A kind of in vivo traceable and controllable degradable nanocomposite material and its preparation method
A technology of nanocomposite materials and composite materials, applied in the field of in vivo traceable and controllable degradable nanocomposite materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of degradation, long cycle, and inability to guarantee materials, so as to accelerate the degradation rate and realize controllable Degradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] The present invention also provides a method for preparing a traceable and controllable degradable nanocomposite in vivo, comprising: combining biodegradable materials and GdPO 4 ·H 2 O mixed to obtain a composite material.
[0032] According to the present invention, the present invention combines biodegradable material and GdPO 4 ·H 2 O mixed to obtain a composite material, according to the present invention, the biodegradable material and the GdPO 4 ·H 2 The mass ratio of O is preferably 1000 mg: (0.005-60) mg, more preferably 1000 mg: (2.5-35) mg, most preferably 1000 mg: (8-30) mg. The biodegradable material is preferably polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, polycaprolactone, polyhydroxybutyrate, polyanhydride or polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, polycaprolactone, polyhydroxybutyrate and polyanhydride. Two or more copolymers, more preferably polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, polycaprolactone, polyhydroxybutyrate or polyanhydride; the GdPO 4 ·H 2 O is pref...
Embodiment 1
[0041] Preparation of GdPO 4 ·H 2 O and GdPO 4 nanobeam
[0042] 1mLGd(NO 3 ) 3 (1mM) aqueous solution is added to 25mL ethylene glycol solution, weigh 2.0g PVP and add it to the above solution, weigh NH 4 h 2 PO 4 Dissolve 0.25g and 0.5g of urea in 5mL of aqueous solution, then add to the above solution, weigh 3.0g of glycine and add to the above solution, stir for 30min; The precipitate was washed by centrifugation and dried to obtain GdPO 4 ·H 2 O nanobeams.
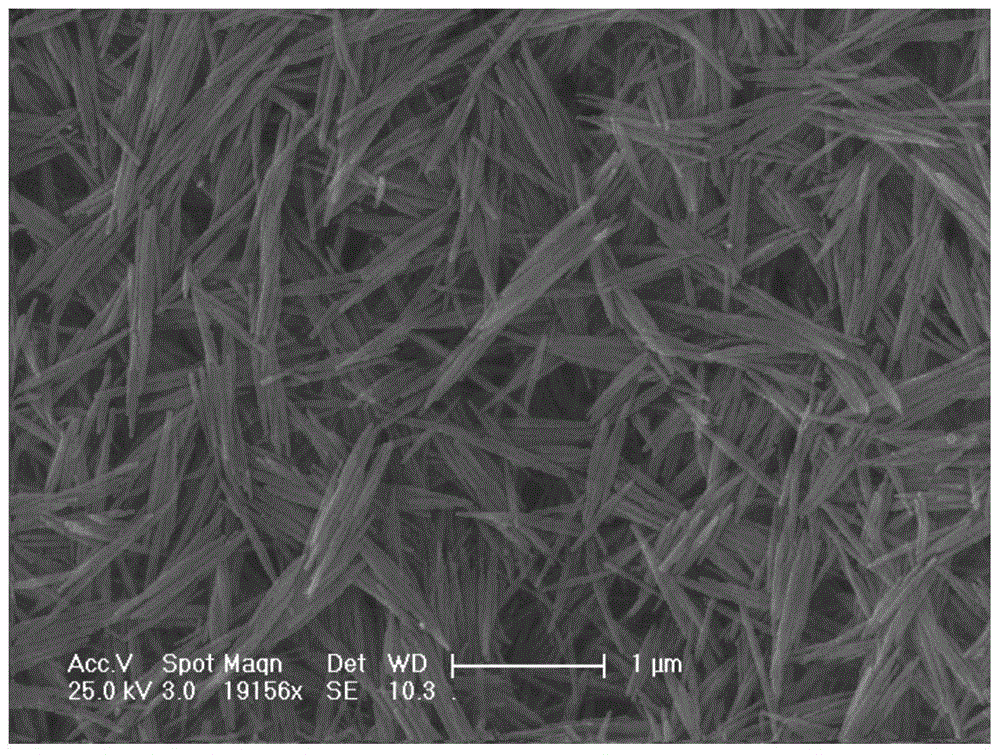
[0043] GdPO prepared by embodiment 1 by scanning electron microscope 4 ·H 2 O for detection, see the results figure 1 , figure 1 GdPO provided for the embodiment of the present invention 4 ·H 2 SEM image of O.
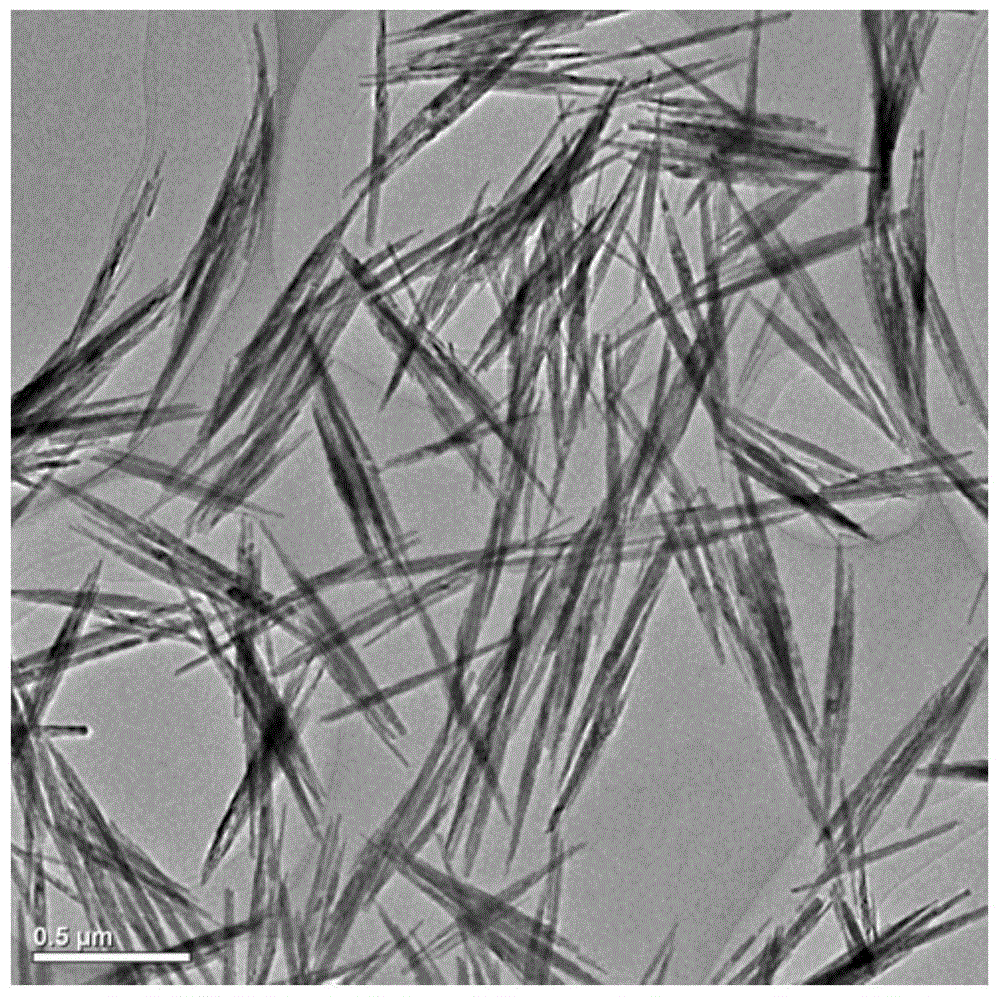
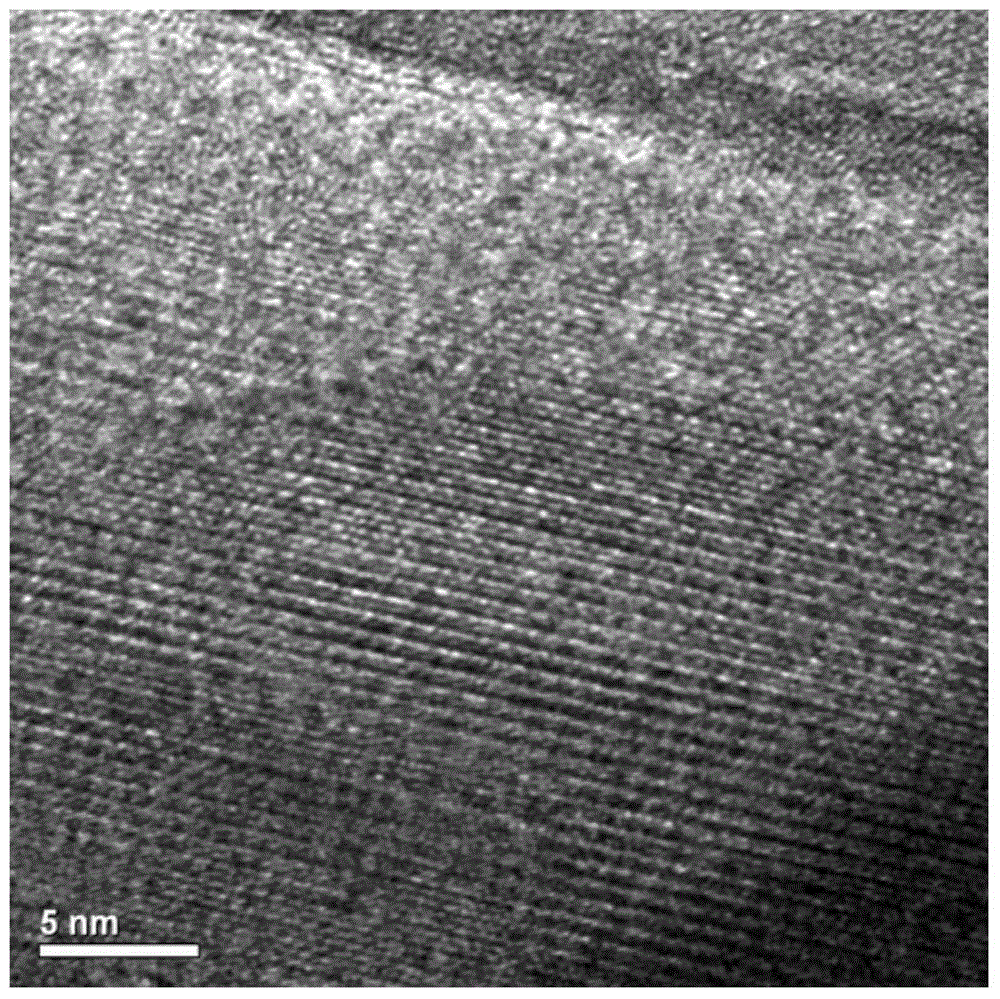
[0044] GdPO prepared by embodiment 1 by transmission electron microscope 4 ·H 2 O for detection, see the results Figure 2-4 , figure 2 GdPO provided for the embodiment of the present invention 4 ·H 2 O beam structure diagram obtained by transmission electron microscopy, image 3 GdPO ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The GdPO prepared by 3mg embodiment 1 4 ·H 2 O was added to 6mL NMP solvent, and ultrasonically mixed; then HA 60mg was added, and ultrasonically mixed; then 1.2g of PLGA was weighed and added to the above solution, and stirred overnight until PLGA was evenly dissolved; , or pour the mixed solution into a centrifuge tube to solidify, then put it into an aqueous solution, and obtain a membrane composite material or a scaffold composite material after the solvent replacement is complete.
[0047] The film composite material prepared in embodiment 2 is carried out magnetocaloric degradation experiment, and its result sees Figure 5 , Figure 5 The weight loss rate of the composite material provided for the embodiment of the present invention under the condition of adding a magnetic field and not adding a magnetic field, it can be seen from the figure that the degradation rate of the composite material is different under the condition of adding a magnetic field and not ad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com