A method for in-situ enrichment of nitrifying bacteria coupled with sludge hydrolysis to enhance nitrogen and phosphorus removal
An in-situ enrichment, denitrification and phosphorus removal technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc. Insufficient sources and other problems to achieve the effect of reducing TN load and reducing demand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The original design treatment capacity of a certain sewage plant is 60,000 m3 / d, and the designed effluent water quality standard is GB18918-2002 Class I B. After four years of operation, the influent water quality of the plant has exceeded the original design standard, and it is planned to implement Class I A standard for the plant According to the actual operation conditions, the plant is mainly due to insufficient nitrification capacity, and the effluent NH 3 -N, TN, TP cannot reach the standard stably. However, the actual situation at the site is that the plant is located in the old city, and the expansion site is limited, so it is not allowed to expand the new biological pool capacity. For this reason, adopt the scheme of the present invention to carry out process design.
[0044] The specific plan is: in the case of keeping the original process hydraulic process unchanged, keep the original biological pool capacity unchanged, use a biological pool abandoned in th...
Embodiment 2
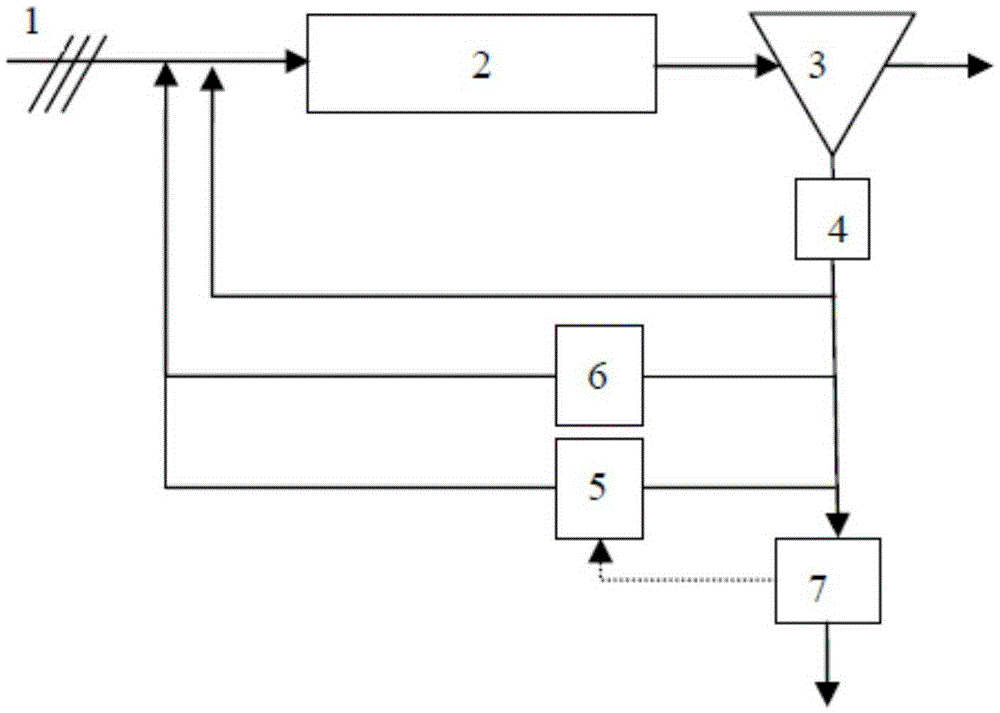
[0047] The concentration standard of influent pollutants remains unchanged and the hydraulic load is increased. Example: The original design treatment capacity of a sewage plant is 100,000 m3 / d. After two years of operation, the influent water volume has far exceeded the treatment capacity, but the influent concentration meets the design requirements. For this reason, it is planned to carry out expansion and upgrading, and the processing capacity is required to reach 130,000 m 3 / d, while meeting the original design effluent standards, but the sewage plant faces factors such as limited expansion sites, and cannot build a new bio-pool capacity. For this reason, adopt the scheme of the present invention to carry out process design, adopt flow chart to see figure 1 , the specific plan is:
[0048] In the case of keeping the original process flow unchanged, according to the process calculation, the design parameters are as follows: 25% of the pool volume at the front end of the o...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The hydraulic load remains unchanged and the concentration of pollutants increases. Example: The original design treatment capacity of a sewage plant is 100,000 m3 / d, but the current influent water quality of the plant has far exceeded the original design standard by 20-30%, and the effluent cannot meet the standard stably. , it is planned to carry out expansion and standard upgrading, and it is required that the effluent can reach the standard stably under the condition that the treated water volume remains unchanged. However, the sewage plant is facing factors such as limited expansion site and cannot build a new biological pool capacity.
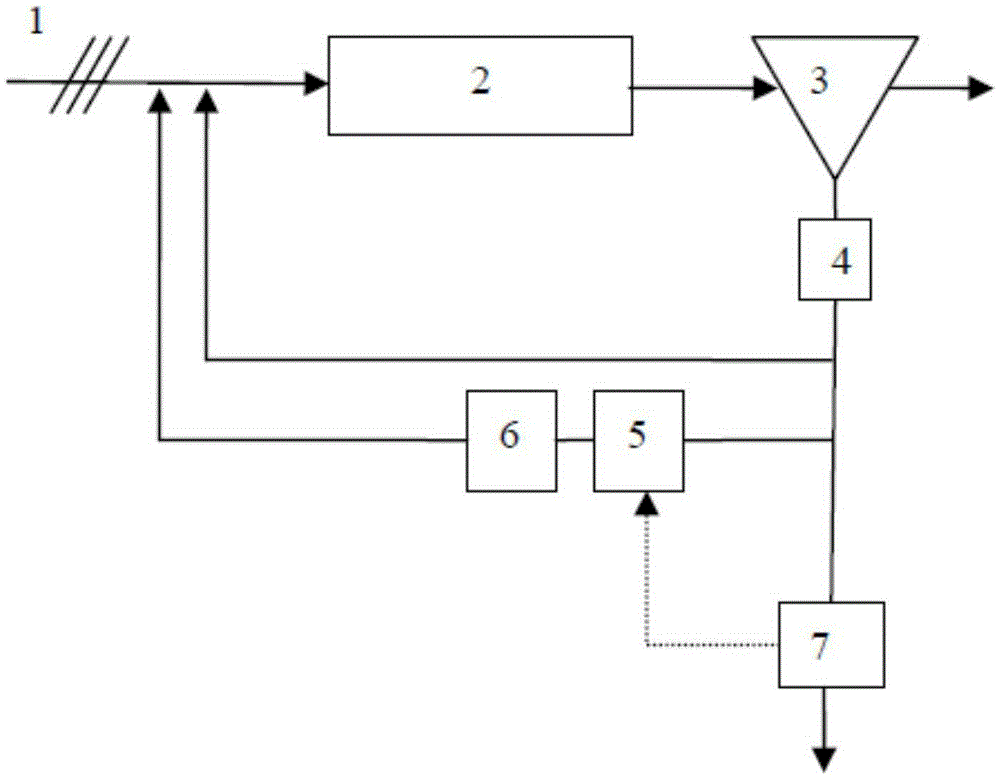
[0052] For this reason, adopt the scheme of the present invention to carry out process design, adopt flow chart to see figure 2 , the specific plan is: in the case of keeping the original process hydraulic flow unchanged, keep the volume of the original biological pool unchanged, transform the original biological pool, and separate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com