Detection method for phytopathogen content in soil
A technology for plant pathogenic bacteria and detection methods, applied in the direction of microbial-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve the problems of poor biological representation and unsuitability for the detection of a large number of soil samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Embodiment 1, utilize the detection method of plant pathogen content in soil to detect the content of cruciferous clubroot in soil
[0080] The complete set of reagents for identifying Cruciferous Clubroot consists of PCR primer pairs and probes for identifying Cruciferous Clubroot; the primer pair for identifying Cruciferous Clubroot consists of a single sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 Strand DNA and the single-stranded DNA composition shown in SEQ ID No.2; The probe is the single-stranded DNA shown in SEQ ID No.3 in the sequence listing, and the 5' end of the probe is marked with FAM, and the The 3' end of the probe is labeled with TAMARA.
[0081] The specific steps of the method for detecting the content of cruciferous clubroot bacteria in soil are as follows:
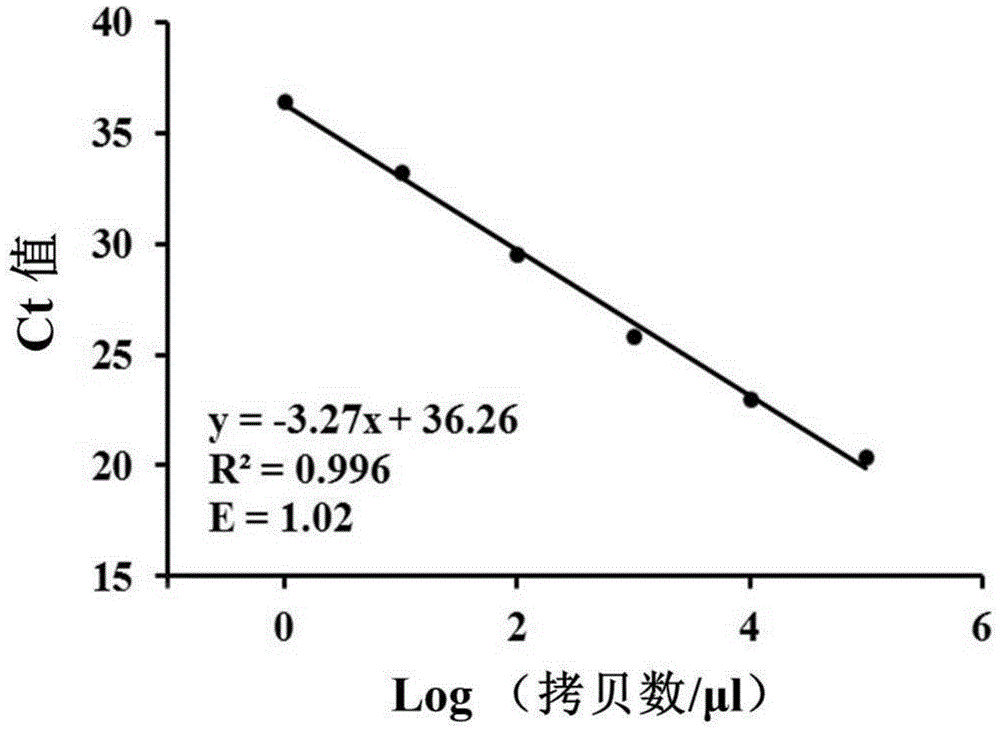
[0082] 1. Preparation of standard curve
[0083] 1.1 Construction of standard plasmids
[0084] The DNA molecule shown in the DNA sequence of the cruciferous clubroot bacterium whose gene accession number i...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Embodiment 2, the sensitivity experiment of the detection method of cruciferous clubroot content in soil
[0109] 1. Sensitivity experiment of a complete set of reagents for identification of Cruciferous clubroot
[0110] The concentration in Example 1 is 1×10 9 The copy / μl linear carrier T solution was serially diluted with sterile water to obtain linear carrier T solutions with concentrations of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 and 1.2 copies / μl, respectively.
[0111] Using the DNA in the linear carrier T solution with a concentration of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 and 1.2 copies / μl respectively as a template, carry out fluorescent quantitative PCR with the complete set of reagents for identifying Brassicaceae clubroot in step 1.3 of Example 1 Reaction, the reaction system is 1 copy / 25 μl reaction system, 2 copies / 25 μl reaction system, 3 copies / 25 μl reaction system, 4 copies / 25 μl reaction system, 5 copies / 25 μl reaction system and 6 copies / 25 μl reaction system.
[0112] The...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Embodiment 3, the specificity experiment of the detection method of cruciferous clubroot content in soil
[0119] According to the method of 2.1 of embodiment 1 step 2, clubroot pathogen of cruciferae is replaced by Java different water mold (Allomyces javanicus), tobacco red spot fungus (Alternaria alternata), cabbage black spot fungus (Alternaria brassicae), white radish black Alternaria raphani, Aspergillus niger, Bipolaris sp., Botrytis sp., Colletotrichum dematium, Fusarium graminearum ), Fusarium oxysporum (Fusarium oxysporum), Penicillium sp. (Penicillium sp.), Rhizoctonia solani (Rhizoctonia solani) and Verticillium dahliae (Verticillium dahliae), other steps are all unchanged, respectively to get Java different water Standard soil microbial DNA for mould, standard soil microbial DNA for Alternaria Alternaria in tobacco, standard soil microbial DNA for cabbage black spot fungus, standard soil microbial DNA for white radish black spot fungus, standard soil microb...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com