Method for preparing solid oxide fuel cell composite cathode through low-temperature sintering
A solid oxide, composite cathode technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of particle growth, uneven mixing, specific surface and three-phase interface loss, etc., to achieve large specific surface area and good contact. , the effect of oxygen reduction active site increase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
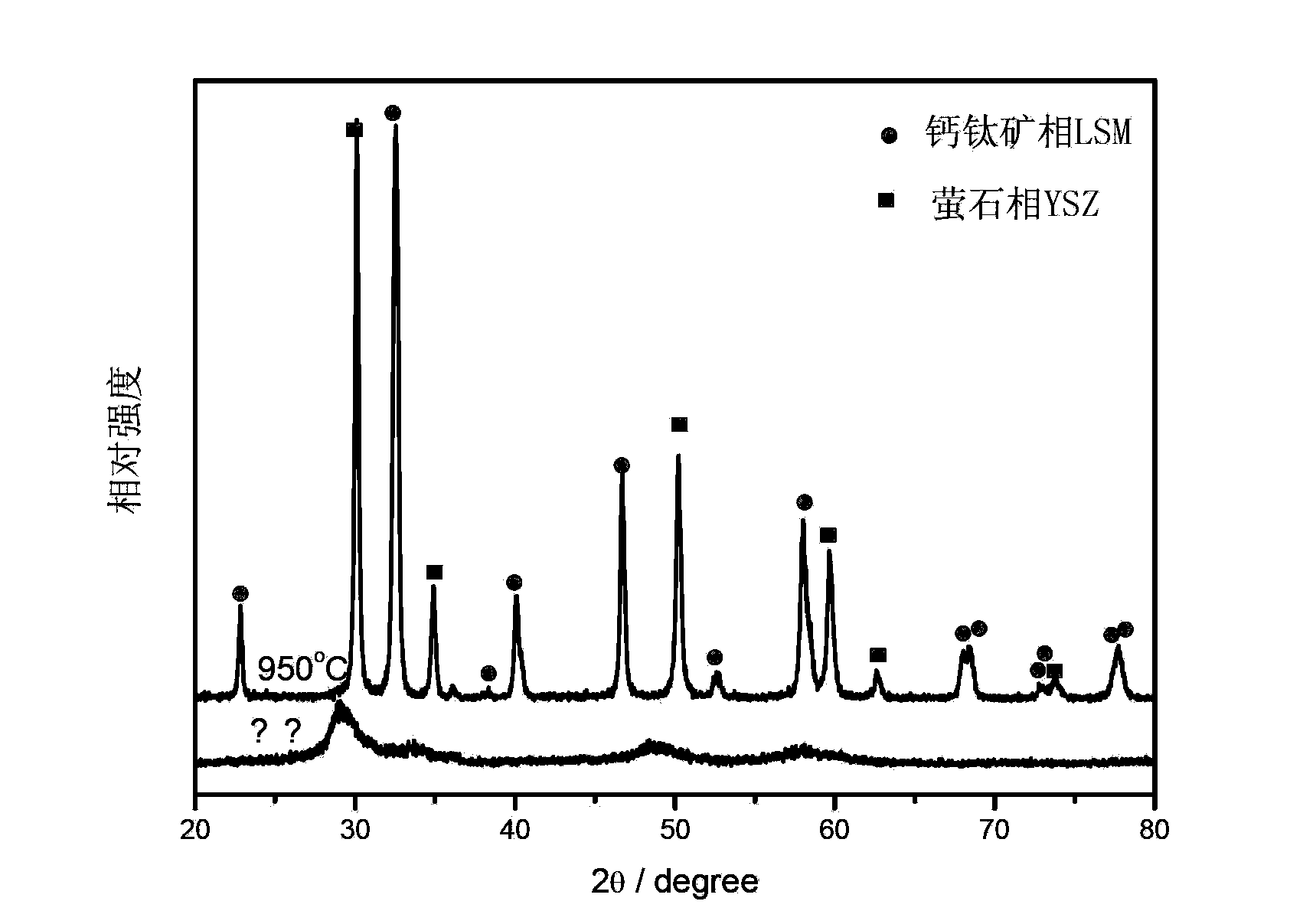
[0026] Synthesized by triammonium citrate method (La 0.8 Sr 0.2 ) 0.9 MnO 3±d –YSZ=60:40wt%, composite cathode material, where (La 0.8 Sr 0.2 ) 0.9 MnO 3+d is 0.02mol, weigh 6.2361g La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (analytically pure), 0.7657g Sr(NO 3 ) 2 (analytically pure), 7.158g Mn(NO 3 ) 2 (analytical pure 50wt% solution), 8.7686gZr(NO 3 ) 4 ·5H 2 O (analytically pure), 1.3560g Y (NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (analytical pure), completely dissolved in 100ml deionized water, then add 19.0406g triammonium citrate (analytical pure) according to the ratio of triammonium citrate: total molar number of metal ions=1:1.2 (molar ratio), and use nitric acid Adjust the pH value of the mixed solution to 1 to completely dissolve it, then heat it to cause a reaction in the solution system and evaporate water, the solution gradually becomes viscous and becomes a transparent sol, then move it to a heating furnace for heating to cause self-propagating combustion. Collect the primary powder obta...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Synthesized together by the glycine method (La 0.8 Sr 0.2 ) 0.9 MnO 3±d –YSZ=60:40wt% composite material, where (La 0.8 Sr 0.2 ) 0.9 MnO 3+d is 0.01mol, weigh 3.1181g La(NO3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (analytically pure), 0.3828gSr(NO 3 ) 2 (analytically pure), 3.579g Mn(NO 3 ) 2 (analytical pure 50wt% solution), 4.3804gZr(NO 3 ) 4 ·5H 2 O (analytically pure), 0.6797g Y (NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (analytical pure), completely dissolved in 100ml deionized water, add 3.8267g glycine (analytical pure) according to the ratio of glycine:total moles of metal ions=1:2.31 (molar ratio), heat complexation and evaporate water after complete dissolution After the solution becomes viscous gradually, it is moved to a heating furnace for heating, and it is burned, and the primary powder obtained is collected, and part of the primary powder is taken and roasted using the same heating program as the electrode (sintering program in the same embodiment 3). SEM photos as figure 2 with image...
Embodiment 3
[0030] As prepared in Example 1 (La 0.8 Sr 0.2 ) 0.9 MnO 3±d – YSZ (mass ratio) = 55:45%, 60:40%, 65:35%, 70:30% primary powder, grind evenly, add 711 glue to make cathode slurry, coat 0.0100g on the anode electrolyte Combined, the temperature is programmed to sinter.
[0031] The sintering program is: from room temperature to 400°C, heat up at 1°C / min; when it is greater than 400°C~800°C, heat up at 5°C / min; when it is greater than 800~950°C, heat up at 2°C / min, Hold at 950°C for 180 minutes; drop to 400°C at 2°C / min; then cool with the furnace.
[0032] Battery evaluations were performed on self-assembled devices. The I-V curve was measured after polarization at 800°C for 16h. The result is as Figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com