Preparation method for flue gas mercury-removing active carbon
A technology of activated carbon and granular activated carbon, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of low saturation adsorption capacity of mercury, easy secondary shedding of mercury, etc. Mercury efficient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
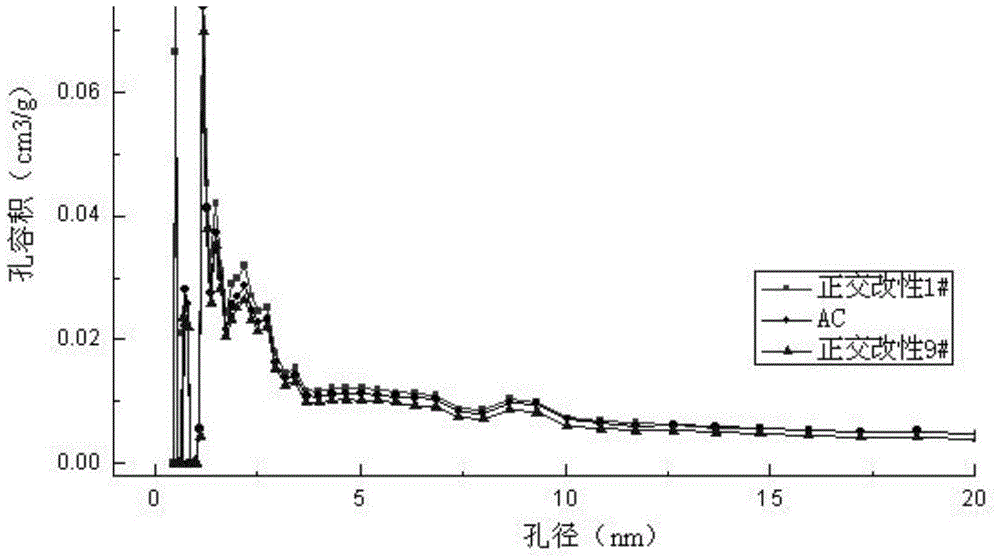
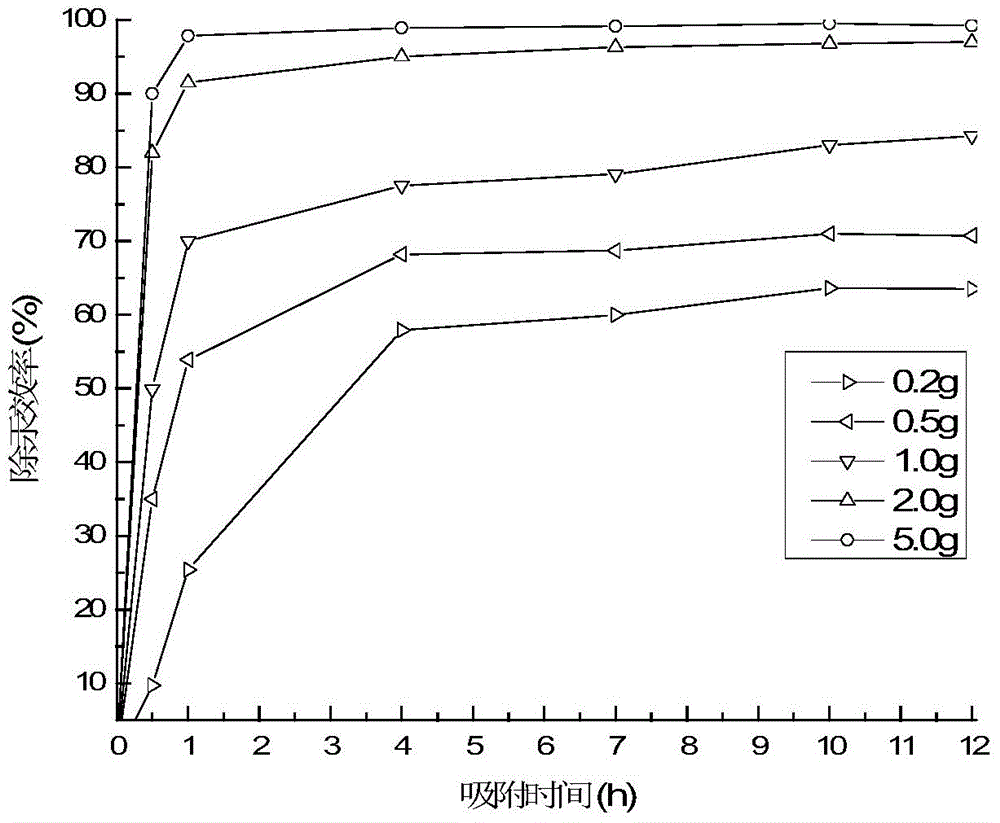
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Removal of chemical groups on the surface of the raw material: the coconut shell-based granular activated carbon raw material was washed with 10 wt.% NaOH solution and dried at 150 °C.
[0035] (2) Impregnation of halide salts: immerse 30 g of activated carbon raw material in a potassium chloride solution with a mass concentration of 15 wt.%, stir for 4 hours, and filter and dry.
[0036] (3) Halogen loading: Put the activated carbon loaded with potassium chloride into the U-shaped tube to form a filling layer, and input 300mL / min air with chlorine gas from the top of the filling layer, the chlorine gas concentration is 0.13mg / L, and maintain it at room temperature for 10h. Chlorine gas molecules are evenly loaded into the micropores of activated carbon, and chlorine gas combines with potassium chloride to form thermally stable trichloride KCl 3 .
[0037] (4) The chlorine-loaded activated carbon was heated at 110°C for 1 hour to remove volatile halogens, and the f...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Removal of surface chemical groups from raw materials: The coconut shell-based granular activated carbon raw material was washed with 30 wt.% NaOH solution and dried at 150 °C.
[0041] (2) Impregnation of halide salts: immerse 30 g of activated carbon raw material in potassium bromide solution with a mass concentration of 20 wt.%, stir for 12 hours, and filter and dry.
[0042] (3) Halogen loading: put the activated carbon loaded with potassium bromide in the U-shaped tube to form a filling layer, and input bromine from the top of the filling layer with 300mL / min air, the bromine concentration is 0.21mg / L, and maintain at room temperature After 10 hours, bromine molecules are evenly loaded into the micropores of activated carbon, and bromine combines with potassium bromide to form a thermally stable tribromide KBr 3 .
[0043] (4) The bromine-loaded activated carbon was heated at 110°C for 2 hours to remove volatile bromine, and a flue gas mercury-removing activat...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Removal of surface chemical groups from raw materials: The coconut shell-based granular activated carbon raw material was washed with 30 wt.% NaOH solution and dried at 150 °C.
[0047] (2) Impregnation of halide salts: 50 g of activated carbon raw materials were impregnated in a potassium iodide solution with a mass concentration of 50 wt.%, stirred for 12 hours, and filtered and dried.
[0048] (3) Halogen loading: Put the activated carbon loaded with potassium iodide in the U-shaped tube to form a filling layer, and input iodine from the top of the filling layer with 300mL / min air, the iodine concentration is 0.23mg / L, maintain at room temperature for 10h, bromine Molecules are evenly loaded into the micropores of activated carbon, and bromine combines with potassium bromide to form thermally stable triiodide KI 3 .
[0049] (4) The iodine-loaded activated carbon was heated at 100°C for 1 hour to remove volatile iodine, and a flue gas mercury-removing activated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com