Molecular design and application of a readily degradable plant cell wall
A technology for plant stems and plant expression vectors, which is applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, applications, plant products, etc., can solve problems such as the synthesis of 2-phenylethanol, and achieve great research value and application potential, and improve glucose efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The construction of the plant expression vector of embodiment 1 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway:
[0026] 1. 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway gene: petunia phenylacetaldehyde synthase gene PAAS and tomato phenylacetaldehyde reductase gene LePAR1 clone
[0027] In order to construct the 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway in plants, the petunia phenylacetaldehyde synthase gene was selected according to the report on the 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway in plants PAAS (DQ243784) and tomato phenylacetaldehyde reductase gene LePAR1 (NM_001247894) Construction of 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway. The petunia (Petunia hybrida) blooming petals and the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fully mature fruit were taken, and the total RNA was extracted by CTAB method, and the full-length cDNA sequences of the two were obtained by searching GenBank, and gene-specific primers were designed respectively, and RT-PCR technology amplification PAAS and LePAR1 The full-length cDN...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Construction of 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway to reduce the application of plant lignin synthesis:
[0035] 1. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis
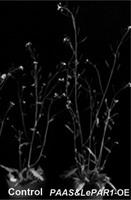
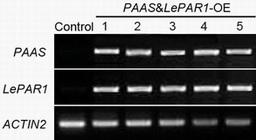
[0036]The plant expression vector was transformed into Agrobacterium, and positive clones were picked and cultured overnight until OD=2.0. Centrifuge 300ml of the overnight cultured bacterial solution, collect the bacteria by centrifugation at room temperature, and resuspend in 150ml of transformation buffer (transformation buffer: 0.5% sucrose solution contains 0.02% Silwet). Put the inflorescences of Arabidopsis thaliana upside down and immerse them in the bacterial solution. Try to immerse all the inflorescences in the bacterial solution for 5-6 times. Then put the Arabidopsis thaliana upside down in the water receiving tray, cover it with plastic wrap, and place it in the culture room. (22°C) overnight, and then cultured normally. After one week of transformation, it can be retransformed...
Embodiment 3
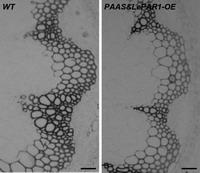
[0050] Example 3 Construction of 2-phenylethanol synthesis pathway to improve the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification of plant cell walls
[0051] Efficiency analysis of cell wall extracts from Arabidopsis thaliana stems hydrolyzed by cellulase. The specific steps are:
[0052] (1) The cell wall extracts were divided into two treatment groups. The first group was directly treated with cellulase (Cellulose) and glucosidase (β-glucosidase), and 20 mg of cell wall extracts from control and transgenic plants were used for enzymatic hydrolysis treatment 24 Hours, take 500ul of the enzymatic hydrolyzate at 1, 3, 6, and 24 hours respectively, and measure the glucose content in the hydrolyzate;
[0053] (2) The second group took the cell wall extract and treated it with hot water (121°C) for 1 hour, then treated it with cellulase and glucosidase at 1, 3, 6, and 24 hours to measure the glucose content in the enzymatic hydrolysis product . According to the instruc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com