Method for detecting contents of glyceride and free fatty acid in biodiesel
A free fatty acid and biodiesel technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, material separation, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large instrument damage, inaccurate quantification, and low sensitivity, and achieve the effect of shortening the detection time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: The detection of each fatty acid and glyceride in the biodiesel (sample 1) to be tested by thin-layer chromatography combined with heat-assisted hydrolysis methylation gas chromatography
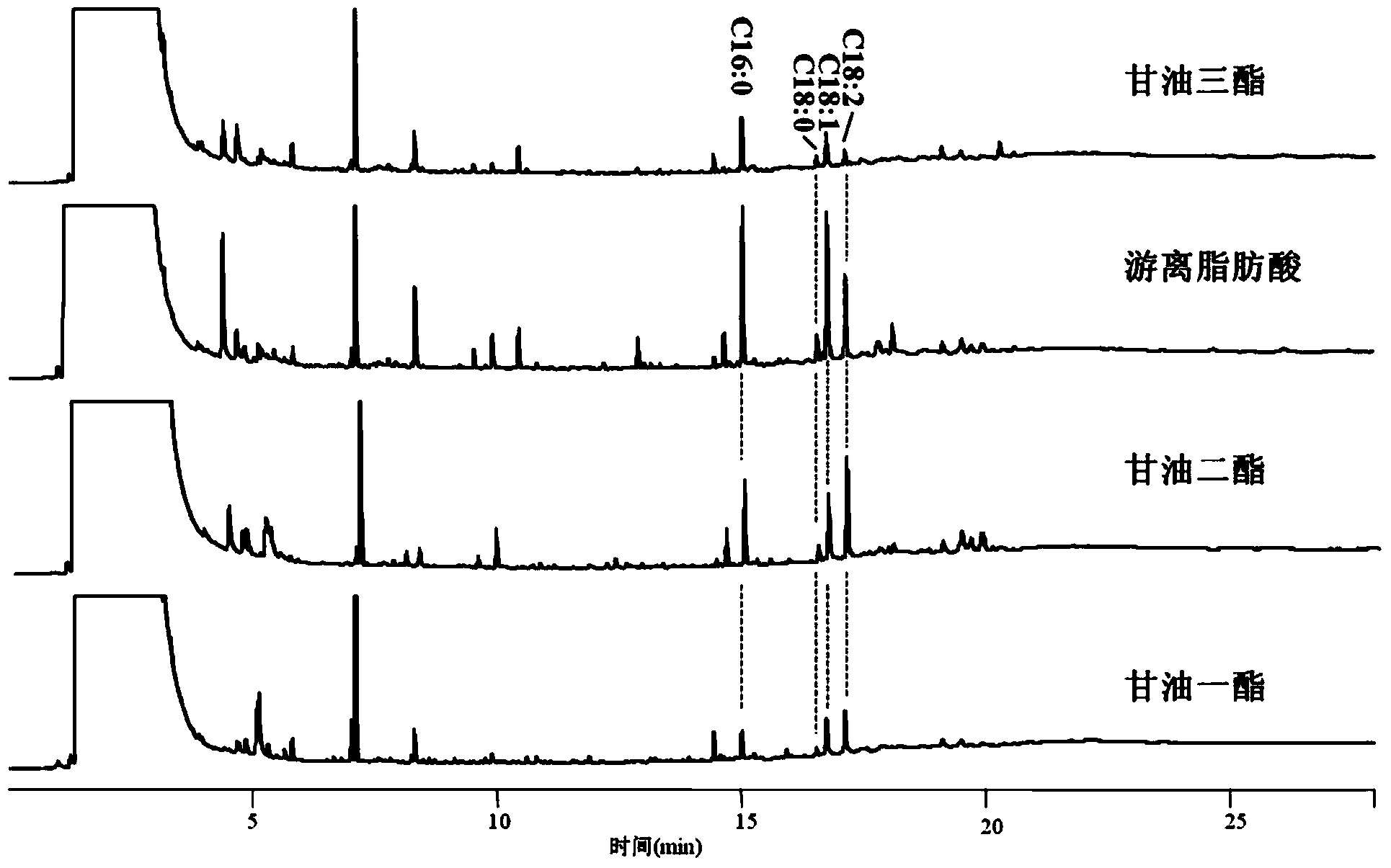
[0030] (1) Separation process of thin-layer chromatography: firstly, 100 μL of the biodiesel sample to be tested (sample 1) was dissolved in 500 μL of ethyl acetate, and diluted 6 times. After mixing evenly, draw 1 μL with a liquid phase blunt needle, point it on one end of a 10 cm aluminum foil base chromatography silica gel plate, and develop it in the developer n-hexane / ethyl acetate / formic acid (90 / 10 / 2). When the front of the solvent extends to the other end of the TLC, the TLC is taken out, and after the solvent is evaporated, the color is developed with iodine vapor. At this time, the analytes to be measured on the thin layer appear as brown or yellow spots, and the thin layer chromatogram is shown in figure 1 far right, figure 1 On the left are thin layer chrom...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Detection of Fatty Acids and Glycerides in 5 Kinds of Biodiesel to be Tested by Thin Layer Chromatography Combined with Heat-Assisted Hydrolysis Methylation Gas Chromatography
[0045] See Example 1 for the detection process and data of Sample 1. Samples 2, 3, and 4 were diluted 3 times, sample 5 was diluted 2 times, and other operations were the same as sample 1.
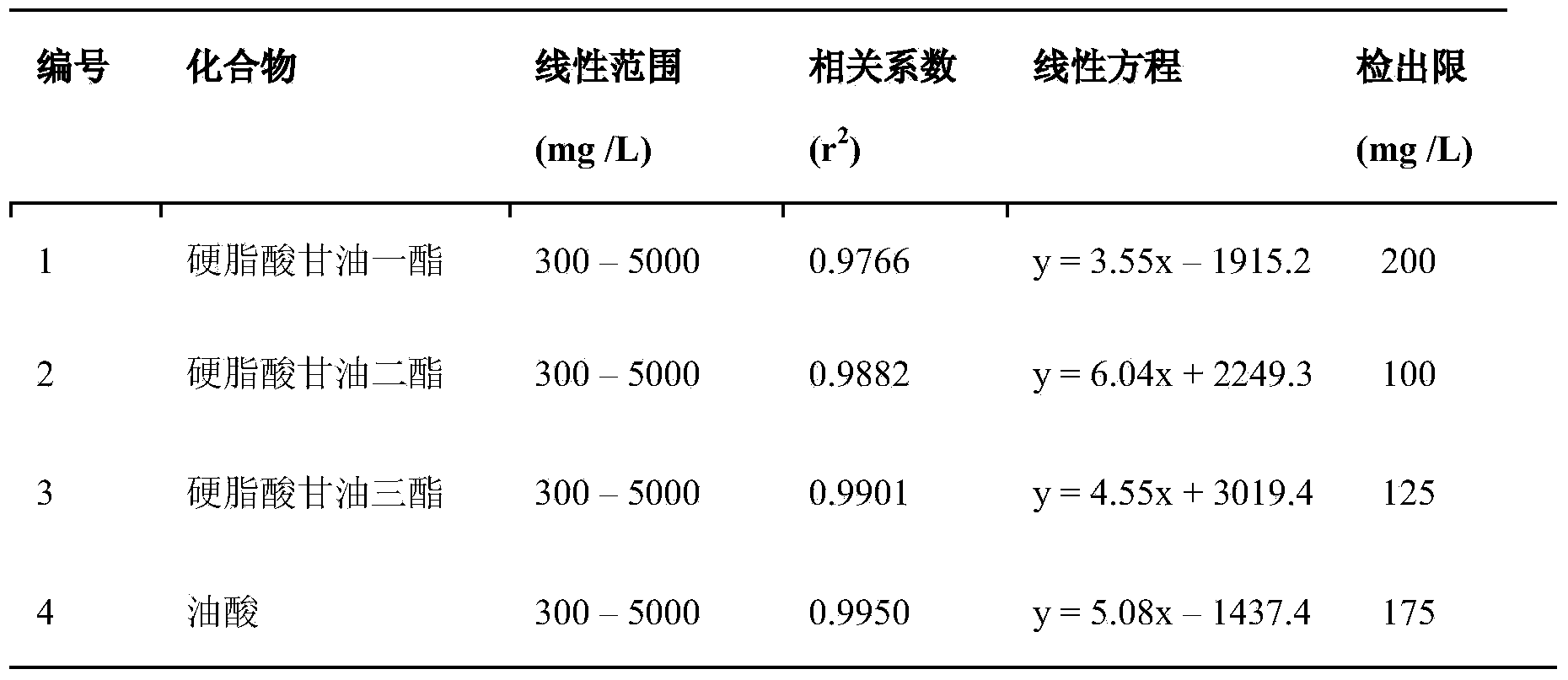
[0046] According to the peak area and standard curve of the gas chromatogram of the sample to be tested, the concentration of monoglyceride, di-ester, tri-ester and free fatty acid in the sample to be tested, and the distribution of fatty acid components in the molecule are obtained, see Table 2.
[0047] Table 2
[0048] Contents of residual glycerides and free fatty acids in 5 biodiesel samples, and their fatty acid composition distribution
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] *Fatty acid composition refers to the percentage of each methyl ester peak area to the total methyl ester peak area. Does...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In sample 4, add standard product stearic acid monoglyceride 2380mg / L, stearic acid diglyceride 1230mg / L, stearic acid triglyceride 2240mg / L, oleic acid 2460mg / L, obtain spiked sample 4, After mixing evenly, conduct thin-layer chromatography-heat-assisted hydrolysis methylation gas chromatography analysis. The operating conditions are the same as sample 4. Calculate respectively the content of monoglyceride, diglyceride, triglyceride and free fatty acid in this spiked sample 4 according to the standard curve, subtract the original content of each glyceride and free fatty acid in sample 4 in Table 2, can get its recovery rate. The spiked recoveries of monoglyceride, diglyceride, triglyceride and free fatty acid were 110.8%, 116.7%, 87.5%, 97.2%, respectively. The operation was repeated three times, and the obtained RSD values were 9.7%, 10.3%, 5.8%, and 7.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com