Reconstruction method of cellulosome gene and obtained cellulase
A cellulase and cellulosome technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low cell density, waste of biological energy, harsh culture conditions, etc., achieve high activity, high activity and stability, and facilitate genetic engineering. production effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Target gene amplification from Clostridium thermocellum genomic DNA
[0034] Primer design: According to the gene sequence of Clostridium thermocellum (ATCC 27405) cellulase (CelD) reported in NCBI, see SEQ ID NO.1, the signal peptide sequence of the gene was removed, and two primer sequences (5' end containing Pst I and Xho I restriction sites respectively):
[0035] celD-1: 5' AAAACTGCAGGCAAAAATAACGGAGAATTATC 3'
[0036] celD-2: 5' CCGCTCGAGTTATATTGGTAATTTCTCGATTAC 3'
[0037] Genome PCR amplification conditions: Cultivate Clostridium thermocellum cells, extract genomic DNA as a template. Add 2 μL (20 ng) template, 2 μL 10 μM primer, 4 μL 2.5 μM dNTP, 10 μL 5×Prime STAR HS DNA polymerase buffer, 31.5 μL ultrapure water and 50 μL PCR reaction system. 0.5 μL of Prime STAR HS DNA Polymerase. According to the temperature cycle (denaturation at 98°C for 10 s, annealing at 60°C for 15 s, extension at 72°C for 2.5 min), amplify for 30 cycles, and extend at 72°...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: Construction of the expression plasmid of monomeric enzyme gene in Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome
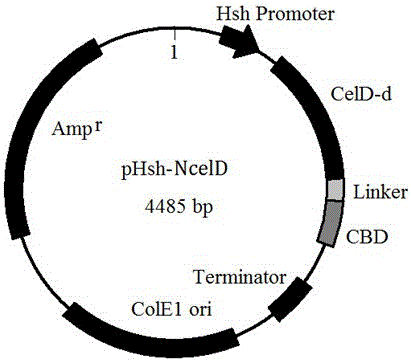
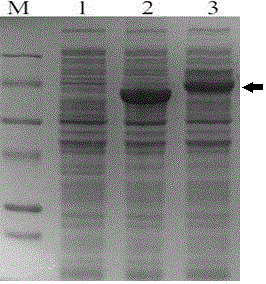
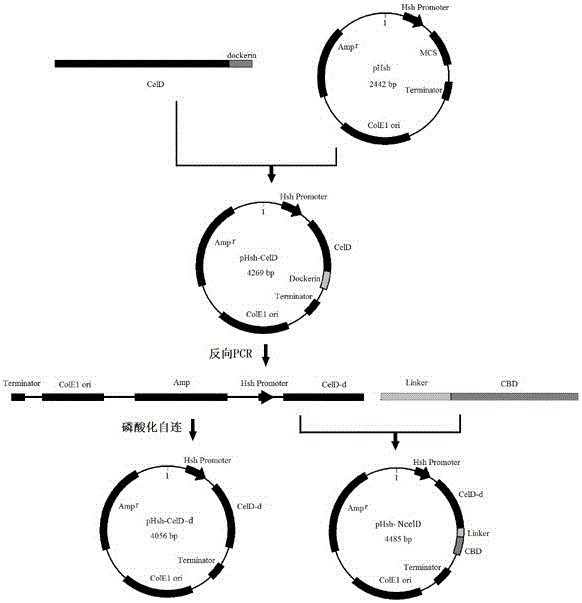
[0039] The above PCR product was recovered by tapping rubber, subjected to Pst I and Xho I double enzyme digestion, and cloned into the prokaryotic expression vector pHsh plasmid. Transform into E. coli DH10B, and culture transformants in LB medium containing ampicillin (100 μg / mL). Plasmids were extracted from transformants, digested with Pst I, and the inserted gene was verified and sequenced. The results showed that the length of the inserted gene was 1827bp, the code contained 609 amino acid residues, and the sequence was consistent with the celD sequence in the database. The expression plasmid was named pHsh-CelD.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Molecular reconstruction of gene celD
[0041] Primer design: According to the anchor domain information in the peptide chain of the CelD protein in the NCBI website database, two reverse PCR primers were designed and synthesized, using pHsh-CelD as a template, and PCR amplified to obtain the anchor domain coding sequence celD- The plasmid fragment of d (SEQ ID NO.2) forms a new plasmid pHsh-celD-d after concatenation; according to the NCBI data, the cbd gene cbd (SEQ ID NO.3 ), at the same time, design primers to link celD-d and cbd together to obtain the gene sequence celD-d+cbd (SEQ ID NO.4), and finally design and synthesize a pair of PCR primers to amplify Lcbd with a linking fragment ( SEQ ID NO.5), the new enzyme gene celD-d+Lcbd is formed after linking celD-d and Lcbd, which we renamed ncelD (SEQ ID NO.6).
[0042] dockerin-up: TAACTCGAGCACCACCACC
[0043] dockerin-dn: TTGAGGAGAATTATAGTTGACA
[0044] cbd-1: AACGTTGGCAATGCAACACC
[0045] cbd-2: GCT...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com