Experimental apparatus for in-vitro circulating perfusion and digestion of liver tissues
An extracorporeal circulation and experimental instrument technology, applied in biochemical instruments, bioreactors/fermenters for specific purposes, sterilization methods, etc., can solve problems such as experimental failure, low culture success rate, loss of digestive enzymes, etc. Experimental cycle, simple experimental operation, and the effect of reducing difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
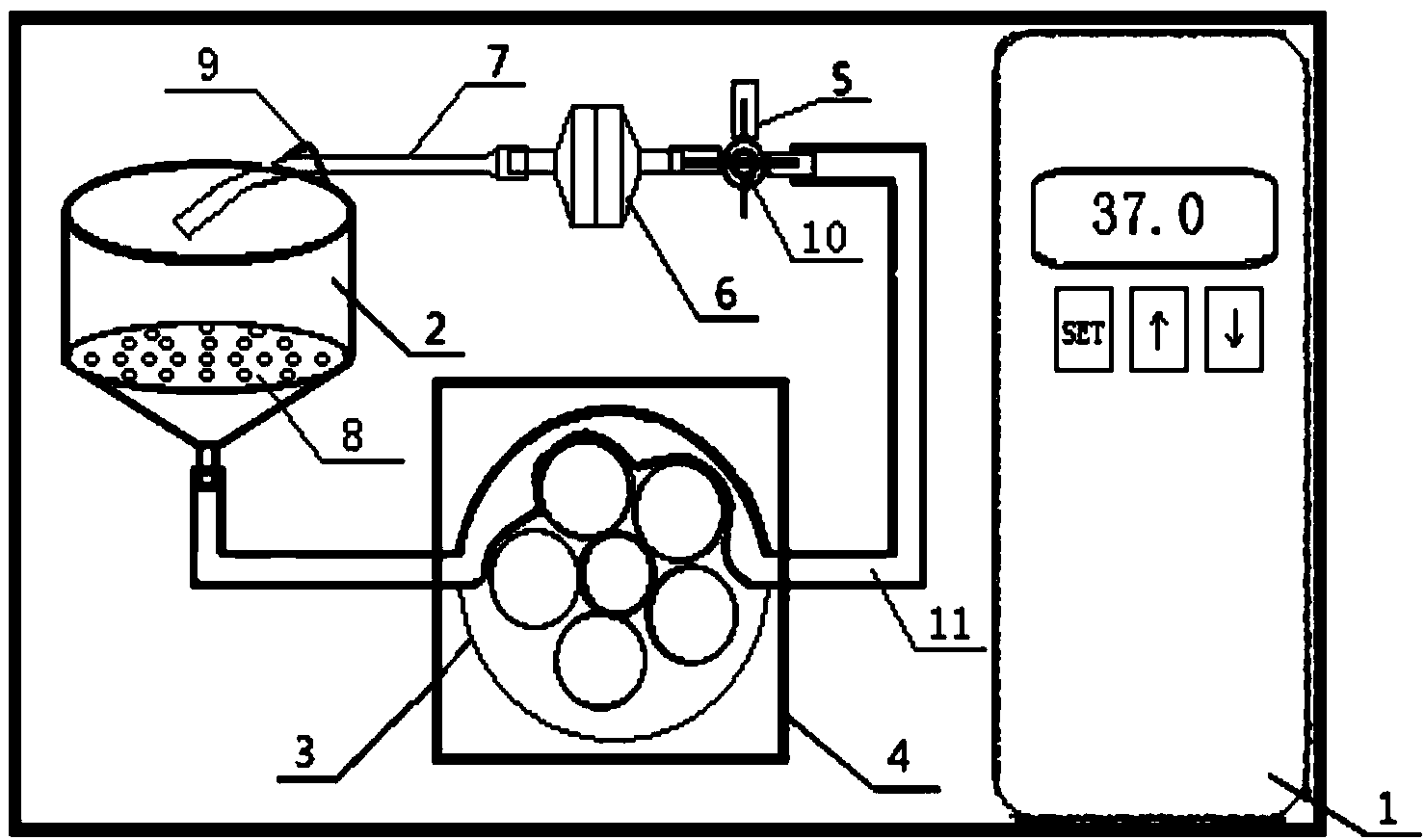
[0026] Embodiments of the present invention: an experimental instrument for extracorporeal circulation perfusion digestion of liver tissue, such as figure 1As shown, it includes an incubator 1 and a perfusion circuit arranged in the incubator 1. The perfusion circuit includes: a container for holding liver tissue 2 connected in sequence, a peristaltic pump device 4, a three-way pipe 5, a filter device 6 and Sterile pipeline 7; the peristaltic pump device 4 includes a peristaltic pump 3 and a flexible pipeline 11 corresponding to the peristaltic pump 3, the flexible pipeline 11 bypasses the corresponding peristaltic pump 3 and the two ends are respectively connected to the liver tissue container 2 and the three Through pipe 5 communicates. The temperature of the thermostat 1 is 37°C. The bottom of the container 2 for holding liver tissue is funnel-shaped, and a partition 8 with holes is arranged inside it. A hook 9 is provided at the top of the container 2 for holding liver t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com