Synthesis method of nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots
A technology of fluorescent carbon dots and synthesis methods, which is applied in the field of synthesis of nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots, which can solve the problems of cumbersome preparation methods, difficult separation and purification, and low quantum yield of fluorescent carbon dots, and achieve uniform size and good water solubility , good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
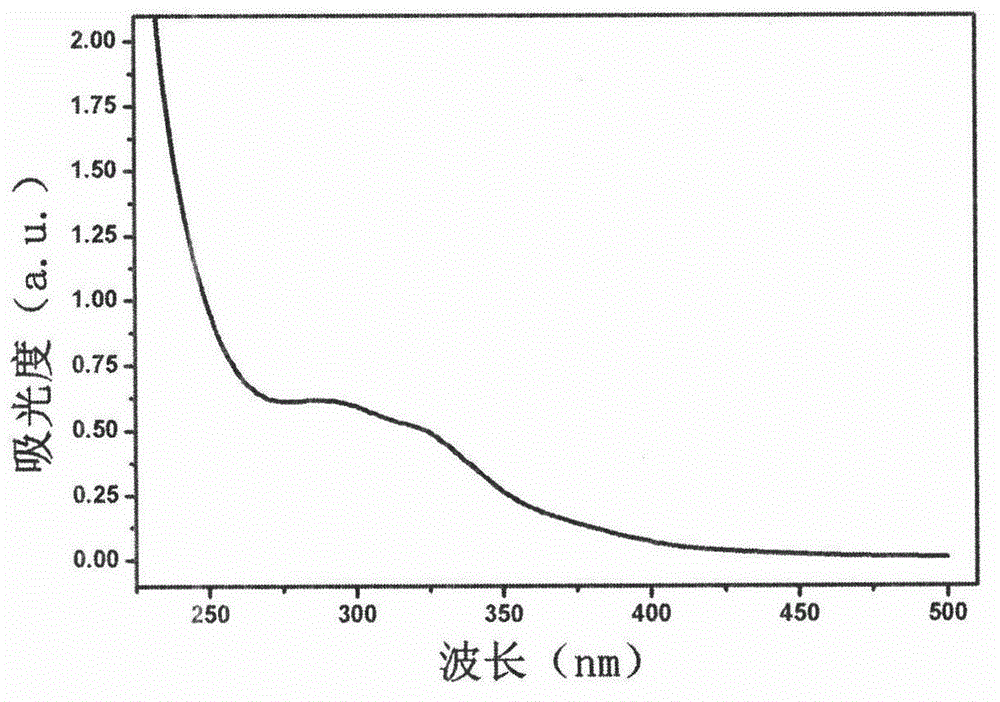
[0021] Weigh 1.3g of L-arginine solid powder in a 50mL round-bottomed flask at room temperature, add 30mL of deionized water and stir until the solid powder is completely dissolved, then add 0.2g of citric acid weighed, and slowly stir the mixed solution. The pH of the mixed solution is about 7.0; the mixed solution is placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal reactor and reacted at 180°C for 3 hours to obtain a brown-yellow solution; the obtained brown-yellow solution is dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 1000Da for 48h, the dialysis process The deionized water should be replaced regularly to remove the unreacted citric acid and L-arginine to obtain a fluorescent carbon dot solution with narrow particle distribution.
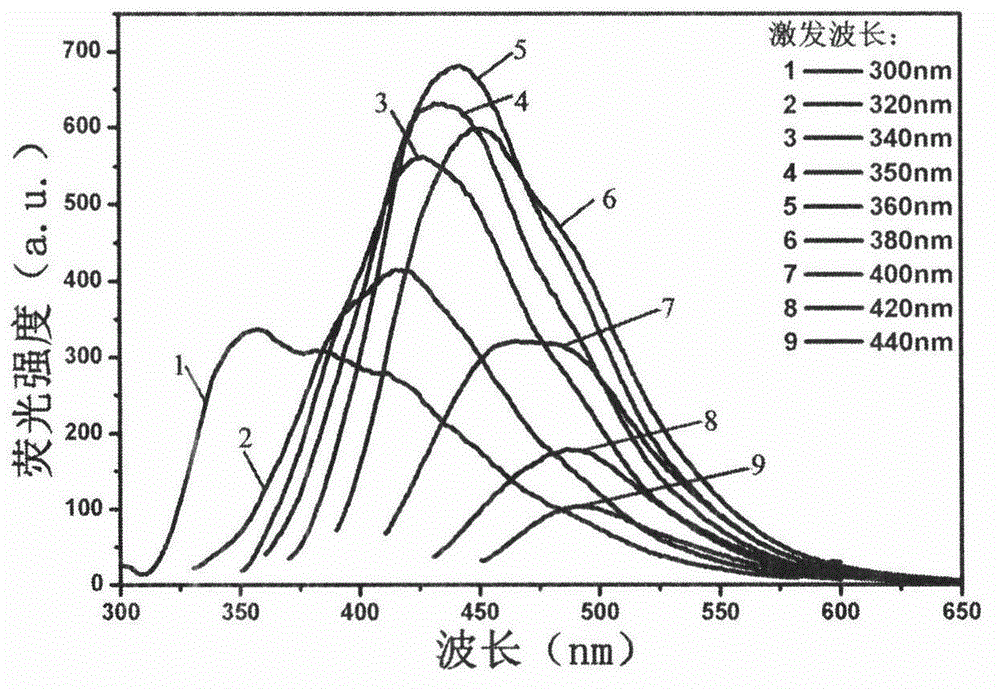
[0022] Transmission electron microscopy showed that the obtained fluorescent carbon dots had a particle size range of 9-10nm, and quinine sulfate was used as a reference standard (0.1mol / L H 2 SO 4 , 22°C, the quantum yield is 58...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Weigh 1.3g of L-arginine solid powder in a 50mL round-bottomed flask at room temperature, add 30mL of deionized water and stir until the solid powder is completely dissolved, then add 0.2g of citric acid weighed out, slowly stir the mixed solution, and then mix The pH of the solution is about 7.0; the mixed solution is placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal reactor and reacted at 180°C for 6 hours to obtain a brown-yellow solution; the resulting brown-yellow solution is dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 1000Da for 48h, during the dialysis process It is necessary to continuously replace the deionized water and remove the unreacted citric acid and L-arginine to obtain a fluorescent carbon dot solution with a narrow particle distribution.
[0025] Transmission electron microscopy shows that the obtained fluorescent carbon dots have a particle size range of 9-10nm, and quinine sulfate is used as a reference standard (0.1mol / L H 2 SO 4 , 2...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Divide human breast cancer cells into 1×10 5 Cultivate at a density of pcs / mL in a special small dish for confocal laser. After culturing for 24 hours, change the medium to a fresh medium containing 0.2mg / mL fluorescent carbon dots, continue culturing for 20 hours, observe and record the carbon dots under a laser confocal microscope For the labeling of the cells, see the results Figure 4 . The picture is a photo of cells labeled with fluorescent carbon dots under a laser confocal microscope. Figure 4 It shows that under the excitation of 405nm ultraviolet light, the cells labeled with fluorescent carbon dots emit blue fluorescence. The experiment showed that the prepared fluorescent carbon dots emit blue fluorescence in the cells and successfully labeled human breast cancer cells.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com