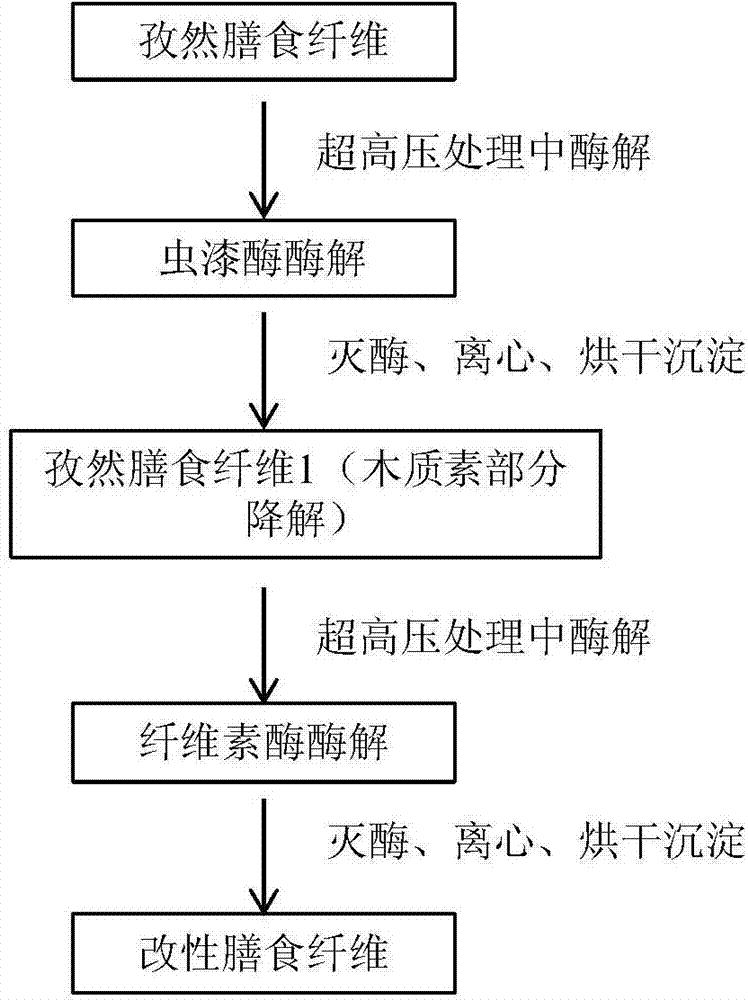
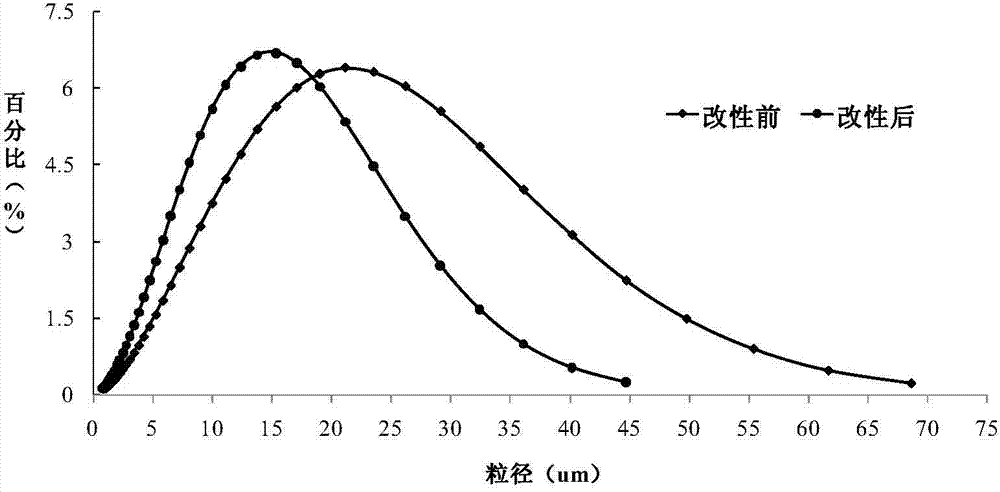
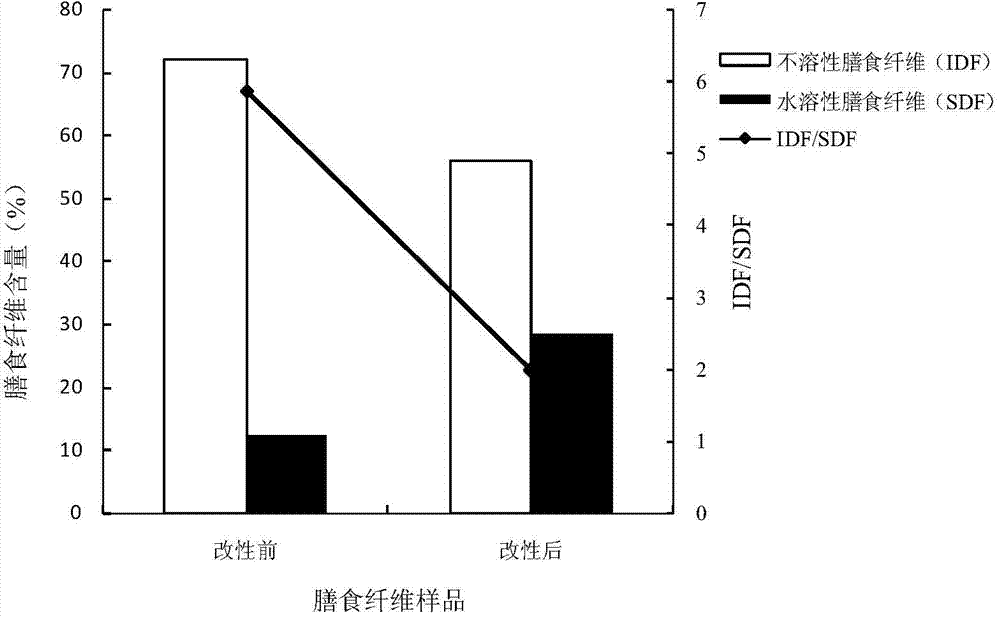
Modification method of dietary fiber and prepared product
A dietary fiber and modification technology, which is applied to the modification method of plant dietary fiber and its products, can solve the problem of insufficient utilization of fiber, and achieve the effects of small particles, wide sources and short enzymatic hydrolysis time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Effect of laccase hydrolysis pH on lignin degradation effect
[0037] Take cumin dietary fiber (see Figure 4(a)) and sodium acetate buffer solution with pH 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5 and 8.5 and mix them at a ratio of 1:10 (g / mL). After adding laccase at 20U / g, pour it into a vacuum packaging bag and seal it; put the sample into an ultra-high pressure device, treat it at 400MPa and 25°C for 15 minutes, and heat the obtained enzymatic hydrolyzate in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes to inactivate the enzyme activity. Centrifuge, remove the supernatant, dry and pulverize the obtained precipitate, and measure the lignin content.
[0038] The lignin content was determined according to the method of Claye (1996) et al. The specific steps are:
[0039] Accurately weigh 5g sample (the weight is denoted as W 1 ) mixed with 0.2M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) at a ratio of 1:10 (w / v), stirred and extracted at room temperature for 2 hours, the mixture was centrifuged at 3000g ...
Embodiment 2
[0048]Embodiment 2, the impact of laccase enzyme and substrate concentration ratio (E / S) on lignin degradation effect
[0049] According to Example 1, only the enzymatic hydrolysis pH was fixed at 6.5, and the enzyme-to-substrate concentration ratio (E / S) was replaced with 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 U / g, and the lignin content was calculated.
[0050] The results obtained are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from the table that when the E / S is 15U / g, the lignin content is the lowest, which is 10.08%. Compared with the control group, the lignin content is reduced by 13.83%.
[0051] Table 2. Effect of E / S on lignin degradation effect
[0052]
[0053]
[0054] Note: Different letters (a, b, c) in the same group indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3, the impact of laccase enzymolysis temperature on lignin degradation effect
[0056] According to Example 1, the enzymolysis pH was fixed at 6.5, the E / S was fixed at 15 U / g, the enzymolysis temperature was replaced with 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60°C, and the lignin content was calculated.
[0057] The obtained results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen from the table that the lignin content in the cumin dietary fiber increases first and then decreases with the increase of the enzymatic hydrolysis temperature. The enzymatic hydrolysis temperature continued to increase, and the lignin content increased.
[0058] Table 3. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis temperature on lignin degradation effect
[0059]
[0060] Note: Different letters (a, b, c, d) in the same group indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com