Endophytic fungus strain having high paclitaxel yield and method for producing paclitaxel by endophytic fungus strain
A technology of endophytic fungi and paclitaxel, which is applied in the field of bioengineering and biopharmaceuticals to achieve the effects of low production cost, short fermentation cycle and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Isolation of taxol-producing endophytic fungi
[0029] In this embodiment, the taxol-producing endophytic fungus J11 strain is isolated from the stem of Taxus chinensis var.mairei. The paclitaxel-producing J11 strain of the present embodiment is isolated and obtained according to the following steps: 1) Rinse the stems of Taxus chinensis with sterile water (to remove impurities such as dust on the surface of the bark), then soak them in 75% ethanol for 3 to 10 minutes, and then Rinse with sterile water (wash away ethanol), and then cut into small pieces with an area of 0.5cm × 0.5cm with sterile scissors; ~5 samples), put them in a 25-28°C incubator and cultivate them until colonies grow obviously around the small pieces; 3) Pick colonies with better growth and inoculate them on PDA solid medium, and cultivate them at a constant temperature of 28°C , purification, preservation.
[0030]The above PDA (potato dextrose agar) medium was prepared according to ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: the species identification of microbial bacterial strain J11
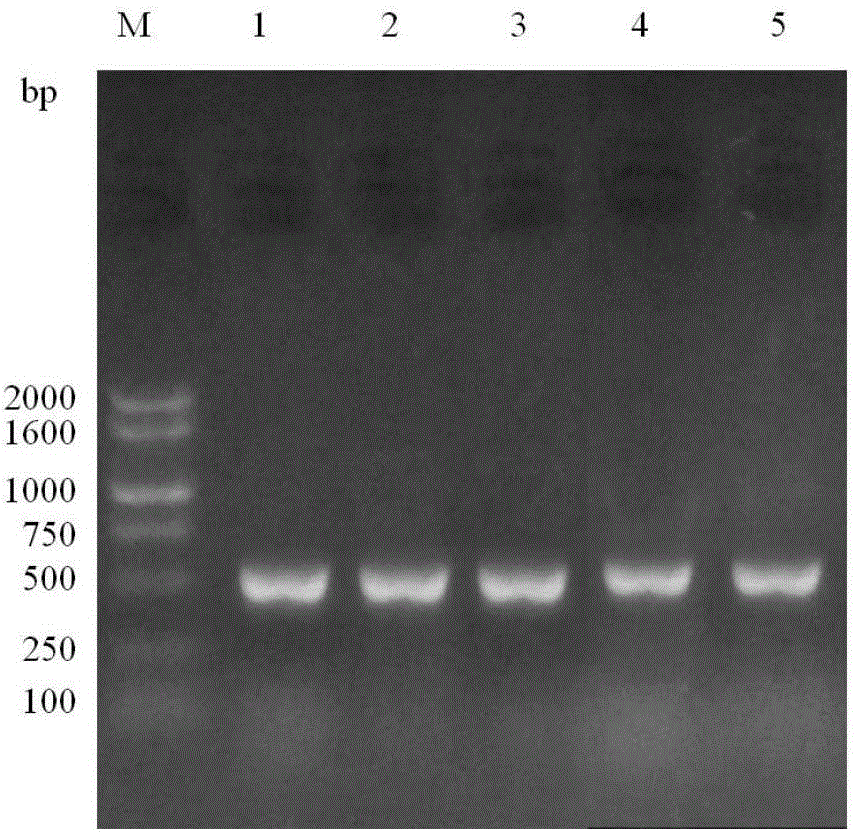
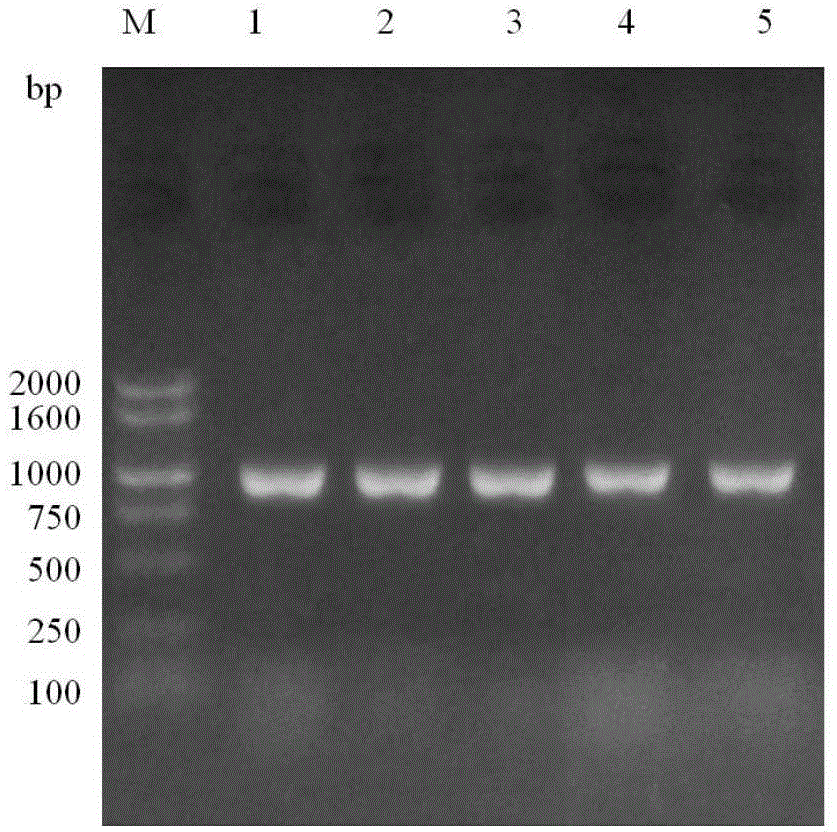
[0033] For the identification of paclitaxel-producing endophytic fungi, since the identification of fungal microorganisms needs to be based on sexual spores as the main basis for judgment, it is difficult in practice, especially for endophytic fungi that are difficult to produce sexual spores. It seems untenable. With the continuous development and improvement of modern molecular biology and its experimental methods, DNA barcodes are also used internationally as the main means and methods for identifying fungi. Ribosomal ITS (internal transcribed spacer) sequence and ribosomal LSU (large subunit rRNA gene) sequence are used as molecular tags (barcodes), which are summarized by scientists after a long period of extensive experiments. Compared with other molecular tags, these two molecular tags are more reliable, and have universal significance for the molecular identification of fungi and endop...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: Identify whether the J11 strain produces paclitaxel
[0044] Thin layer chromatography (TCL) uses Rf value, and high performance liquid chromatography (HPCL) uses retention time (retention time) as a method to identify paclitaxel-producing endophytic fungi, but due to the large error range , has gradually been eliminated, and is only used as a preliminary basis for judging paclitaxel-producing endophytic fungi, and cannot be used as a final identification method. Although the nuclear magnetic resonance (nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, NMR) method has reliable identification results and can identify the chemical results of paclitaxel, it involves the separation and purification of high-purity paclitaxel from the fermentation broth, such as the purification of high-purity paclitaxel by preparative liquid chromatography. , the operating procedures are complex and require high experimental conditions. High resolution mass spectrometry (high resolutio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com