Chemical microwave treatment method of industrial methyldiethanolamine wastewater
A technology of methyldiethanolamine and microwave chemistry, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, natural water treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult degradation, ineffective treatment of wastewater, high COD of wastewater, and promote Degradation, accelerating the speed and efficiency of flocculation and sedimentation, and improving the removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
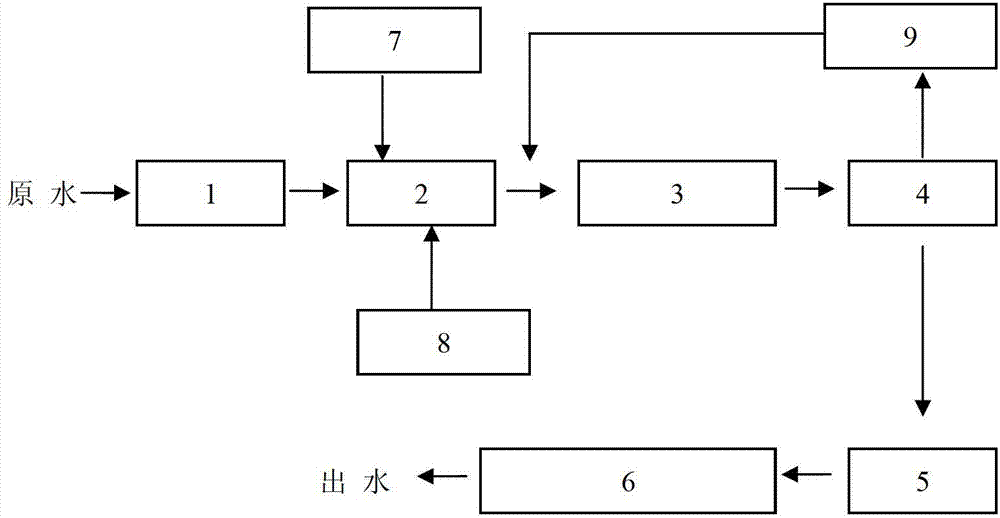
[0060] Take 2000ml of raw water, measure its pH=9, COD Cr =1080mg / L, the water quality is slightly muddy.
[0061] Add 2000ml of raw water into the water tank, add 2ml of oxidant sodium hypochlorite, turn on the mixer, stir evenly for 1 minute, and the pH is reduced to 7 after measurement.
[0062] Take 1ml of the prepared mass concentration of 5% diatomite and calcium oxide sensitizer suspension, wherein the mass concentration of diatomite and calcium oxide are both 2.5%, add it to the waste water, turn on the mixer, and stir evenly for 30 seconds , the pH rose to 11 by measurement.
[0063] Take 1 ml of the prepared polyferric sulfate coagulant solution, the concentration of which is 5%, add the mixed solution, turn on the mixer, stir evenly for 30 seconds, and the pH is reduced to 8 after measurement.
[0064] Turn on the small liquid lift pump, start the microwave equipment at the same time, and introduce the mixed liquid into the microwave processing equipment.
[0065...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Dilute the wastewater of MDEA to be treated to a COD of about 1000 mg / L.
[0070] Add sodium hypochlorite solution with a concentration of 10% into the aeration box at a volume ratio of 1:1000, and aerate the box at the same time to maintain a stable air-dissolving ratio and aeration time.
[0071] Introduce the waste water into the stirring box, add 5% diatomite and calcium oxide mixed sensitizer solution to the waste water, and its volume is 1 / 2000 of the volume of the waste water. The volume of the coagulant solution is 1 / 2000 of the volume of the waste water. Continue to stir and mix until it is uniform. Because the solution of the sensitizer itself is alkaline and the solution of the coagulant itself is acidic, in this way, the MDEA to be entered into the microwave reactor is The pH of the wastewater was controlled to neutral.
[0072] The mixed wastewater enters the microwave sensitization reactor with a microwave power of 1.6kW, and the wastewater stays here for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com