, the performance of the solid phase interface film (SEI) is improved, and at the same time, a film can be formed on the surface of the positive electrode, which greatly reduces the dissolution of the material and is conducive to improving the high-temperature cycle performance of the battery; adding The anti-overcharge additive can prevent the batte...
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: At room temperature, weigh 25.05 g of ethylene carbonate (EC), 8.35 g of ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC), 41.75 g of diethyl carbonate (DEC), and propylene carbonate ( PC) 8.35g, ethylene carbonate (VEC) 0.5g, methylene disulfonate (MMDS) 1.0g, biphenyl 1.0g, dimethyl methyl phosphate (DMMP) 2.0g, hexamethyl disulfonate Silamine 0.001g, lithium bisoxalate borate (LiBOB) 2g and lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6 ) 10g; then pour the above-mentioned various raw materials into a beaker and place it on a magnetic stirrer, control the stirring rate until the lithium salt is completely dissolved, and mix various solvents evenly to obtain 100g of non-aqueous electrolyte.
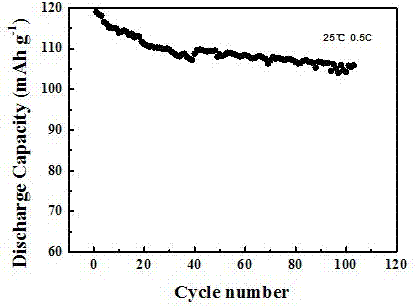
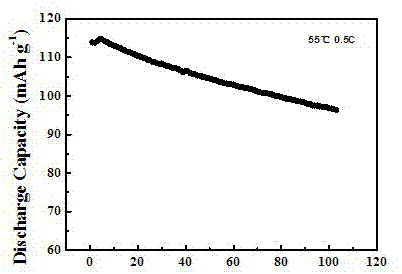
[0022] Using spinel lithium manganese oxide as the positive electrode, metal lithium sheet as the negative electrode, Celgard2300 microporous polypropylene membrane as the diaphragm, and the prepared sample as the electrolyte, it was assembled in a glove box with a relative humidity of less than 5% ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2: At room temperature, weigh 25.05 g of ethylene carbonate (EC), 8.35 g of dimethyl carbonate (DMC), 41.75 g of diethyl carbonate (DEC), and propylene carbonate ( PC) 8.35g, ethylene carbonate (VEC) 0.5g, methylene disulfonate (MMDS) 1.0g, biphenyl 1.0g, dimethyl methyl phosphate (DMMP) 2.0g, hexamethyl disulfonate Silamine 0.001g, lithium bisoxalate borate (LiBOB) 2g and lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6) 10g; then pour the above-mentioned various raw materials into a beaker and place it on a magnetic stirrer, control the stirring rate until the lithium salt is completely dissolved, and mix various solvents evenly to obtain 100g of non-aqueous electrolyte.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com